War of 1812 and Ch 7
advertisement

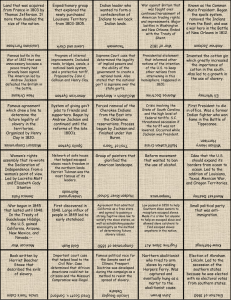
Chapter 7 Growth and Division “Era of Good Feelings” Presidency of James Monroe One party controlled national politics Republicans Economic Nationalism Second National Bank Protective Tariffs Improvements to transportation systems Judicial Nationalism Martin v. Hunter’s Lessee Established Supreme Court as final court of appeal McCulloch v. Maryland Bank is legal under “necessary and proper” clause State can’t interfere with federal actions Gibbons v. Ogden Federal control over interstate commerce Nationalist Diplomacy Andrew Jackson and the Seminoles Adams-Onis Treaty Acquisition of Florida Monroe Doctrine No European intervention in the Americas Quadruple Alliance (Britain, Austria,, Prussia, Russia) Section 2 – Early Industry National Road Only great federally funded transportation project of the time Most paid for by state and local government and private businesses Steamboats and Canals Erie Canal Barges could carry more than wagons Steamboat Robert Fulton Barges could usually only go downstream but riverboats could go both ways “Iron Horse” Peter Cooper “Tom Thumb” – Not popular with everyone at first Noisy, pollution, dangerous Advantageous Faster Could go anywhere track could be laid Helped settle the west Increased demand for iron and coal Industrial Revolution Helped by the American free enterprise system Incorporation laws, limited liability Started in Northeast Samuel Slater, Francis Lowell Eli Whitney Interchangeable parts Samuel Morse Morse code, Telegraph Rise of Large Cities Industrialization drew people to the cities More people became educated Worker Organizations Labor Unions Strikes Family Farms Agriculture was country’s leading economic activity North had prosperous farms, but industry expanded, too South stayed tied to agriculture and slavery Southern Economy After Eli Whitney invented the Cotton Gin, textile mills that were booming in Britain wanted more and more cotton The high demand for cotton created a huge demand for slave labor From 1820 to 1860 slavery in the south tripled Slavery Task System – small farms or plantations, workers were given specific jobs to finish each day. When done they were allowed to do other things Gang System – workers were put into work gangs that labored from sun-up to sun-down Anti-Slavery Movement Frederick Douglas was a former slave who became a leader of the antislavery movement Slave Codes – state laws that forbade slaves from owning land, leaving without permission, or learning to read or write Sec 4 Growing Sectionalism In 1819 Missouri applied for statehood as a slave state At the time the U.S. had 11 free and 11 slave states This would upset the balance and spread slavery westward The Missouri Compromise called for admitting Maine as a free state and Missouri as a slave state, and prohibiting slavery in the Louisiana Purchase Later in 1819 Alabama became the 22nd state on Dec. 14, 1819 Election of 1824 Four Candidates – favored sons Henry Clay of Kentucky Andrew Jackson of Tennessee John Quincy Adams of Massachusetts William Crawford of Georgia Henry Clay’s plan was called the American System – favored the national bank, the protective tariff, and nationwide internal improvements, like roads and canals Jackson won the popular vote but no candidate won the majority in the Electoral College So the House selected from the top 3 Clay was eliminated so he threw his support to John Quincy Adams Adams won Jackson accused Adams and Clay of a “corrupt bargain” Jackson’s supporters took the name democrats Election of 1828 John Quincy Adams VS Andrew Jackson Bitter campaign, the first where both candidates participated in mudslinging Jackson won the election with support from the West and South