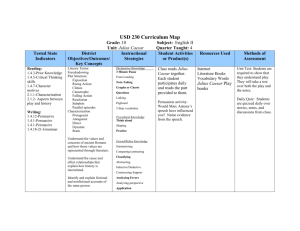
753-716 Rule of Romulus
advertisement

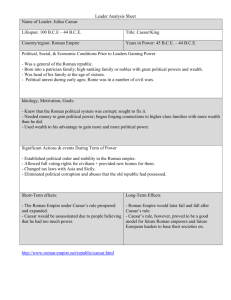
ROMAN MILITARY ACHIEVMENTS AND LEADERS By: Matt Bacon, David Stone, and Julian Autar Geography • • • The Roman Empire was full of many terrains, many of which were rough. In order for armies to go from one battle to another roads were built to accommodate them. The geography of Rome was transformed through roads, which helped for transportation. Social Impacts By The Military • • • For a long time, most military personnel could not marry because they were in the military. Military conquest allowed many different cultures to mix in Rome. Resulting from this, Rome was seen as the center of the Mediterranean. Economics • • • • Wars created great revenue for Rome because when they won the battles they gained land and spoils of war (money from the land acquired). The stated of Rome , which were acquired had to pay taxes to Rome to fuel the economy. Most the soldiers enlisted in the Roman army because they had no jobs before. Therefore, the military created job for the unemployed. Political • • • Generals were politically involved in the government of Rome. Some generals overthrew the government through civil war (e.g. Julius Caesar) In fact, overthrew Pompey’s government through civil war using his army. Religion • • • Aries was the roman god of war. The Romans thought Mars, also another god representing war, was very important. It was said that he was the father of Romulus and Remus, the founders of Rome. Statue of Aries Technology • The first ancient pieces of artillery were non-torsion bolt throwers. • The Onager (catapult) was specifically designed for siege warfare. It could be used to bombard enemy walls and artillery, or to hurl large stones or missiles at oncoming forces. Roman Soldiers and Tactics Different Types of Soldiers The first Roman soldiers were just ordinary Roman citizens like farmers, blacksmiths, merchants and businessmen. The average age of a legionary was between 17 and 46 years old, every citizen might of been asked to join the army. The army was divided into legions, each containing about 6,000 men, there was four lines of soldiers. The front line was made up of Velites, these men throw spears at the enemy, behind them were the Hastatus and the Princeps, these men did most of the fighting. Hastatus and Princeps had light armour and used swords, in the last line were the Triarius, these men wore heavy armour. It was these legions that began the expansion of Rome by capturing other cities. Roman Tactics The Romans used 3 main battle formations to fight with The first was the Tortoise formation. Used as protection against sustained enemy archery and other projectiles. Generally speaking, this formation was used as a last attempt in holding off the enemy, if the Roman line broke or if they got surrounded by enemy troops. This is a more complex formation designed to repel enemy cavalry but very effective. The Romans also used many other different formations such as the Skirmish formation, the Wedge and the Fake Retreat Basic Roman Soldier Equipment A Roman soldier had a helmet to protect his head A metal jacket to protect to protect his chest A shield to form a line of defense when working with other soldiers A pilum which is a kind of spear Sometimes a javelin to throw at the enemy And a sword Also sometimes a dagger just in case Military Leaders Caesar JULIUS CAESAR: HISTORICAL BACKGROUND 102/100 BCE: Gaius Julius Caesar was born His family had noble, patrician roots, although they were neither rich nor influential in this period. 85 BCE: at age 18 he married Cornelia, the daughter of a prominent member of the Popular faction; she later bore him his only legitimate child, a daughter, Julia. When the Optimate dictator, Sulla, was in power, he ordered Caesar to divorce her; when Caesar refused, Sulla proscribed him (listed him among those to be executed), and Caesar went into hiding. Caesar's influential friends and relatives eventually got him a pardon. JULIUS CAESAR: HISTORICAL BACKGROUND 79 BCE: Caesar, on the staff of a military legate, was awarded the civic crown (oak leaves) for saving the life of a citizen in battle. His general sent him on an embassy to Nicomedes, the king of Bithynia, to