What is “Competency” in the New Millennium?
advertisement

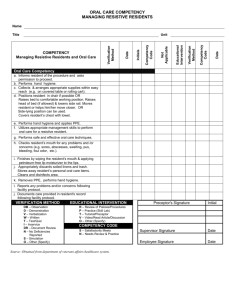
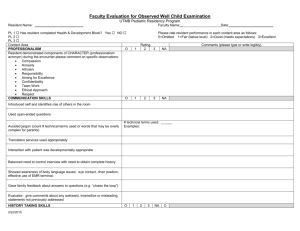
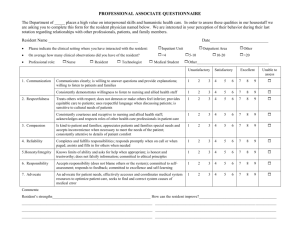
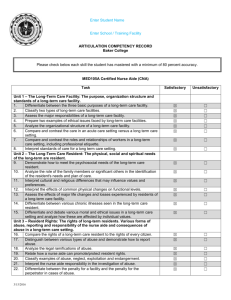
What is “Competency” in the New Millennium? Shirley Schlessinger, MD, FACP Associate Dean for Graduate Medical Education University of Mississippi Medical Center “Competency” Main Entry: com·pe·tent 1 : proper or rightly pertinent 2 : having requisite or adequate ability or qualities : FIT 3 : legally qualified or adequate 4 : having the capacity to function or develop in a particular way; specifically : having the capacity to respond (as by producing an antibody) to an antigenic determinant synonym see SUFFICIENT Competency In GME Historically like pornography? (“know it when you see it…”) Ad hoc local standards, assessment tools Traditionally defined around “Knowledge, Skills, Attitudes” National focus on “accountability,” patient safety, quality of medical care 2001 ACGME and ABMS defined 6 domains of “competency” ALL physicians completing graduate medical training must be competent in all 6 areas Domains of Competency Medical Knowledge Patient Care Professionalism Communication Skills Practice Based Learning & Improvement Systems Based Practice Medical Knowledge Must demonstrate knowledge of established and evolving biomedical, clinical, and social sciences Application of medical knowledge to patient care: clinical problemsolving, clinical decision-making, and critical thinking Apply an open-minded, analytical approach to acquiring new knowledge Patient Care Provide compassionate, appropriate and effective patient care Promote health, prevention of illness, treatment of disease, and end of life care Gather accurate essential information from all sources Develop and implement effective patient management plans Perform competently diagnostic and therapeutic procedures (essential to IM) Professionalism Reflect commitment to continuous professional development, ethical practice, and understanding and sensitivity to diversity Responsible attitude toward patients, profession, and society Demonstrate respect, compassion, integrity, and altruism Adhere to principles of confidentiality, scientific integrity, and informed consent Recognize and identify deficiencies in peer performance Interpersonal & Communication Skills Establish and maintain professional relationships with patients, families, and other health care team members Use effective listening, nonverbal, questioning, and narrative skills to communicate with patient and families Interact with consultants in a respectful, appropriate manner Maintain comprehensive, timely, and legible medical records Practice Based Learning & Improvement Use scientific evidence and methods to investigate, evaluate, and improve patient care practices Implement strategies to enhance knowledge, skills, attitudes and processes of care Analyze clinical practice to improved quality of patient care Be willing to learn from errors Use technology to manage information Systems Based Practice Understand the contexts and systems in which health care is provided Effectively utilize resources to provide optimal care Apply evidence-based, cost-conscious strategies to prevent, diagnose, and manage disease Collaborate with other health care team members to improve processes of care The Competency Framework Use the 6 domains of competency to “frame” both formative and summative feedback ABIM standard evaluation requires scoring the resident in each area Ask residents to perform “selfassessments” in the competency domains Focus on PBLI & SBP Conceptually “newest” competencies Often hardest for attending faculty to develop comfort in evaluating Questions can help guide the assessment of your resident… PBLI Does the resident voluntarily discuss and research relevant literature to support decision-making processes? Does the resident effectively and efficiently use consulting services to improve both patient care and self-knowledge? Does the resident teach junior colleagues and peers appropriately? Does the resident use information about self-errors to change behavior/improve care? Does the resident participate actively in QI practices (M&M) and review autopsies? SBP Does the resident identify the patient’s resources, and provide optimal care within those boundaries? Does D/C planning begin at admission? Does the resident arrange appropriate patient care follow-up? Does the resident use hospital and outpatient resources effectively? Does the resident use practice guidelines appropriately? And the true challenge… Strive not for “competence” but for excellence!