Respiratory System
advertisement

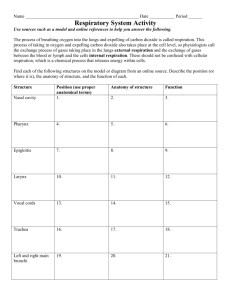
Bio 9D: Thursday, 12.9.10 Title: Patterns in Nature: Biomimicry and the Respiratory System Silent Do Now (in NB w/ title and date) Sketch this image into your notebook Write down what you think it is Write a description of how it is structured When finished, take out your stapled lab report and put it on your desk. Bio 9D: Thursday, 12.9.10 Title: Patterns in Nature: Biomimicry and the Respiratory System Homework: Read pages 956-960 in (first half of section 37.3) In notebook, answer questions on back of Assign. Sheet (Notebooks collected tomorrow!) Today’s Objective: Identify patterns of different structures in nature in order to connect structures with functions. Agenda: Observation Exercise: Patterns in Nature Clicker Review Questions Rules for Observations Exercise You will be drawing and writing in your notebook based on prompts on the slides For each image, you will: Silently draw and write (2 min) Talk w/ a partner (1 min) Listen and raise hand to participate in class discussion (2 min) (We will start at this step for Image 1, which you drew during the Do Now) Image 1: What do you think this is? Describe its structure… Image 2: Sketch it into your notebook. What do you think this is? Describe how it is structured. Reflect on the First Two Images Why do you think these first two objects are structured or “designed” the way they are? Images 3 and 4: • What similarities do you notice between these two images? • Why do you think these similarities exist? • What do you think these things are (hint: they are not the same thing)? X-ray image of a lung! Satellite image of a river delta! Let’s look at some other patterns… Why do trees have leaves? Clicker Review Questions Take out your clicker Take out the Cell Membrane Review Q’s if you didn’t turn them in yesterday 1. If a cell can’t regulate the passage of water, food, and wastes in/out of the cell, which structure is defective? 90% A. Cell Wall B. Chloroplasts C. Cell Membrane D. Endoplasmic reticulum 5% A. 5% B. 0% C. D. 2. What is the function of active transport? A. Packaging proteins for export from the cell B. Distributing enzymes throughout the cytoplasm C. Moving substances against a concentration gradient D. Equalizing the concentration of water inside and outside the cell 86% 10% 5% 0% A. B. C. D. 3. Why would an animal cell swell up and burst when it is placed in pure water? A. Active transport 95% B. Enzyme activity C. Osmosis D. Respiration 5% A. 0% B. 0% C. D. 5. Which diagram best represents osmosis? A A. B. C C. D. D B 55% 35% 10% 0% A. B. C. D. 6. Which process is illustrated in the diagram? A. Active transport B. Diffusion C. Osmosis D. Passive filtration 38% 33% 29% 0% Fastest Responders (in seconds) 4.13 Owen Thurston 7.33 10.44 19.78 Samantha Bergman Lorreno Pierre Warren Jackson 31.53 Loveng Francois Participant Scores 5 Owen Thurston 5 5 5 Samantha Bergman Davnys Policard Courtney Ertilien 4 Lorreno Pierre Bio 9D: Friday, 12.10.10 Title: Respiratory System: Structures & Functions Homework: Double Block NONE - Enjoy the weekend Silent Do Now: (in NB w/ title and date) What is the function of the respiratory system? How does this relate to cell respiration? Today’s Objectives: Describe the structures and functions of respiratory system organs, and explain how they relate to each other Explain the processes of breathing and gas exchange RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PHA Biology 9 Moretti and Dickson Agenda Respiratory System: Structures and Functions Day 1 (1st Half of Double Block) • Complications of the Respiratory System • Purpose of the Respiratory System Transport O2 from the air into the bloodstream Release CO2 from the bloodstream into the air Link to CELL RESPIRATION: Cells need O2 for cell respiration to make ATP Cells release CO2 as a waste product from cell resp. Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system How the Internal Organs Fit Together Image shows major digestive, respiratory, and circulatory system organs Front View Back View Images: http://www.turbosquid.com/FullPreview/Index.cfm/ID/270177 Structures of the Respiratory System Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system Structures of the Respiratory System: Mouth & Nose: Air enters the body; gets moistened/filtered Trachea (aka windpipe): The main airway to the lungs. Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system Structures of the Respiratory System: Lungs: Main organs of the respiratory system where gas exchange takes place. Bronchi: Tubes that branch off from trachea. One major bronchi for each lung that branches into smaller and smaller “bronchioles” in the lung Major Bronchi Branching Smaller Bronchioles Branching in the lung Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system Structures of the Respiratory System: Alveoli: Tiny air sacs at the ends of the bronchioles where gas exchange takes place. Look like GRAPES! Surrounded by a network of capillaries – tiny blood vessels that trade O2 and CO2 with alveoli Structures of the Respiratory System: Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system Agenda Respiratory System: Structures and Functions Day 1 (1st Half of Double Block) • Complications of the Respiratory System • Complications of the Respiratory