Lecture 10
advertisement

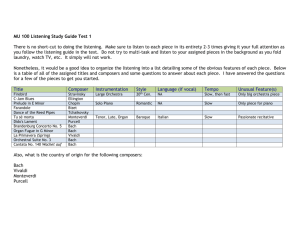
Announcement • New web page • www.colorado.edu/music/courses/em us1832004 Exam on February 25 • Will cover Medieval, Renaissance, and Baroque period • Will also cover some basic musical terminology • Listening examples (refer to GUIDES not CD tracks): 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20, and 21 • Bring a #2 pencil Lutheran Cantatas • Liturgical music for Protestant • • • • (Lutheran) service Bach wrote one every week during his first few years in Leipzig. Bach’s works consist of several movements (5-8) with arias, recitatives and choruses some based on a single tune that appears throughout the movements Cantata: A Mighty Fortress • Choral tune “A Mighty Fortress” … • Created in the time of the Reformation, by Martin Luther himself • hymn tune- in German rather than Latin • originally sung monophonically- then in homophonic settings • permeates the entire cantata by Bach Cantata: A Mighty Fortress • Last movement: Das wort, sie sollen (#8) • Straightforward, homophonic setting of the tune. • Bach harmonized the original tune in 4-parts • His son Wilhelm added the timpani and trumpets … for grandeur Cantata: A Mighty Fortress • First movement: chorale fugue • Fugue: a type of imitation (very systematic and formal way of writing music) • Fugue theme (called subject) is based on chorale tune Cantata: A Mighty Fortress • Second movement • Duet for soprano and bass • Also derived from chorale tune George Frederic Handel • Born in Germany • Spent most of life in England • Known for writing opera in Italian • Also known for ORATORIOS Oratorio • Definition: a work for chorus, vocal soloists, and orchestra on a sacred subject (usually Old Testament stories) • Many of Handel’s were in English • Most famous: Messiah • Written for a charity concert in Dublin, Ireland Handel’s Messiah • written in 1742 • Not a typical oratorio because it doesn’t tell a single story • in three parts, each articulating a part of Christian doctrine. • Christmas- prophesy • Easter- suffering and death, Resurrection • Redemption Messiah: first excerpt • (skip the overture-start your listening at track 21) • Chorus “glory to God” • Preceded by recitative (first with basso continuo, then with orchestra) • Examples of text painting in chorus? Messiah: second excerpt • “Rejoice greatly” • Aria for soprano • Form ABA (with orchestra introduction) • Virtuoso singing • Listen for which words are emphasized • (Emphasis on certain words is a way of interpreting the text) Messiah: third excerpt • Famous “Hallelujah!” • Listen for the differences between homophonic texture and fugue • Fugue is an older style used for serious subjects, a musical symbol of tradition (eg. ”he shall reign forever and ever”) Antonio Vivaldi • Spent much of his life in Venice, Italy • Taught at a high-class orphanage for girls • Girls were highly trained musically • Wrote hundreds of CONCERTOS for them Concerto • Definition: work for soloist (or a group of soloists) and orchestra • Most of Vivaldi’s were written for his students to play • Most of Vivaldi’s were for stringed instruments, but he also wrote concertos for unusual instruments like piccolo and mandolin Concerto • Famous example: The Four Seasons • Group of concertos for violin • Intended to depict winter, spring, summer, and fall Vivaldi, ‘Spring” • From The Four Seasons • Form: alternating orchestra part (called RITORNELLO) with soloist part (called EPISODE) • Solo episodes depict scenes from spring: birds, brook, thunder