Assessing Readability
advertisement

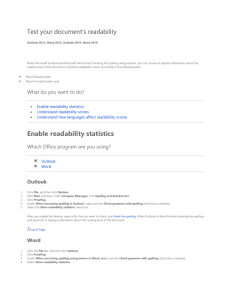
Assessing Readability What is Readability? Readability is a way of deciding how hard a text is. It is a good idea to know how hard a text is before you assign it to be read in a class. Readability formulas take into account the length of words as well as the length of sentences. You can use this readability method on the handouts you give to make sure they are at an appropriate level of readability. How to Assess Readability One of the easiest ways to measure readability is to use the Flesch Reading Ease formula, which is readily available on Microsoft Word. Type in approximately 200 words of the text, in their original sentence structure. Under “Tools,” go to “Options.” When the menu box appears, click on “Spelling and Grammar” and make sure the “Show Readability Statistics” choice has a checkmark beside it. After you have typed in your text and made sure the spelling/grammar tool will give you readability stats, then do a grammar check on the text you have typed in. Ignore everything it finds (unless you made a typo). At the end of the grammar check, a box will pop up with the statistics, including a Reading Ease score and an approximate grade level. More information will be provided about the Reading Ease Score. Quick SMOG* Method Total polysyllabic word ct. Approx. grade level (+/- 1.5) 0-2 4 3-6 5 7-12 6 13-20 7 31-42 9 43-56 10 57-72 11 73-90 12 91-110 13 111-132 14 133-156 15 157-182 16 183-210 17 211-240 18 Count the number of polysyllabic words in a chain of 30 sentences and look up the approximate grade level on this table. *I have no idea what “SMOG” stands for. I found this method on the web about four years ago. Flesch Reading Ease Information The Flesch Reading Ease Scale measures readability on a scale of 1-100: 100 Very easy to read. Average sentence length is 12 words or less. No words of more than two syllables. 65 Plain English. Average sentence length is 15 to 20 words. Average word has two syllables. 0 Extremely difficult to read. Average sentence length is 37 words. Average word has more than two syllables. Flesch Reading Ease scores of some typical texts No wonder it’s hard to do Comics 92 Consumer ads in magazines 82 Movie Screen 75 Seventeen 67 Reader's Digest 65 Sports Illustrated 63 New York Daily News 60 Atlantic Monthly 57 Time 52 Newsweek 50 Wall Street Journal 43 Harvard Business Review 43 New York Times 39 New York Review of Books 35 Harvard Law Review 32 Standard auto insurance policy 10 Internal Revenue Code minus 6 taxes or understand one’s insurance! Which One Do I Use? Accuracy: The Quick SMOG is for higher grade levels (above 4th grade). The Flesch grade level ends at grade 12 and does not differentiate between 12th grade, college level, and graduate level texts. The Flesch Readability Ease formula is great for all levels of readers. Therefore: for younger students (grades k-5) use the Microsoft Word method. For older students, use either Microsoft Word or Quick SMOG. Convenience: Choose the most do-able one if time is of the essence. If you don’t want to type in a text, then Quick SMOG is very easy. If you are using a text from the web, copy it into Microsoft Word and use the grammar check method (Flesch grade level and Flesch Reading Ease). Many student text books are now available in digital versions, so you can also use that instead of having to type in a text. So, do they work? Flesch’s perspective I developed the formula in the early 1940s. It measures the average sentence length in words and the average word length in syllables. You put these two numbers into an equation and get a number between 0 and 100 that shows you the difficulty of your piece of writing. If it's too hard to read for your audience, you shorten the words and sentences until you get the score you want. At first blush you may think this is a very crude way of dealing with writing. Writing means conveying ideas from one mind to another. To use a mechanical gadget for this doesn't seem like an intelligent approach. But wait a minute. I spent several years of my life doing the underlying research for this formula and got my Columbia University Ph.D. degree for it. I can assure you that it is based on some very complicated facts of human psychology. It works because it is based on the way the human mind works. Flesch’s perspective continued When you read a passage, your eyes and mind focus on successive points on the page. Each time this happens, you form a tentative judgment of what the words mean up to that point. Only when you get to a major punctuation mark-a period, a colon, a paragraph break-does your mind stop for a split second, sum up what it has taken in so far, and arrive at a final meaning of the sentence or paragraph. The longer