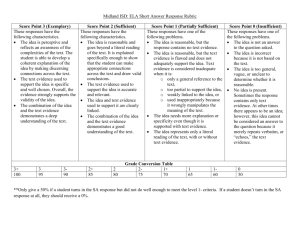
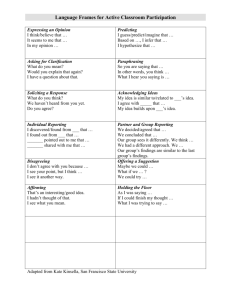
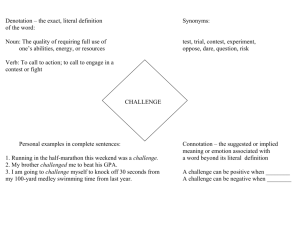
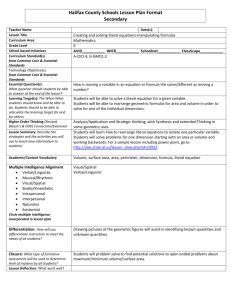
Reading Vocabulary Name__________________ Figurative
advertisement

Reading Vocabulary Name__________________ 1. Figurative language—using figures of speech to express meaning or relationship within writing; you don’t use the exact literal meaning of the words. 2. Metaphor—comparing two objects or ideas without using the words “like” or “as” (example: He is the apple of her eye.) 3. Simile—comparing two objects or ideas using the words “like” or “as” (example: She is as busy as a bee.) 4. Context clues—looking at the parts of a sentence surrounding an unknown word to figure out the meaning of that word 5. Prefix—one or more letters put at the beginning of the word that changes the word’s meaning (e.g. bi-) 6. Suffix—one or more letters put at the end of a word that changes the word’s meaning (e.g. –able) 7. Root word—the form of a word (without prefixes or suffixes) (also called a base word) (e.g. geo) 8. Idiom—A set expression of two or more words that means something other than the literal meanings of its individual words. (e.g. It was a blessing in disguise.) 9. Adage—a traditional saying that expresses something considered to be a general truth (e.g. The early bird gets the worm.) 10. Proverb—a short well-known saying that expresses an obvious truth and often offers advice (e.g. All that glitters is not gold.) Reading Vocabulary Name__________________ 1. Figurative language—using figures of speech to express meaning or relationship within writing; you don’t use the exact literal meaning of the words. 2. Metaphor—comparing two objects or ideas without using the words “like” or “as” (example: He is the apple of her eye.) 3. Simile—comparing two objects or ideas using the words “like” or “as” (example: She is as busy as a bee.) 4. Context clues—looking at the parts of a sentence surrounding an unknown word to figure out the meaning of that word 5. Prefix—one or more letters put at the beginning of the word that changes the word’s meaning (e.g. bi-) 6. Suffix—one or more letters put at the end of a word that changes the word’s meaning (e.g. –able) 7. Root word—the form of a word (without prefixes or suffixes) (also called a base word) (e.g. geo) 8. Idiom—A set expression of two or more words that means something other than the literal meanings of its individual words. (e.g. It was a blessing in disguise.) 9. Adage—a traditional saying that expresses something considered to be a general truth (e.g. The early bird gets the worm.) 10. Proverb—a short well-known saying that expresses an obvious truth and often offers advice (e.g. All that glitters is not gold.)