Mollusks Notes Three Classes of Mollusks Class Gastropoda
advertisement
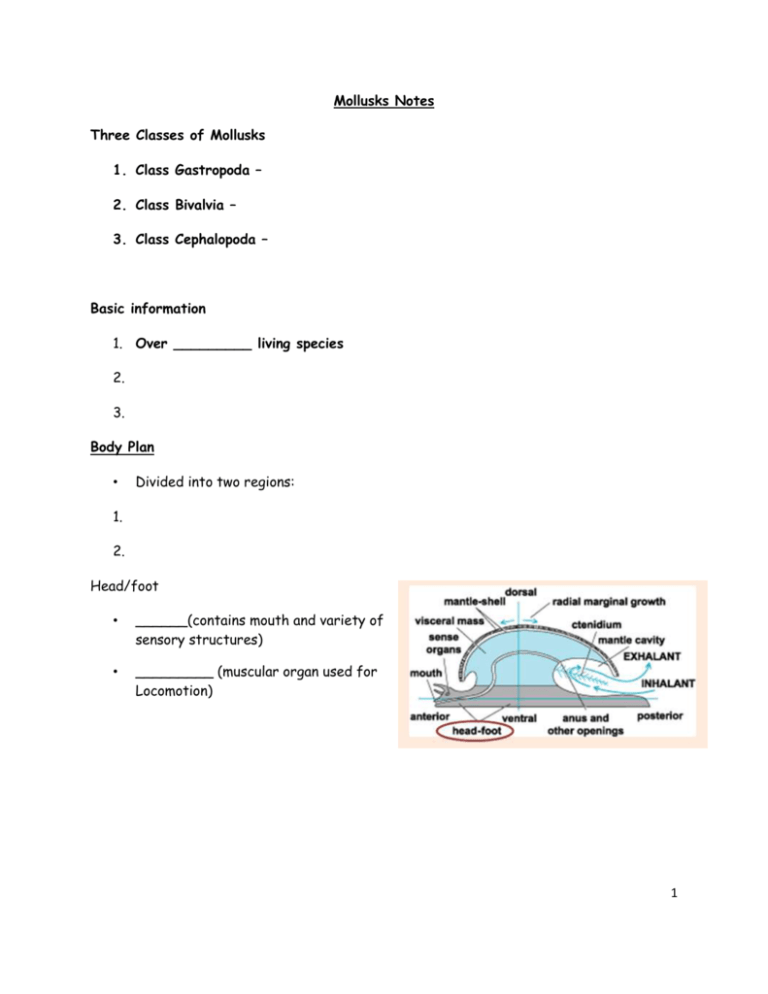
Mollusks Notes Three Classes of Mollusks 1. Class Gastropoda – 2. Class Bivalvia – 3. Class Cephalopoda – Basic information 1. Over _________ living species 2. 3. Body Plan • Divided into two regions: 1. 2. Head/foot • ______(contains mouth and variety of sensory structures) • _________ (muscular organ used for Locomotion) 1 Visceral Mass 1. 2. 3. 4. Mantle 1. 2. mantle cavity 1. 2. nervous system • __________: paired cluster of nerve cells 1. 2. 3. 2 Feeding • _______________: flexible, tongue like strip of tissue covered with tough abrasive teeth that point backward Feature Gastropoda Bivalvia Cephalopoda External Shell Head Radula Locomotion 3 Class Gastropoda • Most diverse class of mollusks • 90,000 species • Snails, abalones, conches= single shell • Slugs = no shell Torsion • __________________ twists around 180° in relation to the head • Twisting results in mantle cavity, gills, and anus to the front of the animal • Gastropod is now able to with _________________________ when threatened Movement • foot secrets a substance allowing animal to glide over surfaces (Slime Trail) Open Circulatory System • ______________ (blood in an organism with open circulation) does not remain in vessels 1. Collected from gills or lungs 2. Pumped through heart 3. Released directly into ________________ a) Fluid filled spaces or blood cavity 4 Bivalvia: Clams Notes Characteristics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Anatomy of Valves • Shell is divided into two halves (_____________) • Connected by a ______________ • _______________ – Contract: _______________ – Relax: _________________ Clam Sensory information • 3 pairs of ganglia – mouth (______________) – digestive system (__________) – Foot (____________) Foot _________ helps burrow in the sand or mud 5 Water Flow water enters through _______________________ Water exits through _____________________ Steps in digestion: Filter Feeders 1. ___________ in gills set up water current 2. ______________ for small organisms 3. ___________: flaplike structures that surround & guide food into the clam's mouth 4. Food then enters the mouth 5. Stomach: ______________________ 6. _______________: digested particles are absorbed 7. _______________: collects and removes digestive wastes 8. Waste are passed through the ______________________ Function of Gills 1. 2. 6 Growth Rate _____________oldest part of the clam Growth rings_________________ CLASS CEPHALOPODA: Most advanced class Head-foot • foot is concentrated in the _______ region • foot is modified into ___________________ equipped with ____________ • Foot also forms _________________ for expelling water, allowing movement by "jet propulsion" What two features can a squid have on its suction cups? What are these structures used for? How do the following cephalopods move: Squid: Octopi: Squid Octopi # of tentacles # arms Suction cups present Sucker rings or hooks present on suction cups? 7 Why would an octopus or squid release ink? _______________– pigment cells that expand and contract to produce color change. – Used as danger signals, protective coloring, and for courtship. What do cephalopods eat? Which cephalopods contain poison in their saliva? What type of circulatory system doe cephalopods have? What is a closed circulatory system? ____________ delivers ___________________ directly to organs through veins and arteries Do octopi and squids have cephalization? Reproduction 1. Male or Female 2. The male uses __________ to take sperm from own ___________ and insert into females __________________ 8 3. The female lays ~100 eggs and guards them until they hatch (approx 50 days) 9