BioQuest Carbohydrates - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement
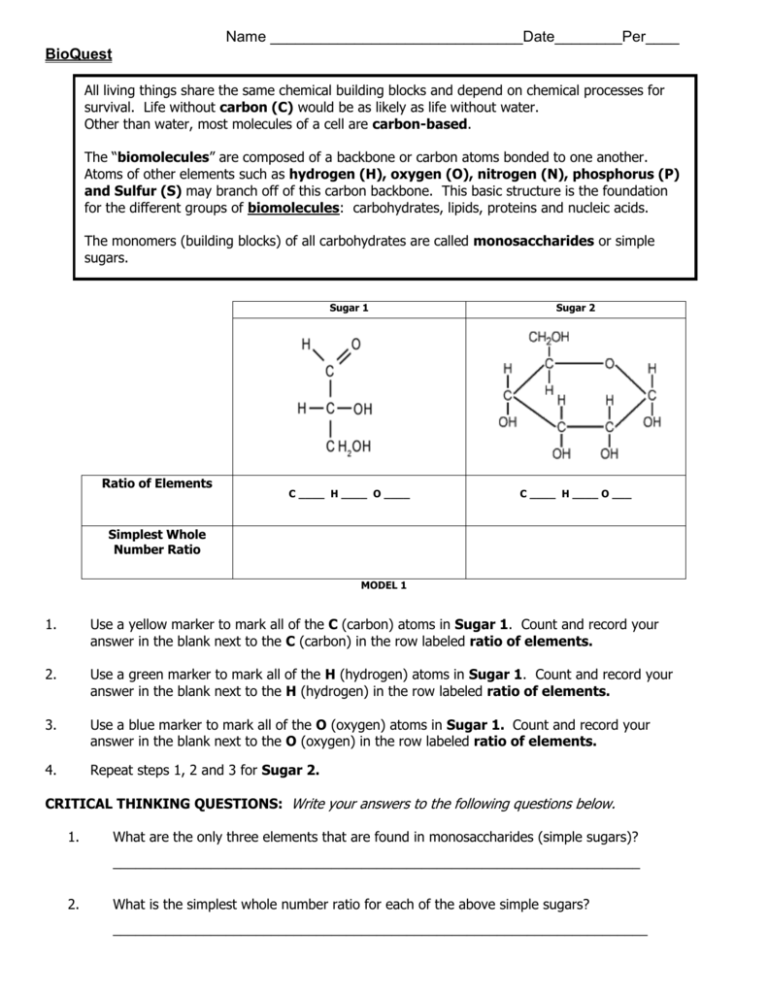
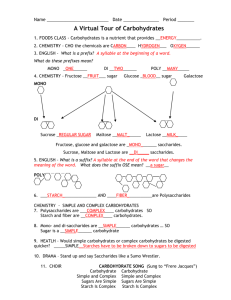
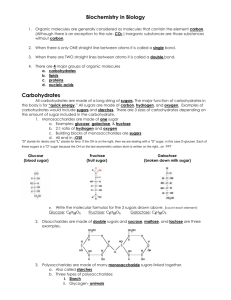
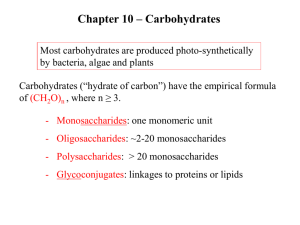
Name ______________________________Date________Per____ BioQuest All living things share the same chemical building blocks and depend on chemical processes for survival. Life without carbon (C) would be as likely as life without water. Other than water, most molecules of a cell are carbon-based. The “biomolecules” are composed of a backbone or carbon atoms bonded to one another. Atoms of other elements such as hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) may branch off of this carbon backbone. This basic structure is the foundation for the different groups of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. The monomers (building blocks) of all carbohydrates are called monosaccharides or simple sugars. Ratio of Elements Sugar 1 Sugar 2 C ____ H ____ O ____ C ____ H ____ O ___ Simplest Whole Number Ratio MODEL 1 1. Use a yellow marker to mark all of the C (carbon) atoms in Sugar 1. Count and record your answer in the blank next to the C (carbon) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 2. Use a green marker to mark all of the H (hydrogen) atoms in Sugar 1. Count and record your answer in the blank next to the H (hydrogen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 3. Use a blue marker to mark all of the O (oxygen) atoms in Sugar 1. Count and record your answer in the blank next to the O (oxygen) in the row labeled ratio of elements. 4. Repeat steps 1, 2 and 3 for Sugar 2. CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS: Write your answers to the following questions below. 1. What are the only three elements that are found in monosaccharides (simple sugars)? ______________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the simplest whole number ratio for each of the above simple sugars? _______________________________________________________________________ Straight Chain H Ring Form O Glucose C C H 2 OH H C OH O H HO C H H C OH HO H C OH H C OH H H OH H H OH OH H CH 2 OH Fructose O H H OH HO HO H C H 2 OH Model 2 3. Glucose is an example of a monosaccharide. List 3 differences between glucose and fructose using Model 2 as your guide. _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Carbohydrates can be “simple” monosaccharides, or they can be combined into disaccharides (two sugars) or even polysaccharides (many sugars). Polysaccharides are sometimes called complex carbohydrates. When monosaccharides are put together, water is a byproduct. Monosaccharides are the monomer, and disaccharides and polysaccharides are the polymer. H H H C OH C H 2 OH H HO O H OH H H OH CH 2 OH H OH H O + H H OH HO HO C HO H C OH C H OH C O H H C H OH C H O C O H H OH C C C HO H + H2O H C OH C H 2 OH sucrose H 4. What two sugars are being combined in the picture above to form sucrose?___________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is the name of the biomolecule that is formed when 3 or more monosaccharides are combined? ______________________________________________________________________ 6. What chemical is also produced when sugars are combined? _______________________________ Polysaccharides Starch Structure Information CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH O O O O O O O OH O OH Cellulose OH Found in plants Used for structure (cell walls) Glycogen OH Found in plants Energy storage a.k.a. amylose Found in animals and fungi Used for energy 7. Look at starch and cellulose carefully. How are they different? How are they the same? _______ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. Humans can digest starch and glycogen but not cellulose. Looking at the structural differences, what is preventing our enzymes from being able to break down cellulose? __________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. Animals can move quickly and plants move slowly. Suggest a reason for the branched structure of glycogen and the straight structure of starch based on this information. ___________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Monosaccharides Glucose Fructose 10. Disaccharides Sucrose Lactose Polysaccharides Amylose Cellulose Look at the table with names of carbohydrates. What is the pattern in the way they are named? _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________