File
advertisement

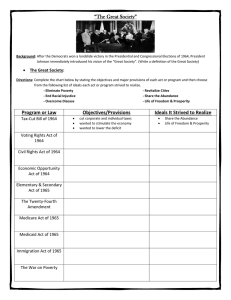
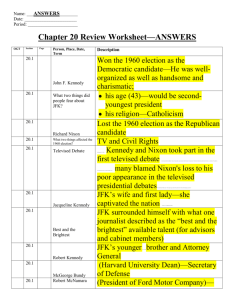
The 1960s KENNEDY’S PRESIDENCY 1. Election of 1960 A. Nominees 1. Republicans 2. Democrats nominated B. Campaign 1. Catholicism 2. Debates 3. African Americans C. Result 1. 2. 3. D. Inaugural speech: "Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country." 2. Kennedy’s domestic policy A. Legislative failures: B. Minimum wage C. Area Redevelopment Act of 1961 D. Housing Act of 1961: F. Space Race Use space below for notes Page 2 Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin E. Crime 3. JFK and Civil Rights: See Civil Rights Era Notes 4. Kennedy and the Cold War A. "Flexible Response": See Cold War Notes Set up Green Berets (elite commando force) Built up nuclear arsenal for 2nd strike capability. B. Bay of Pigs: See Cold War Notes D. Peace Corps E. Alliance for Progress F. Berlin Wall, 1961: See Cold War Notes G. Cuban Missile Crisis (October 1962) : See Cold War Notes H. New spirit of cooperation 1. Kennedy and Khrushchev 2. Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (July, 1963) 5. Assassination of JFK A. November 22, 1963, -- Lyndon Johnson B. Lee Harvey Oswald, C. Warren Commission, Page 3 D. A congressional investigation in the 1970s JOHNSON’S PRESIDENCY 6. President Lyndon B. Johnson and the Election of 1964 A. Pledged to continue Kennedy’s policies 1. Kennedy 2. "War on Poverty" 3. 1964 tax cut. B. Election of 1964 1. Democrats nominated LBJ on the platform of "The Great Society" 2. Republicans nominated Barry Goldwater, senator from Arizona 3. Campaign a. Gulf of Tonkin Resolution b. Goldwater 4. Results: 7. The Great Society War on Poverty (after election of 1964): Office of Economic Opportunity ("Equal Opportunity Act") 8. Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 Page 4 Head Start 9. Medicare Act of 1965 10. Dept of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) created in 1966 11. Immigration Act of 1965 12. Culture A. National Endowment for the Arts (NEA) B. Public Broadcasting System created (PBS) 13. Water Quality Act (1965) 14. Space program continued: U.S. eventually won the space race. 15. Triumph of civil rights (part of the Great Society) 1. 24th Amendment (1964): See Civil Rights Notes 2. Civil Rights Bill of 1964: See Civil Rights Notes 3. Title VII: See Civil Rights Notes 4. Voting Rights Act of 1965: See Civil Rights Notes 5. Affirmative Action (part of the Great Society) 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. "reverse discrimination” Bakke case, 1978 Jesse Jackson: See Civil Rights Notes Thurgood Marshall: See Civil Rights Notes Forced busing : See Civil Rights Notes Rise of Black Power and racial violence: See Civil Black Separatism: See Civil Rights Notes Marcus Garvey: See Civil Rights Notes Nation of Islam: See Civil Rights Notes Malcolm X: See Civil Rights Notes Stokely Carmichael: See Civil Rights Notes Black Power: See Civil Rights Notes Black Panthers: See Civil Rights Notes Racial violence : See Civil Rights Notes "Long Hot Summers": See Civil Rights Notes Rights Notes Page 5 16. President Lyndon Johnson’s legacy A. 1. 2. a. b. c. B. No president since Lincoln had worked harder or done more for civil rights. C. "Great Society" programs heavily criticized by conservatives in subsequent years. 1. 2. D. The Vietnam War Page 6 Summaries Page 7 Page 8 Page 9