obtain a fleet of ships; Caesar was successful, but subsequently he became the butt of gossip that he had persuaded the king (a homosexual) only by agreeing to sleep with him When Sulla died in 78, Caesar returned to Rome and began a career as a orator/lawyer JULIUS CAESAR: MAJOR EVENTS 75 - Pirates capture Caesar 73 - Caesar is elected Pontifex 69 - Cornelia, the wife of Caesar, dies 67 - Caesar marries Pompeia 65 - Caesar is elected Aedile 63 - Caesar is elected Pontifex Maximus 62 - Caesar divorces Pompeia JULIUS CAESAR: MAJOR EVENTS 61 - Caesar becomes Governor of Further Spain 60 - Caesar is elected Consul and forms the Triumvirate 59 - Caesar is elected Consul 58 - Caesar defeats the Helvetii and Germans 55 - Caesar crosses the Rhine and invades Britain 54 - Caesar's daughter, who is also Pompey's wife, dies 53 - Crassus is killed JULIUS CAESAR: MAJOR EVENTS 52 - Clodius is murdered; Caesar defeats Vercingetorix 49 - Caesar crosses the Rubicon - Civil War begins 48 – Caesar defeats Pompey 45 - Caesar is declared dictator for life 44 - Ides of March, Caesar is assassinated JULIUS CAESAR: Untimely Death Julius Caesar had many men conspiring against him, among these 60 men were 16 senators, including Cassius, Casca, Cimber and Brutus. Thei'r motives were obvious -- personal gain; they masked it as a nobly patriotic cause. On the 15th of Martiae, 710 AUC, the Senate held a meeting in the hall adjoining the theater Pompey had built 11 years previously. A man named Cimber knelt at Caesar's feet to plead for his brother's recall from banishment. When Caesar irritably refused him, Cimber yanked Julius' toga down from his neck and the other conspirators began to stab Caesar. When they were finished, Caesar lay dead with 23 wounds. Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa 56-12 B.C Agrippa was a renowned Roman general and close friend of Octavian (Augustus) As general, Agrippa defeated the forces of Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus The Romans had appointed Cincinnatus dictator for six months so he could defend the Romans against the neighboring Aequi who had surrounded the Roman army and the consul Minucius in the Alban Hills. gave up the title of dictator sixteen days after it had been granted. and promptly returned to his farm… Horatius late 6th C. B.C Horatius was an heroic leader of the Roman forces against the Etruscans He deliberately stood alone against the Etruscans on a bridge which the Romans were destroying from their side. In the end, when the bridge was destroyed, Horatius jumped into the Tiber and swam armed to safety. Lucius Cornelius Sulla Sulla was a Roman general who vied successfully with Marius for leadership of the command against Mithridates VI of Pontus In the following civil war Sulla defeated the followers of Marius, had the soldiers of Marius killed had himself declared dictator for life in 82 B.C DECISIVE ROMAN BATTLES TIMELINE OF DECISIVE BATTLES OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE o 496 BC Battle of Lake Regillus - A legendary early Roman victory, won over either the Etruscans or the Latins o 305 BC - Battle of Bovianum - Roman consuls M. Fulvius and L. Postumius decisiviely defeat the Samnites to end the Second Samnite War . o 295 BC - Battle of Sentinum - Romans under Fabius Rullianus and Publius Decimus Mus decisively defeats the Samnites and their Etruscan and Gallic allies, forcing the Etruscans, Gauls, and Umbrians to make peace . o 280 BC - Battle of Heraclea - First engagement of Roman and Greek armies o 242 BC - Battle of the Aegates Islands - Roman sea victory over the Carthaginians, ending the First Punic War . o 216 BC First Battle of Nola - Roman general Marcus Claudius Marcellus holds off an attack by Hannibal. o 208 BC - Battle of Baecula - Romans in Spain under P. Cornelius Scipio the Younger defeats Hasdrubal Barca, who was a Carthagian general. o 207 BC -Battle of the Metaurus - Hasdrubal is defeated and killed by Nero's Roman army. TIMELINE OF DECISIVE BATTLES OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE o 202 BC - Battle of Zama - Scipio Africanus Major decisively defeats Hannibal in North Africa, ending the Second Punic War . o 197 BC - Battle of Cynoscephalae - Romans under Flamininus decisively defeats Philip V in