Water Pollution
advertisement

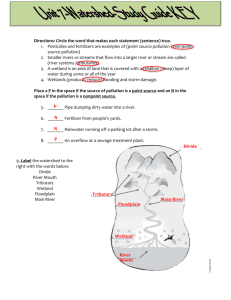
Water Pollution You know water can be healthy or unhealthy… But how does it get this way??? What is Water Pollution? Pollutant – The addition of any substance that damages the water quality and makes it dangerous to drink or use. Where do these pollutants come from? Factories Farms Households What do they each contribute to the pollution problem? Types of Pollutants You Might Not Think Of! Biodegradable Heat Waste Sediments/Erosion Bacteria/Medical Waste Any other examples? How do these pollutants get into the water? There are 2 ways pollutants get into the water: POINT SOURCE POLLUTION NON-POINT SOURCE POLLUTION Point Source Pollution Comes from a single identifiable source Enters the water directly Example: A paper mill pouring chemicals into a stream Non- Point Source Pollution Comes from many sources that are not easily identified Gets into the water eventually (RUN-OFF) Example: Pesticides from a farm runoff into a creek after a rain storm Pollution Protest !!! You will be given an example of either Point or Non-Point Source Pollution. Raise your sign when I tell you to protest which type of pollution you think is correct! Point or Non-Point? Oil spilling from a tanker Point or Non-Point? Irrigation from farms washes pesticide and fertilizer into a river Point or Non-Point? Sewer pipe draining human waste into the ocean Point or Non-Point? Sediment washed into the river from a construction site Point or Non-Point? Fire burning in a landfill; water from fighting the fire will move downhill to the nearest water source… Point or Non-Point? Battery acid leaks from cars onto the parking lot and is followed by a big rain storm Point or Non-Point? Sludge from a chemical plant flows into a stream Point or Non-Point? Factory that produces plastic storage containers dumps liquid wastes into a nearby river Point or Non-Point? A deadly bacteria from cow waste makes its way into a nearby drainage ditch Point or Non-Point? A dangerous acid enters the air from a coal mine in West Virginia and will eventually contribute to acid rain Point-Source examples: Pipe from Sewage Plant Pipe from Industrial Factory Point-Source examples: Non-Point Source examples: Biomagnification/Bioaccumulation Pollution gets into smaller organisms Amount builds up as it gets passed up food chain Chemicals could end up in food eaten by humans What is in place to prevent water pollution? What is the government doing to protect our water? Environmental Sets Protection Agency (EPA) and enforces standards for wastewater that is released into bodies of water or used as drinking water. Clean Water Act (CWA) (Established by the EPA), the Clean Water Act regulates the discharge of pollutants into the waters of the United States and regulates quality standards for surface water Basically makes point source pollution illegal What can YOU do to protect our water? What can you What can YOU do to protect our water? Stewardship: YOUR own personal role in caring for Earth’s waters If our water is polluted… How do we make water safe to drink and use for everyday life? What needs to be taken out before we can use it? Wastewater Treatment Wastewater The dirty water that runs down our drains & sewers that must be cleaned before it can go into lakes, rivers, etc. or be reused. “ The Sparkling Water Story” Listen and follow along as you see firsthand how we impact the cleanliness of our water everyday! Sparking Water Story Part 1 Darin wakes up bright and early to start his day. Since it’s Saturday, it’s his turn to water his mom’s plants. Darin grabs the plants & carries them to the sink. He is not paying attention because he is watching cartoons at the same time. He puts too much water on the plants causing the pot to overflow and spill soil into the sink. He quickly rinses it down the drain so he doesn’t get into trouble, and then runs off to watch his cartoons. Sparkling Water Story Part 1 Dad has managed to get the coffee started and when it is done Dad pours a cup of coffee for himself and a cup for Mom; then goes to read the paper. Mom appreciates his effort but sighs as she realizes he didn’t take the coffee grounds out of the coffee maker and throw them away. She removes them but sees the garbage is full. “It wont hurt to put these down the sink,” she says to herself. Sparkling Water Story Part 1 As mom throws the coffee grounds down the drain she realizes that the garbage disposal smells bad and decides to put a little lemon juice and baking soda in the drain to clean the disposal. Sparkling Water Story Part 1 Becky walks into the kitchen and decides to try to make homemade biscuits for breakfast, but she burns them. Nobody wants to eat the dry, burned biscuits. Darin excuses himself to the bathroom where he flushes his food away. Mom rushes to do the dishes and “accidentally” drops her biscuits down the drain and turns on the water and garbage disposal. Sparkling Water Story Part 2 The family’s day continues as Dad and Darin go outside to wash the car. They spray the car down, soap it up, and rinse it off. The soapy water runs down the driveway into the storm drain. Sparkling Water Story Part 2 Darin notices that the car has been leaking motor oil, so he decides to spray down the driveway. He sprays and sprays, until he is convinced that he has gotten all of the motor oil off and just a stain remains. The motor oil runs into the storm drain. Sparkling Water Story Part 2 Mom and Becky are now outside taking care of Mom’s garden. Mom is spraying the plants down with pesticides so that insects and animals don’t eat them. Becky is sprinkling fertilizer on the plants to make sure that they grow. Darin thinks to himself, “Well, I’m going to help them out and water the garden.” Darin sprays the hose over the plants. Mom screams for him to stop, but its too late, all of the fertilizer and pesticide has been rinsed off, and it too eventually makes it’s way to the storm drain. Filtration Lab: Roles Filtration Engineer/Leader – creates the “blue print” for your system with input from group members BEFORE you just start filtering and waste supplies Supply Management – 2 people responsible for supplies & clean up Scribe – Responsible for leading the discussion, filling out the lab questions for your group & turning them in Filtration Lab: Create your own filtration system!! Use the whiteboard to create a detailed plan that includes step by step instructions and diagram as to how each item in your kit will be used… Please show me your plan BEFORE I allow your supply management person to get water! Filtration Lab Clean-Up: All water can go back into the main tank, all chunks MUST go back into the tank or into the garbage! ONLY clear water can go down the drain at your assigned sink GARBAGE: Used coffee filters & used cotton balls can go straight in the garbage WASH: Other supplies need to be rinsed and dried!! RETURNED BIN SHOULD HAVE: Marker, metal screen, plastic strainer, spoon, pipette, plastic cups LAB QUESTIONS SHOULD BE IN THE BASKET! Steps to the Wastewater Treatment Cycle Step 1. Coagulation Coagulation: Chemicals are added so that waste particles stick together into “floc,” so they can easily be removed. “Stick & Scoop” step Step 2. Sedimentation Sedimentation: The heavy particles settle to the bottom and the clear water moves on Step 3. Filtration Filtration: The water passes through filters made of different materials Step 4. Disinfection Disinfection: A small amount of chemicals are added to kill bacteria (usually chlorine) Step 5. Storage Storage: Water is stored in a closed tank to be used by the community Wastewater Treatment Wastewater Treatment Process: http://www.youtube.com /watch?v=tuYB8nMFxQA But what happens when your city doesn’t have a proper sewer system? Toxic Water: The Sewers of Mexico City http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= 3a_4YhxN2vo&feature=fvst