Chapter 4 and 5 homework
advertisement

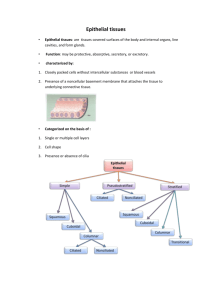
Name:______________________________________________ Period:______ Homework Chapter 4 Date ______________ Using your textbook, Chapter 4 pp118-137 and 141-145 and other sources. complete by _____________ Use these choices to identify the major tissue type in each case. Connective Epithelium ______________ 1. Forms membranes ______________ 2. Supports and reinforces body organs ______________ 3. Cells of this tissue may absorb or secrete substances ______________ 4. Forms exocrine and endocrine glands ______________ 5. Surrounds and cushions body organs ______________ 6. Characterized by large amounts of extra cellular material ______________ 7. Widely distributed throughout body List the 6 (six) major functions of epithelial tissue 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) List the 6 (six) special characteristics of epithelial tissue 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Matching ____1. Lines most of intestines A. pseudostratified ciliated columnar et ____2. Lines inside of mouth B. simple columnar et ____3. Lines much of respiratory tract C. simple cuboidal et ____4. Endothelium D. simple squamous et ____5. Lines urinary bladder E. transitional et ____6. In glands and ducts of glands F. stratified squamous et Matching ____1. Protection from abrasion A. transitional et ____2. Diffusion B. cilia ____3. Propel mucus C. stratified squamous et ____4. Stretches D. simple squamous et ____5. Absorption, secretion E. simple columnar et Glands Define Exocrine: Endocrine: What is the difference between tubular and alveolar glands? True or false. If the statement is false, change underlined word to make it true. ____________1. Exocrine glands are classified functionally as merocrine, holocrine, or apocrine. ____________2. Most exocrine glands are apocrine. ____________3. Holocrine glands store secretions until the whole cell ruptures. ____________4. Sweat glands are examples of holocrine glands ____________5. Merocrine glands release secretions by exocytosis. Choose EXOCRINE or ENDOCRINE ____________1. Has a duct to carry secretions ____________2. Examples are thyroid and adrenal ____________3. More numerous of the two glands ____________4. Secrete hormones directly into blood to be carried to target organ ____________5. Example is pancreas as it produces digestive enzymes Connective tissue Use the following choices to identify the connective tissue A. Adipose ct B. Areolar ct C. Dense regular ct D. Dense irregular ct E. Elastic cartilage F. Fibrocartilage G. Hyaline cartilage H. Reticular ct _____1. Parallel bundles of collagen fibers; forms tendons and ligaments _____2. Stores fat _____3. Dermis of skin _____4. Under epithelial tissue; contains many fibers and cell types _____5. Forms embryonic skeleton; covers surface of long bones _____6. Insulates body _____7. Firm matrix, milky white and glassy. Contains much water. _____8. Parallel collagen fibers in cartilage found in intervetebral discs _____9. Soft “skeleton” or framework for some organs including lymph nodes _____10. External ear and epiglottis Matching _____1. Chondrocytes A. Embryonic tissue that give rise to all connective tissue _____2. Matrix B. in areolar ct; engulf cellular debris _____3. Macrophage C. composed of ground substance and fibers _____4. Mesenchyme D. cells that maintain matrix in cartilage _____5. Collagen fibers E. tough protein fibers that resists longitudinal tearing ____6. Mast cell F. in aerolar ct; contain histamine. Name:______________________________________________ Period:______ Homework Chapter 5 Date ______________ Using your textbook, Chapter 5 pp152-171 and other sources. complete by _____________ 1. Name the tissue composing the epidermis. 2. What two tissues make up the dermis? The largest part of the dermis is made of which one? 3. Define terms briefly a. Lines of cleavage b. Striae c. Flexure lines d. wrinkles 4. Use the following choices a. S. basale (basal layer) c. S. granulosum (granular layer) e S.spinosum (Prickly layer) g. Reticular layer i. Dermis (as a whole) b. d. f. h. j. S. corneum (horny layer) S. Lucidium (clear layer) Papillary layer Epidermis (as a whole) hypodermis _____1. Layer of translucent cells, only in thick skin _____2. Layer containing all or mostly dead cells _____3. Dermal layer responsible for fingerprints _____4. Vascular region _____5. Actively mitotic (dividing) epidermal region, deepest epidermal layer _____6. Cells are flat, dead “bags” of keratin _____7. Site of elastic and collagen fibers _____8. General site of melanin formation _____9. Major skin area where derivatives (hair, nails) reside _____10. Largely adipose tissue, anchors skin to underlying tissues _____11. Also known as stratum germinativum _____12. Layer where melanocytes are found _____13. Cell in this layer contain keratinohyalin and lamellated granules _____14. Accounts for the bulk of epidermal thickness _____15. Provides mechanical strength to skin 5. Use these choices A. Carotene B. Hemoglobin _____1. Responsible for skin color of dark skin _____2. Gives an orange cast to skin _____3. Protects cells from sun damage _____4. Give pink tint to light skinned persons _____5. Phagocytized by keratinocytes _____6. Found in stratum corneum C. Melanin 6. Matching _____1. _____2. _____3. _____4. _____5. Bluish cast of skin; resulting from lack of oxygen Could be caused by anemia or low blood pressure May indicate liver disease Clotted mass of blood under the skin Result of inflammation, allergy, and fever A. B. C. D. E. Erythema Cyanosis Hematoma Jaundice Pallor 7. Explain how each of the following helps to protect the body a. Langerhan’s cells and macrophages b. Bactericidal secretions c. Keratin d. Melanin e. Acid mantle 8. Explain the role of sweat glands in maintaining body temperature. How are sweat glands regulated? 9. What are the two major concerns in burn patients? How can each lead to death? 10. Use the choices A. First degree burn _____1. _____2. _____3. _____4. _____5. _____6. B. second degree burn C. third degree burn Full thickness of skin is burned; skin can be gray white cherry red or charred Blisters Only epidermal damage; redness and some pain Epidermal and some dermal damage Regeneration impossible; requires some type of skin graft procedure Pain is absent because nerve endings in area are destroyed 11. What is the rule of nines? How is it used when treating burn victims? 12. Fill in the type of skin cancer matching the description. ________________cells of s.sinosum develop lesions; metastasizes to lymph nodes ________________cells of lowest level invade dermis and hypodermis; slow to metastasize ________________cancer of pigment producing cell; most deadly