Thessaly. o 191 BC - Battle of Thermopylae - Romans under Manius Acilius Glabrio defeat Antiochus III the Great and force him to evacuate Greece . o 190 BC Battle of Magnesia - (near Smyrna) Romans under Lucius Cornelius Scipio and his brother Scipio Africanus Major defeat Antiochus III the Great leading to a decisive victory of the war . o 168 BC Battle of Pydna - Romans under Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus defeat and capture Macedonian King Perseus, ending the Third Macedonian War . o 146 BC Battle of Corinth - Romans under Lucius Mummius defeat the Achaean League forces of Critolaus , who is killed. Corinth is destroyed and Greece comes under direct Roman rule. o 146 BC Battle of Carthage - Scipio Africanus Minor captures and destroys Carthage, ending the Third Punic War o 89 BC Battle of Asculum - Roman army of C. Pompeius Strabo decisively defeats the rebels in the Social War. TIMELINE OF DECISIVE BATTLES OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE o 86 BC - Battle of Chaeronea - Roman forces of Lucius Cornelius Sulla defeat the Pontic forces of Archelaus in the First Mithridatic War. o 58 BC June - Battle of the Arar (Saone) - Caesar defeats the migrating Helvetians o 58 BC - Battle of Bibracte - Caesar again defeats the Helvetians, this time decisively. o 58 BC - Caesar decisively defeats the forces of the Germanic chieftain Ariovistus near modern Belfort. o 52 BC - Battle of Alesia - Caesar defeats the Gallic rebel Vercingetorix, completing the Roman conquest of Transalpine Gaul. o 48 BC - Battle of Pharsalus - Caesar decisively defeats Pompey, who flees to Egypt o 47 BC - Battle of the Nile - Caesar defeats the forces of the Egyptian king Ptolemy XIII o 47 BC - Battle of Zela - Caesar defeats Pharnaces II of Pontus. This is the battle where he famously said “Veni, vidi, vici.” (I came, I saw, I conquered.) o 45 BC - Battle of Munda - In his last victory, Caesar defeats the Pompeian forces of Titus Labienus and Pompey the Younger in Spain. Labienus is killed in the battle and the Younger Pompey captured and executed. TIMELINE OF DECISIVE BATTLES OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE o 42 BC - First Battle of Philippi - Triumvirs Marc Antony and Octavian fight an indecisive battle with Caesar's assassins Marcus Brutus and Cassius. Although Brutus defeats Octavian, Antony defeats Cassius, who commits suicide. o 43 AD- Battle of Medway - Claudius and general Aulus Plautius defeat a confederation of British Celtic tribes. Roman invasion of Britain begins. o 50 AD- Battle of Caer Caradock - British chieftain Caractacus is defeated and captured by the Romans under Ostorius Scapula. o 101 AD - Battle of Tapae – Roman emperor Trajan defeats Decebalus, ending the Dacian Wars o 268 AD- Battle of Naissus - Emperor Gallienus and his generals Claudius and Aurelian decisively defeat the Goths. o 268 AD Battle of Fano - Aurelian defeats the Alemanni, who begins to retreat from Italy . o 273 AD- Battle of Chalons (273) - Aurelian defeats the Gallic usurper Tetricus, reestablishing central control of the whole empire. PRINCIPLE BATTLES OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE o 312 AD - Battle of Milvian Bridge - Constantine I defeats Maxentius and takes control of Italy. o 324 AD - Battle of Chrysopolis - Constantine decisively defeats Licinius, establishing his sole control over the empire. o 394 AD- - Battle of Frigdus - Christian Roman Emperor Theodosius defeats and kills the pagan usurper Eugenius and his Frankish general Arbogast. o 451 AD- in June - Battle of Chalons - An army of Visigoths, under king Theodoric, and Romans, under general Aëtius, repulses the attack of Attila the Hun. Theodoric is killed in the battle. *AGUSTUS was the Title of the Roman emperor, used first by Julius Caesar (27 BC14 AD) Work Cited List Websites http://www.exovedate.com/ancient_timeline_one.html http://www.pbs.org/empires/romans/special/index.html http://ancienthistory.about.com/od/romebattles/ http://www.geocities.com/caesarkevin/caesar_11.html#Munda http://oncampus.richmond.edu/academics/classics/students/dave/ROMAN/battles.html http://www.unrv.com/military/roman-battle-index.php http://www.vroma.org/~bmcmanus/caesar.html http://ancienthistory.about.com/cs/rome/p/romanmilitldrs.htm