the sentence, the more ideas your mind has to hold in suspense until its final decision on what all the words mean together. Longer sentences are more likely to be complex-more subordinate clauses, more prepositional phrases and so on. That means more mental work for the reader. So the longer a sentence, the harder it is to read. The last little bit of Flesch Exactly the same thing is true of words. Some words are short and simple, others are long and complex. The complexity shows up in the prefixes and suffixes. Take is a simple. short word that doesn't present much difficulty to a reader. But unmistakably has the prefixes un- and misand the suffixes -able and -ly and gives the mind much more to think about than take. (My very first readability formula was based on a count of prefixes and suffices to measure word complexity. A few years later I tried to make it easier to use and changed to a count of syllables. Statistically, the results are about the same.) From: How to Write Plain English By Rudolf Flesch Enough with the propaganda. Does it REALLY work? Think back to what you know about reading and comprehension. Now we will do a little experiment using two texts. Text 1 has a Flesch Reading Ease score of 25. Text 2 is easier: its Reading Ease score is 43. After you read each text, you will be asked to think about your reading experience. At the end of both, you will be asked to draw some conclusions. Text 1 Text 1 is an extremely difficult text (25 on the Flesch Reading Ease scale). This is a text that is appropriate for graduate students. This excerpt is from the middle of the book, not the beginning. Playing with Signs: A Semiotic Interpretation of Classic Music Kofi Agawu If we can assume that the studies by Rosen and Ratner are representative of the range of methodologies followed by students of Classic music, we can go on to observe that the specific concern with normative procedures—whether these are treated axiomatically as with Rosen, or spelled out in the form of formulaic recipes as with Ratner—grows out of the feeling that the classical style approximates a language “spoken” by Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven, and their contemporaries. Most scholars acknowledge the exemplary and polished nature of this music, hence the terms “Classic,” “classical,” and “classic,” even where attempts are made to dispense with the label altogether. The uniformity of intent necessary for this style to attain the status of a language can therefore be inferred from this characterization. But inference is weaker than explicit demonstration—hence my reference to a “feeling,” by which I mean a persistent current that informs these writings in the form of a subtext; it guides the formulation of the authors’ concepts but it is never made explicit. What is the precise nature and the extent of the linguistic analogy in writings about Classic music? To answer this question, we need to examine a few characteristic descriptions of the music. Descriptions of music in terms of language-based disciplines are commonplace in the musicological literature. In the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, rhetoric provided a useful model for such discourse, and theorists freely borrowed the language and terminology of rhetoricians. Thus Joachim Burmeister, in his Musica Poetica of 1601, drew on literary concepts to characterize compositional strategy as a threefold process— exordium, confirmatio, and conclusio. Johann Mattheson also relied a great deal on rhetorical terms in characterizing the process of a piece of music. In his Vollkommene Capellmeister of 1739, Mattheson extended Burmeister’s three-stage model to a six-stage one as follows: exordium (introduction), narratio (report), propositio (proposal), confirmatio (corroboration), confutatio (refutation), and peroratio (conclusion). Later in the century, Heinrich Koch continued, on the one hand, to borrow from rhetoric while, on the other hand, showing a decisive shift from rhetoric to (or, more accurately, back to) linguistics, from rhetorical terms to grammatical ones. These trends have continued to the present day, both informally in music criticism, and more formally in the recent theories of Allan Keiler, Mario Baroni, David Lidov, and Lerdahl and Jackendoff, among others. What distinguishes writing about Classic music from that about other music is not merely a general awareness of the affinities between music and language, but a persistent concern with a shadowy linguistic analogy at all levels. Is it perhaps the case that Mozart and Haydn “spoke one language” whereas Brahms and Wagner, Schumann and Chopin, or Bach and Rameau spoke different languages? Certainly a hasty response to this question might cite the fact that it is, at least superficially, easier