Investigating Polar Bear and Giant Panda Ancestry
advertisement

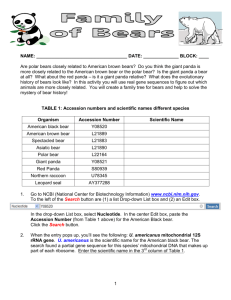
Investigating Polar Bear and Giant Panda Ancestry (Adapted from Maier, C.A. (2001) “Building Phylogenetic Trees from DNA Sequence Data: Investigating Polar Bear & Giant Panda Ancestry.” The American Biology Teacher. 63:9, Pages642646.) Adapted for NGWB by Mark Alan Miller January 2009. Introduction: This activity will allow you to use the tools used by geneticists and evolutionists located and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. These tools will allow you to compare the isolated and sequenced genes from species that are stored in GenBank. Each unique sequence is identified by an “accession number” as unique as your social security number. You will also be able to compare sequences and generate phylogenetic trees using Biology Workbench that contains specific application such as CLUSTALW (sequence similarity tool), CLUSTALDIST (generates a genetic distance matrix) and DRAWGRAM (creates phylogenetic trees). The gene sequence that is being used in this activity is the 12s ribosomal RNA gene sequence from several bear species and the giant panda. The 12s gene is a good candidate for study because it doesn’t undergo recombination (not subject to meiosis) because the gene is found on the mitochondrial chromosome* which is inherited only from the mother via the egg. * Check out this link for a discussion of the use of mitochondrial DNA and if it really is only from the mother. Athena Review †Vol.2, no.2: †Recent Finds in Paleoanthropology Molecular clockwork and related theories http://www.athenapub.com/molclock.htm Instructions for Accessing 12s rRNA Gene Sequences PART 1: a. Open a new web page or new tab and Enter: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov b. In the Search bar; select "nucleotide" from the drop down menu c. Enter the accession number, to obtain each of the following 12s rRNA gene sequences one at a time, and select “GO” to the right of the bar. The information for the bear will appear in the window, click on the accession number. Species Accession Number American Black Bear Y08520 American Brown Bear L21889 Spectacled Bear L21883 Asiatic Black Bear L21890 Polar Bear L22164 Giant Panda Y08521 e. Find the bar with “GenBank” to the right of the “Display” use the drop down menu and select "FASTA" to bring up the sequence in FASTA format. f. Open a new web page or new tab so you can toggle between the two pages and go to: SWAMI, The Next Generation Biology Workbench: (http://www.ngbw.org/), set up a free account (if you need help; http://www.ngbw.org/help/register.htm). Once your registration is complete, you will be logged in to your personal area. g. The NGBW allows you to store data and tasks in folders just like MS Outlook, or other a mail clients. So before working here, you must create at least one folder. Click on the button that says “Create New Folder”. Name your folder, and save the name. If you get stuck, here is the help link (http://www.ngbw.org/help/create_folder.htm). The folder will appear on the left side of the screen. h. Each NGBW folder has a data area and a tool area. For now, we are going to upload some sequences, so click on the data area icon. It will open the Data management page; now click on the Upload/Enter Data button. j. Go back to the NCBI page; highlight the entire FASTA sequence (including the “>”). Copy the highlighted sequence. i. Go back the NGBW Data Upload page. j. In the “label” box, (at the top of the upload form), type in the type of bear. k. Position the cursor in the top left of the data entry box and “Paste” the sequence. You will need to replace the FASTA description with the name of the bear, making sure the “>” symbol is still the first symbol. Use the dropdown boxes at the bottom of the page to tell us what kind of data you are uploading. Entity Type is “Nucleic Acid”, the Data Type is “Sequence”, and the format is “FASTA”. Select “SAVE”. l. Return to GenBank (on the other web page). Copy and Paste the remaining 12s rRNA gene sequences into the NGBW in exactly the same way. Instructions Part II: Analyze the 12s rRNA Gene Sequences 1. Align the five different Bear 12s rRNA Gene Sequences (not the panda) a. In the NGBW, click on the “Tasks” icon in your working folder. When the Task management pane appear, click on the “Create New Task” Button. Enter a description for the task and click the “Set Description” button. b. Now click on the “Select Input Data” button. Check the click boxes to the left of all the bears (not the panda yet). Click the “Select Data” button. c. When the Task Creation Pane re-appears, click the “Select Tool” button. From the Nucleic Acids Sequence Tools tab, choose “CLUSTALW_N” (the tools are alphabetical). Now click the "Save and Run Task" button. d. A new page will load that lets you follow the progress of your jobs. Click the “Refresh Tasks” tab near the top of the page, until the “View Status” button on the right turns into “View Results.” Click on the “View Results”: tab, and a page showing your results will appear. Click on the link “outfile.aln”, and the results of your alignment will be exposed. Click the “Save to Current Folder” button. e. A window will appear that lets you name and specify the kind of data you are saving. Enter a data Label, then select Entity Type: “Nucleic Acid” Data Type: “Sequence Alignment” and Format: “Clustal”. Then click the “Save” button. 2. Determine the Genetic Distance Between Sequence Pairs a. Now go back to the Tasks area of your folder. Click the “Create New Task” button. Give the task a description and “Set the Description”, just like before. Click the “Select Data” button, and find your alignment data, check the box to the left of the alignment, and click “Select Data.” When the task creation page reloads, choose Select Tool, and find “CLUSTALW_DIST” under the Phylogeny/Alignment Tools tab. When the task creation page appears, click the “Save and Run” button. b. When the Task management page reloads, use the “Refresh Tasks” button to monitor when the job completes. When the “View Output” button appears, click on it, and expose the results. Click on the infile.dst link to expose the Distance Matrix results. Record the distance matrix in your journal to examine later. 3. Build a Phylogenetic Tree of the Bear Species a. CLUSTALW_DIST also outputs a phylogenetic tree. Under the “View Output” for CLUSTALW_DIST click on the infile.ph link. Save this data to your current folder, just like in 1.d and 1.e. But this time chose Entity Type: “Taxon” Data Type: “Phylogenetic Tree” and Format: “Newick” b. Now go find this data item in the Data area of your folder, under the tab “Phylogenetic Trees.” Click the data item, and it will open up, revealing these two links “Show/Hide Data Contents | Draw Tree.” Cllck on the Draw Tree link, and you will see an interactive view of the Tree. Record the diagram in your journal. 4. Determine the relationship of Giant Panda to the Bear Phylogenetic Tree a. In GenBank (if you haven’t already) access the giant panda 12s rRNA gene sequence and import it into the your NGBW Data area. b. Run a new alignment with all five bears and the panda sequence. Import the alignment into your data area, use “CLUSTALW_DIST” to create a distance matrix and a phylogenetic tree. Import the phylogenetic tree into your data area do see the tree. Record all information. Analysis: (due typed) 1. Create a table showing the distance matrix of the five bears and the panda (Please note that a distance of 0.00 indicates identical sequences and as the difference in gene sequences increases so does the number). 2. Provide a phylogenetic tree of the bears and the panda. Label the lines on the tree with the corresponding distances. 3. Explain and provide support for the conclusions made by the program (Biology Workbench). 4. Red Panda are reported to be more closely related to raccoon. Find the relationship (provide both the distance matrix and tree) between the Red Panda and raccoons to the others you’ve already examined. Is the first statement supported? 5. Pick a few animals and run their 12s rRNA patterns to see how they are related. Record this information.