Introduction to Spectrophotometry & Beer's Law
advertisement

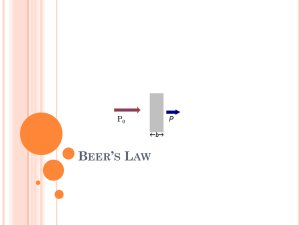
Introduction to Spectrophotometry & Beer’s Law AP Chemistry Mrs. Weston What is spectrophotometry? • A type of spectroscopy that studies the transmission or reflection of different frequencies of the electromagnetic spectrum (specifically visible, near-IR and near-UV ranges) by a sample of matter (usually a soln) Other types of spectroscopy • • • • • Atomic absorption spectroscopy Atomic emission spectroscopy Mass spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy Spectrophotometer • Measures absorbance or transmittance of light as a function of wavelength • Sample is placed into cuvette • Light of selected wavelength is passed through sample • Amount of light absorbed is measured • Because other compounds in a solution (or the solvent itself) may absorb the same wavelengths as the compound being analyzed, the absorbance of the sample is compared to a reference blank. • Ideally, the reference blank should contain everything found in the sample solution except the substance being analyzed. • When using a Spec 20, every time the wavelength is changed, the instrument needs to be re-zeroed. How it works Transmission = I/Io Absorbance = log T How to choose wavelength • We want to analyze samples using the wavelength at which the most light is absorbed – Wavelength of maximum absorption (λmax) Beer’s Law • Amount of light absorbed is proportional to the concentration of the solution A = abc • A = absorbance • a = proportionality constant (ε = molar absorptivity) • b = path length (same for entire experiment) • c = concentration (M) What does this tell us? • There is a direct relationship between absorbance and concentration. • When we prepare solutions of known concentration and analyze them at λmax, we can plot absorbance as a function of concentration. • The concentration of the unknown can be determined by finding its absorbance and plugging it into the equation for the best fit line. y = mx + b Uses of spectrophotometry • Determining concentration of any colored solution (Fe, Cu, Co, Ni, MnO4, etc) • Biology • Biochemistry • Forensic science