Canada*s Federal, Provincial, and Municipal Governments: A
advertisement

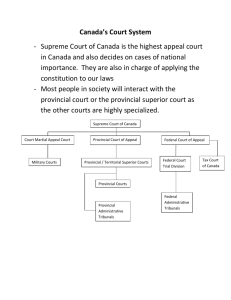
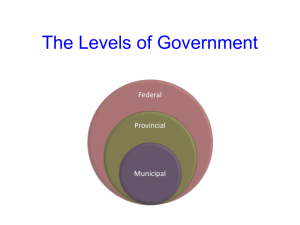
Life without Government would be…. ___________________________: “Rule by the people” Requires: ___________________– the right to vote A _____________– fundamental rules _________________________: follows a constitution and British ___________(Model) The _______is at the head of our government ______________: divided into 3 levels – _______, __________, ____________ ___________: Political system in which individuals who share a ______________organize themselves into parties to ________________for the right to __________ Ex. Liberal, Conservative, NDP, Green, Bloc Quebecois ________ 2) __________ 3) _________ 1) FEDERAL Responsibilities: __________policy ______________ _________and __________ _________laws _______________ National _________ ______________insurance ____________peoples _______system PROVINCIAL Responsibilities: ___________ ____________ **federal government pays a portion of the cost of health care and higher education ___________taxation Provincial ________ Management of _________________ ______and _________ _______________________programs ___________ MUNICIPAL Responsibilities: Libraries Local schools Police & fire departments Public transportation & local roads Parks & recreation Water & sewage Garbage & recycling collection Zoning bylaws, building codes/permits/licenses Structure: Elected municipal members: mayors and councillors work to pass by-laws (laws only for that municipality) Individual citizens most directly participate here Federal Provincial EXECUTIVE BRANCH •Monarch •Governor General •Prime Minister •Cabinet LEGISLATIVE BRANCH •House of Commons (Member of Parliament MP) •Senate JUDICIAL BRANCH •Supreme Court of Canada •Federal Court of Appeal •Federal Court •Tax Court EXECUTIVE BRANCH •Monarch •Lieutenant Governor •Premier •Cabinet LEGISLATIVE BRANCH •Provincial Legislature (Member of the Legislative Assembly – MLA) •n/a JUDICIAL BRANCH •Supreme Court of Canada •Provincial Court of Appeal •Provincial/Territorial Superior Court STEP 1: ______________ STEP 2: _______________________ ________create and run for _______on a __________ All Canadians _____________may vote The country/province is divided into _________(aka: _______, ____________, ________districts) (an area with approx. _______ people) that elect one person The party that won the ____________forms the government The leader of this party becomes the ____________of the country/province The party with the _____________________becomes the _______ ____________(leader of the official opposition) STEP 3: ________________________ The new government begins to run the country following a __________– putting a ______________________ ________________________(ultimate goal of a political party) A party has ______________________________in the country/province This allows the government to ___________________the support of another _______ _______________________ When a government _____________________to Parliament than any other party, _____________than all the other ______________________ To _____________, the government must have the ________of the ________ parties ________________because may be _________by a ____________________by __________members Example Liberal NDP Conservative Green Party Bloc Quebecois 45 21 34 1 3 _______________________ formal arrangement by which political parties work together for a period of time or to meet a specific objective














![[PROVINCE] The Provinces of Canada: [Name] [Date]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014385760_1-fdd8957381c24d338b96b6c2bda8c30d-300x300.png)