System 6 Groups: Smoking (use pg. 961-963 in book) Pneumonia Cystic Fibrosis Bronchitis Asbestos Asthma Complications of the Respiratory System Task I - In Small Groups of 3 and 4: Task II - “Jigsaw” into groups with members from different groups: Research one complication of the respiratory system and be able to describe it to the other students in your group. In the “Diagram Box”, draw how your issue damages the respiratory system by modifying and annotating the diagram of the lung. In the “Information Box”, describe the characteristics of your issue, explain how it affects the structures of the respiratory system, and describe how it effects the function of the respiratory system (you can think of these as symptoms). Each person shares the information from their issue As each person presents, all other group members should be comparing and contrasting that issue to their own. Task III - Individually: Compare and contrast 2 of the respiratory system complications to determine their similarities and differences Complications of the Respiratory System Task I - In Small Groups of 3 and 4: (15 min) Research one complication of the respiratory system and be able to describe it to the other students in your group. In the “Diagram Box”, draw how your issue damages the respiratory system by modifying and annotating the diagram of the lung. In the “Information Box”, describe the characteristics of your issue, explain how it affects the structures of the respiratory system, and describe how it effects the function of the respiratory system (you can think of these as symptoms). Complications of the Respiratory System Task II - “Jigsaw” into groups with members from different groups: (25 Min) Each person shares the information from their issue As each person presents, all other group members should be comparing and contrasting that issue to their own. Task III – Individually (15 Min) Compare and contrast 2 of the respiratory system complications to determine their similarities and differences Bio 9A: Monday, 12.13.10 Title: Breathing & Gas Exchange Homework: Study for tomorrow’s quiz by answering the questions on Study Guide (back of Assignment Sheet) Silent Do Now: (in NB w/ title & date) Write today’s title & date in your notebook Get a balloon and, without stretching it, try to inflate it. Observe what your body is doing to inflate the balloon. Write down at least 3 observations in your notebook. Today’s Objectives: Explain how the diaphragm control the process of breathing. Explain how diffusion and concentrations create gas exchange in the lungs. Agenda & Announcements • Balloon Exercise - Debrief • Notes: Breathing and Gas Exchange • Breath-Holding Exercise & Debrief Extra-Credit Opportunity! Teach class on Wednesday – • Must do Tuesday night’s HW tonight • Must meet w/ Dickson during lunch on Tuesday Today’s Objectives: Explain how the diaphragm control the process of breathing. Explain how diffusion and concentrations create gas exchange in the lungs. Two Important Processes in the Respiratory System: (Don’t need to write this down – just a preview) Breathing – controlled by the diaphragm Gas exchange – happens in the alveoli Today’s Objectives: Explain how the diaphragm control the process of breathing. Explain how diffusion and concentrations create gas exchange in the lungs. Breathing Diaphragm: •A large flat muscle that controls breathing •Located at the bottom of the chest cavity Today’s Objectives: Explain how the diaphragm control the process of breathing. The Process of Breathing Inhaling: Diaphragm contracts & lowers 2. Volume of lungs increases (partial vacuum) 3. Air rushes in (through mouth/nose, trachea, bronchi, to alveoli) to fill the space 1. Exhaling: Diaphragm relaxes & bends upward 2. Volume of lungs decreases 3. Air is forced out (from alveoli through bronchi, trachea, mouth/nose) Today’s Objectives: 1. Explain how the diaphragm control the process of breathing. Quick Activity – Holding Your Breath Hold your breath for as long as you can (on my start) While you are holding your breathe, observe what happens to your body the longer you try not to breathe. Record these observations in your notebook. • • • • Quick Activity – “Holding your Breath”: Debrief: What did you observe about your body as you tried to hold your breath? Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system The Process of Gas Exchange Alveoli Blood w/ little O2 (air sacs at ends of branches in lungs) Capillary (tiny blood vessel) O2 diffuses into blood in capillary O2 CO2 CO2 diffuses into alveoli Blood w/ lots of O2 The Process of Gas Exchange Gas exchange – the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across cell membranes Happens in the alveoli of the lungs Oxygen diffuses from alveoli into capillaries (tiny blood vessels) and binds to red blood cells Carbon dioxide diffuses from capillaries into alveoli Objectives for Class: Describe the difference between structure and function, and explain how an object’s structure relates to its function Describe the major structures and functions of all organs in the respiratory system The Process of Gas Exchange Gas exchange in the lungs needs MAD surface area for enough O2 and CO2 to diffuse! Lungs contain 1.3 million alveoli!! The total surface of all the alveoli would cover half a tennis court!!