to mistake, for example, Haydn for Mozart (and vice versa) than it is to mistake Brahms for Wagner, or Rameau for Bach. One might then go on to cite sociological factors—such as the presence of certain societal uniformity in the late eighteenth century, which was then overthrown in the nineteenth, leading to a profound individualization in artistic expression—to support such a viewpoint? Yet our hasty response will still have left many questions unanswered. Reflecting on Agawu What are the main ideas of this text? How hard did you find it to read this text? What helped you/hindered you in your comprehension? Text 2 Text 2 is a less difficult text in terms of readability. It has a Flesch Reading Ease of 43 (about the same as the Wall Street Journal). This excerpt is from the beginning of an essay. Structure, Sign and Play in the Discourse of the Human Sciences Jacques Derrida “We need to interpret interpretations more than to interpret things.” Montaigne Perhaps something has occurred in the history of the concept of structure that could be called an “event,” if this loaded word did not entail a meaning which it is precisely the function of structural—or structuralist—thought to reduce or to suspect. Let us speak of an “event,” nevertheless, and let us use quotation marks to serve as a precaution. What would this event be then? Its exterior form would be that of a rupture and a redoubling. It would be easy enough to show that the concept of structure and even the word “structure” itself are as old as the episteme—that is to say, as old as Western science and Western philosophy—and that their roots thrust deep into the soil of ordinary language, into whose deepest recesses the episteme plunges in order to gather them up and to make them part of itself in a metaphorical displacement. Nevertheless, up to the event which I wish to mark out and define, structure—or rather the structurality of structure—although it has always been at work, has always been neutralized or reduced, and this by a process of giving it a center or of referring it to a point of presence, a fixed origin. The function of this center was not only to orient, balance, and organize the structure—one cannot in fact conceive of an unorganized structure—but above all to make sure that the organizing principle of the structure would limit what we might call the play of the structure. By orienting and organizing the coherence of the system, the center of a structure permits the play of its elements inside the total form. And even today the notion of a structure lacking any center represents the unthinkable itself. Nevertheless, the center also closes off the play which it opens up and makes possible. As center, it is the point at which the substitution of contents, elements, or terms is no longer possible. At the center, the permutation or the transformation of elements (which may of course be structures enclosed within a structure) is forbidden. At least this permutation has always remained interdicted (and I am using this word deliberately). Thus it has always been thought that the center, which is by definition unique, constituted that very thing within a structure which while governing the structure, escapes structurality. This is why classical thought concerning structure could say that the center is, paradoxically, within the structure and outside it. The center is at the center of the totality, and yet, since the center does not belong to the totality (is not part of the totality), the totality has its center elsewhere. The center is not the center. The concept of centered structure—although it represents coherence itself, the condition of the episteme as philosophy or science—is contradictorily coherent. And as always coherence in contradiction expresses the force of a desire. The concept of centered structure is in fact the concept of a play based on a fundamental ground, a play constituted on the basis of a fundamental immobility and a reassuring certitude, which itself is beyond the reach of play. Had enough? What are the main ideas of this text? How hard did you find it to read this text? What helped you/hindered you in your comprehension? Confessions The Agawu text is a whole book on the semiotic interpretation of music. Semiotics is the study of how things make meaning. Agawu’s book is one of the best I have ever read about how music means. Jacques Derrida is a French philosopher who is best known for coining the word, “deconstruction.” Deconstruction uses post-structural linguistics and psychoanalysis in order to analyze cultural artifacts for underlying contradictions and constructs. Your Turn What is the utility of readability in the classroom? What other factors do you need to take into account when you are choosing texts for your students to read?