Reproduction Review – Answer Key
advertisement

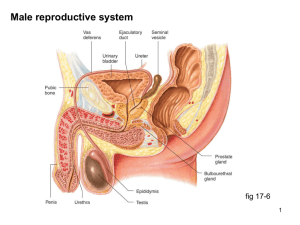
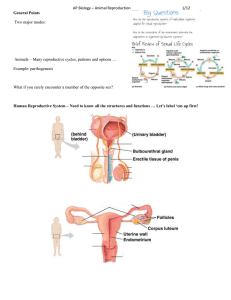
Reproduction Review – Answer Key Pretest 1. Seminiferous tubules, 2. follicle, 3. oviduct, epididymus, 4. testosterone 5. estrogen, progesterone, 6. 1 through 5, 7. corpus luteum, 8. ejaculation, 9. birth canal, copulatory (sex) organ, 10. vulva Study Questions – Male System 1a) bladder – stores urine, b) vas deferens – stores sperm and carries it to urethra, c) prostate – add secretion to seminal fluid, d) urethra – transport urine or sperm to outside, e) penis – male organ of copulation, f) seminal vesicle – add secretion to seminal fluid, g) Cowper’s gland – add secretion to seminal fluid, h) epididymis – maturation and storage of sperm, i) testis – production of sperm and testosterone (*** know specifically where) 2a) seminiferous tubules, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, b) urethra 3a) prostate gland, b) seminal vesicle, c) Cowper’s gland (**know components and function of each one) 4a) FSH, sperm, b) LH, testosterone 5. Erection – penis becomes hard and filled with sperm, ejaculation – semen leaves the penis 6. Impotency – inability to achieve erection, sterility – inability to cause pregnancy in females 7. development of primary sexual characteristics (sex organs) development of secondary sexual characteristics in males: - are taller - have more facial hair - have broader shoulders - have more body hair - have deeper voice - have more muscular mass - get receding hairline and male pattern baldness - are more aggressive Female System 8a) oviduct/fallopian tube – conduct egg (ovum) towards uterus b) ovary – produce eggs (ova) and estrogen c) uterus – implantation of fertilized egg and development of fetus d) bladder – stores urine e) urethra – transports urine only out of the body f) cervix – opening to uterus, dilates during childbirth g) vagina – birth canal and copulatory organ 9a) Follicle forms and produces egg and estrogen, some progesterone b) menstruation c) endometrium breaks down d) proliferative pahse e) endometrium rebuilds f) corpus luteum produces progesterone g) secretory phase h) endometrium thickens, becomes glandular and secretory 10a) dotted lines going from: - estrogen to anterior pituitary to shut off FSH - progesterone to anterior pituitary to shut off LH b) FSH and LH; estrogen and progesterone 11) development of primary sexual characteristics (sex organs) development of secondary sexual characteristics in females: - have wider hips/pelvic girdle - have fat deposits in different places than males - develop breasts - develop body hair - have protruding buttocks - have more lower back curve and abdominal bulge Also causes endometrium to thicken 12a) mons pubis, b) labia majora, c) clitoris, d) labia minora, e) urethra, f) vagina, g) anus 13 both have vasocongestion and release of muscular tension but only males have ejaculation. Female orgasm can also be more subtle. 15a) when the zygote /embryo has implanted itself in the endometrium. b) Estrogen and progesterone produced by the placenta exert negative feedback control to shut off FSH and LH c) presence of HCG in urine (HCG produced by placenta) **Explain how birth control pills work (have estrogen and progesterone in them)















![04 Lecture 4[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009259632_1-99448882b99895746cd105d04644046b-300x300.png)