Cell Organelle Review
advertisement

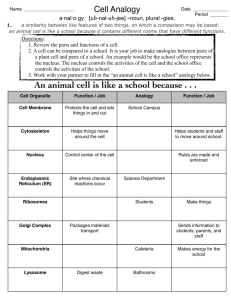
Cell Organelles http://vimeo.com/37107992 Prokaryotic Cells • First cell type on earth • Cell type of Bacteria and Archaea Prokaryotic Cells • No membrane bound nucleus • Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration • Organelles not bound by membranes Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus bound by membrane • Include fungi, protists, plant, and animal cells • Possess many organelles Protozoan Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell Parts • Cells – the basic unit of life • Organelles - small structures inside a cell with specific functions. Analogy – City of Franklin A) Cell Membrane/Plasma Membrane Cell membrane 1. Function: Regulates materials entering and exiting the cell. 2. Structure: Two layers of phospholipids, proteins Analogy – Franklin city limits B) Cytoplasm Cytoplasm 1. Function: All cell contents that lie between the cell membrane and the nucleus. 2. Structure: made up of fluid and organelles except for nucleus Analogy – All air, water, life that are in Franklin, except City Hall C) Nucleus Nucleus 1. Function: “Control Center.” Regulates DNA & RNA actions. 2. Structure: membrane bound, contains DNA Analogy – City Hall D) Nuclear Envelope Nuclear Envelope 1. Function: Regulates what enters or exits the nucleus. 2. Structure: Double Layer of Lipids Analogy – Walls & Doors of City Hall E) Nucleolus Nucleolus 1. Function: Produces RNA, which are used to make all proteins. 2. Structure: Inside Nucleus, separate from DNA Analogy – The Mayor F) DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA (chromatin) 1. Function: information on how to make proteins. 2. Structure: Made up of nucleotides, locked in the nucleus Analogy – The Laws or City Code G) Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER 1. Function: Transportation route for proteins. a. Rough ER: has ribosomes b. Smooth ER: no ribosomes 2. Structure: tubes and channels Analogy – Roads & Sidewalks Endoplasmic Reticulum H) Ribosomes Ribosomes Free Ribosomes 1. Function: Makes proteins. 2. Structure: small circular organelles Analogy – Restaurants, Factories, Builders. I) Vacuoles & Vesicles Vesicles 1. Function: Storage for water, nutrients or waste. 2. Structure: small membrane-bound organelle. Analogy – Grocery stores, water tanks. Vacuole J) Lysosomes Lysosomes 1. Function: packets of enzymes that break down materials in a cell. 2. Structure: Small membrane-bound organelles Analogy – Recycling center K) Mitochondria Mitochondria 1. Function: Produce energy for the cell – site of cellular respiration. “The Powerhouse” 2. Structure: Double membrane-bound, kidney shaped. Analogy – Franklin Electric Plant Board Mitochondria L) Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus 1. Function: Packages, labels and ships proteins out of the cell. 2. Structure: Pancake-shaped layered organelle Analogy – Post Office Golgi Apparatus N) Centrioles (Animals Only) Centrioles 1. Function: microtubules that help divide the cell during cell division. 2. Structure: Tubules Analogy – Franklin Elementary, Simpson Elementary, Lincoln Elementary O) Cilia & Flagella Flagella Flagella Cilia 1. Function: provides movement for the cell or objects moving by the cell. 2. Structure: a. Flagella – 1 long fiber b. Cilia – many short fibers Analogy – Cars or bicycles. P) Chloroplasts (Plants only) Chloroplasts 1. Function: site of photosynthesis (converting sun and CO2 into sugar). 2. Structure: Membrane bound organelles that contain chlorophyll Analogy – Solar Panels Q) Cell Wall (Plant cells only) Cell Wall 1. Function: Provides support for the cell and the plant. 2. Structure: Made of cellulose Analogy – ground, rock wall