pollination OHT - Papanui High School
advertisement

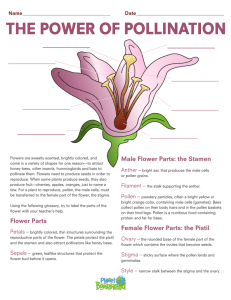
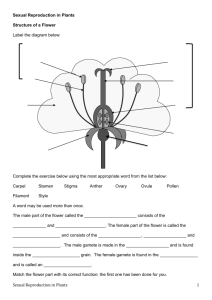
Focusing Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the female and male parts of the flower, where pollination occurs? What are some benefits and disadvantages of self and cross-pollination? How do the pollen grains travel? How are plants adapted for pollination to occur by the insects? Fill in the gaps in the paragraph below: brightly, carpels, coloured, female, four, fruit, fruit, insects, insects, insects, insects, male, nectar, ovary, pollen, pollen, pollination, protected, rings, stamen, stigma, style, wind, wind, wind, sexual A flower is usually made up of f____ parts which are arranged in r_____ inside each other. The sepal is the outermost ring. It pr_____ the flower when it was in bud. The petals of a plant are often b_______ c______ to attract in_____. The stamens are the m____ parts of the plant which produce the yellow, dust-like p_____. The carpel is the f_____ part of the plant which produces the f______ once p________ has taken place. A flower can be pollinated either by in_____ or by w_______. When a flower is pollinated by in_____ the in_____ go to feed on the n_____ of the flower. They brush against the s______ and collect the p_______. Then they brush against the c______ of the same or different flower and pass on the pollen that way. When a flower is pollinated by w_______ the w_______ blows the pollen. In this case the flowers usually have small or non-existent petals. The pollen reaches the carpel at the place called the s______. It travels down the s______ until it reaches the o_______ where a f_______ is formed. Pollination is a form of s_______ reproduction. The body parts of a Honey BEE are adapted to be an insect pollinator Wings – allow the bee to move between their food source and hives. Hairs on Body – hold the sticky pollen grains. Head - Eyes detect the colour on the flower. Antennae detect the scent from flowers. Sucking tube (mouth) collects the nectar. Hind Legs – they collect the pollen. The comb and brush remove pollen from the body and pass it to the pollen basket on the opposite leg. They then take this back to their hive. The coloured petals signal a source of food. The bee pushes its body deep into the flower and the pollen rubs off from the anther. The bee then flies to another flower. The pollen is rubbed of its body onto the stigma of the second flower: cross-pollination has occurred. YOUR TASK: Conduct a simple research assignment on an insect pollinator for home work. Ensure to include any body adaptations that are required for the insects to be able to pollinate, also any reasons to do with their lifestyle of why they happen to be pollinators. Could be presented in poster, essay, or speech form. Flower Research Table The difference between Wind and Insect pollinated flowers Fill in this table by putting brief descriptions of the different parts of the flower. Pollinators Insect Wind Name of plant/ Flower Petals Anthers Pollen Stigma Fertilization Definition Fertilization is the fusion of the male and female gametes. During the process of fertilization, the pollen lands on the stigma. A tube grows down the style and enters the ovary. Male sperm cells travel down the tube and join with the ovule, fertilizing it. The fertilized ovule becomes the seed and the ovary becomes the fruit. The wall of the ovary changes becoming either hardened and dry, or fleshy and succulent. The female orgasm, sepals and petals wither away and may fall off. Fertilizes ovules Ovary swells as seed ripens POLLINATION Definition Pollination is the transfer of the male gametes (pollen grains) to the female part of the plant (carpel). This transfer can either be within the same flower (selfpollination) or from one plant to another (crosspollination). Self-pollination In self-pollination pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same plant. This is very efficient as the pollen doesn’t travel very far but doesn’t allow much chance for genetic variation. Cross-pollination In cross-pollination pollen is transferred from anther to the stigma of another plant of the same species. It is very risky as the pollen may not reach the other plant but if it does succeed then it offers greater genetic variation.