Photosynthesis Overview modified
advertisement

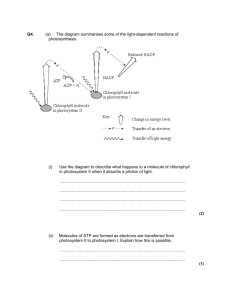
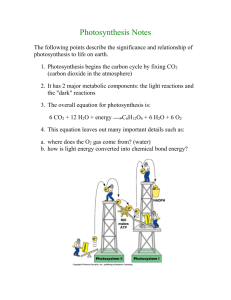
SBI 4U DATE: ______________________ OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS INTRODUCTION: - metabolic process occurring in green plants, algae, some protists and cyanobacteria - Photosynthesis is an ______________ PROCESS (building organic molecules which store radiant energy as chemical potential energy) - Recall: Cellular Respiration is a _______________ PROCESS Summary Reaction for Photosynthesis: CO2: - used in light__________________ reactions (sometimes called ________ reactions) - enters through stomata and goes to mesophyll cells H2O: - used in light____________________ reactions (sometimes called ________ reactions) - enters through veins of leaf and goes to mesophyll cells chlorophyll: - light absorbing ___________ coloured pigment that begins the process of photosynthesis - found in _______________ - primary function: convert ___________ energy into ___________ and __________ in order to be used to convert __________ to ___________ molecules Note: if any of the raw materials is absent, photosynthesis will NOT occur Chloroplast - organelle involved in photosynthesis - contains its own: - (a) ________________________ - (b) ________________________ You should be able to: - label a diagram of a chloroplast - explain the structure/function of the chloroplast OVERVIEW OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS Photosynthesis consists of two complex series of events; (1) __________________________________ (2) __________________________________ Light Dependent Reactions - capturing light energy - occur within the __________ membrane of the chloroplast - produces: (1) ______________________ (2) ______________________ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, a coenzyme; similar to NADH) Light Independent Reactions OR _____________________________________________________ - occur in either the presence or absence of __________ - occur within the ______________ of the chloroplast - uses ATP and NADPH from the light reactions to form organic molecules like glucose, from CO2 - produces: (1) ______________________ (2) ______________________ - completely enzyme catalyzed LIGHT - Electromagnetic (EM) radiation - o Travels in wave packets called ____________ o Photons with short wavelength = ________________ o Photons with large wavelength = ___________________ Light is a mix of photons of different energies o Most of it we can’t see o If passed through spectroscope, photons can separate from one another Called Electromagnetic Spectrum Light – Photosystems (briefly) - Photosystems o Clusters of photosynthetic pigments embedded in thylakoid membrane o They absorb photons of particular wavelengths o Through light reactions they convert ADP to ATP and NADP+ to NADPH Occurs in the stroma PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS Chlorophyll - found within _________________ - ___________ pigments - contain: - (1) _____________________________ - (2) _____________________________ - chlorophyll a: absorbs _______________ and _____________ wavelength photons (reaction centre of a photosystem) - chlorophyll b: absorbs _______________ and _____________ wavelength photons (accessory pigment) Carotenoids - _____________ and _____________ pigments (accessory pigments) - absorb only in the ______________ end of the spectrum - Excess energy absorber to protect chlorophyll and dissipate it as heat o E.g. β-carotene from carrots Photosynthetically Active Radiation - Ideal wavelengths for photosynthesis o - Ranges from __________________________________ Combination of chlorophyll a and b, and all of the other accessory pigments that “help out” - LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTIONS PHOTOSYSTEMS - consists of: (1) _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ (2) _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Location of Photosystems: __________________________________________ Photosystem I: ___________________________________________________ Photosystem II: __________________________________________________ There are two separate light powered systems in the membranes of the thylakoid disc: (1) _____________________________________ (2) _____________________________________ Cyclic Photophosphorylation - used by prokaryotes (eg bacterial photosynthesis) - involves only ___________________ (PS I) - PS I contains ______________ - chlorophyll a electrons return to chlorophyll a - product = __________ (no NADPH is made) Description: (1) PS I (P700) absorbs ___________ energy, causing the two ____________ to become excited. (2) The two excited electrons enter an _______________________________. (3) The two excited electrons are captured by the protein _________________, causing some of their energy to be lost. (4) The two excited electrons are then captured by the _____________________ protein complex and lose more energy. At this point, enough energy has been lost to add a P to ADP forming ________. (5) The passing of electrons from cytochrome b6-f complex to the next electron carrier, ___________________(Pc) results in further lowering of the energy in the electrons to almost the ground state (6) The passing of the two electrons to ______ returns the electrons to both the _______________ molecule and the __________ state. Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation - used in photosynthesis of green plants - involves both ___________________ (PS I) and ___________________ (PS II) - chlorophyll a electrons are passed along to make ____________ and are replaced by __________ electrons Description: (1) PS II absorbs __________ energy causing two electrons of chlorophyll P680 to become excited. (2) A Z protein, associated with PS II and facing the thylakoid _________, splits __________ into ____________, _____________ and ______________. Two __________ are used to replace the excited electrons in chlorophyll P680. ___________ leaves the chloroplast as a byproduct. The _________ remain in the thylakoid space add to the proton gradient that powers chemiosmosis. (3) The two excited __________ travel through a series of proteins within the _______________________________. (4) As the two excited ____________ move from the excited reaction centre of PS II to ___________________(PQ), energy is lost. (5) This energy is used to move _________ protons from the _____________ to the ____________. This creates a proton gradient for chemiosmosis. (6) The increase in proton concentration within the thylakoid lumen drives protons out of the lumen to the ________ via a special protein called _____________. This proton motive force is used to produce ___________. (7) The electrons continue to move from PQ to other components of the electron transport chain (cytochrome b6-f complex to Plastocyanin to PS I) eventually replacing the 2 electrons that were lost by PS I when it was struck by photons. (8) The two excited electrons from PS I pass through another electron transport chain containing the protein _________________(Fd). (9) The two excited electrons are then captured by ___________________, which uses the two electrons and protons from the stroma to reduce ___________ to ___________. (10) The ____________ and ________ are used to drive light independent reactions. LIGHT INDEPENDENT REACTIONS Calvin Cycle - reactions that convert ________________ into _______________ molecules - occur in the ___________ of chloroplasts Summarize the 3 phases listed below: (1) Carbon Fixation: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ (2) Reduction Reactions: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________ (3) Regeneration of RuBP: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________