15
The Demand for Resources
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Resource Pricing
• Firms demand resources
• Focus on labor
• Resource prices are important
• Money-income determination
• Cost minimization
• Resource allocation
• Policy issues
LO1
Resource Demand
• All markets are competitive
(good and resource)
• Derived demand depends on:
• Productivity of resource (MP)
• Price of the good it helps produce (P)
• Marginal revenue product (MRP)
• Change in TR resulting from unit
change in resource (labor)
LO1
Resource Demand
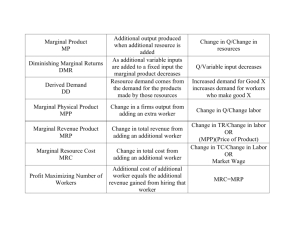
•Rule for employing resources:
• MRP = MRC
• Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
Marginal
Revenue
Product
=
Change in Total Revenue
Unit Change in Resource Quantity
• Marginal Resource Cost (MRC)
Marginal
Resource
Cost
LO1
=
Change in Total (Resource) Cost
Unit Change in Resource Quantity
MRP as Resource Demand
(1)
(2)
Units of Total Product
Resource
(Output)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(3)
Marginal
Product (MP)
(4)
Product
Price
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
$2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
0]
7]
13 ]
18 ]
22 ]
25 ]
27
]
28
(5)
Total Revenue,
(2) X (4)
$0
14
26
36
44
50
54
56
$18
Purely
Competitive
Firm’s
Demand for
A Resource
Resource Wage
(Wage Rate)
16
14
12
10
8
6
D=MRP
4
2
0
-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Quantity of Resource Demanded
LO1
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
(6)
Marginal Revenue
Product (MRP)
$14
12
10
8
6
4
2
MRP as Resource Demand
(1)
(2)
Units of Total Product
Resource
(Output)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(3)
Marginal
Product (MP)
0]
7]
13 ]
18 ]
22 ]
25 ]
27
]
28
(4)
Product
Price
(5)
Total Revenue,
(2) X (4)
$2.80
2.60
2.40
2.20
2.00
1.87
1.75
1.65
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
$ 0.00
18.20
31.20
39.60
44.00
46.25
47.25
46.20
$18
Imperfectly
Competitive
Firm’s
Demand for
A Resource
Resource Wage
(Wage Rate)
16
14
D=MRP
(Pure Competition)
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
D=MRP
(Imperfect
Competition)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-2
Quantity of Resource Demanded
LO1
]
]
]
]
]
]
]
(6)
Marginal Revenue
Product (MRP)
$18.20
13.00
8.40
4.40
2.25
1.00
-1.05
Determinants of Resource Demand
• Changes in product demand
• Changes in productivity
• Quantities of other resources
• Technological advance
• Quality of the variable resource
LO2
Determinants of Resource Demand
• Changes in the price of substitute
•
LO2
resources
• Substitution effect
• Output effect
• Net effect
Changes in the price of
complementary resources
Occupational Employment Trends
• Rising employment
• Services
• Health care
• Computers
• Declining employment
• Labor saving technological change
• Textiles
LO2
Elasticity of Resource Demand
Erd =
Percentage Change in Resource Quantity
Percentage Change in Resource Price
• Ease of resource substitutability
• Elasticity of product demand
• Ratio of resource cost to total cost
LO2
Optimal Combination of Resources
• All resource inputs are variable
• Choose the optimal combination
• Minimize cost of producing a given
output
• Maximize profit
LO3
The Least Cost Rule
• Minimize cost of producing a given
•
output
Last dollar spent on each resource
yields the same marginal product
Marginal Product
Of Labor (MPL)
Price of Labor (PL)
LO3
=
Marginal Product
Of Capital (MPC)
Price of Capital (PC)
Profit Maximizing Rule
• MRP of each resource equals its
price
PL = MRPL and PC = MRPC
MRPL
PL
LO3
=
MRPC
PC
=1
Income Distribution
• Paid according to value of service
• Workers
• Resource owners
• Inequality
• Productive resources unequally
•
LO3
distributed
Market imperfections
Income Distribution
• Numerical Illustration
• Data for finding the least-cost and
profit-maximizing combination of
labor and capital