Cells Definition of a cell: A cell is the smallest structural and
advertisement
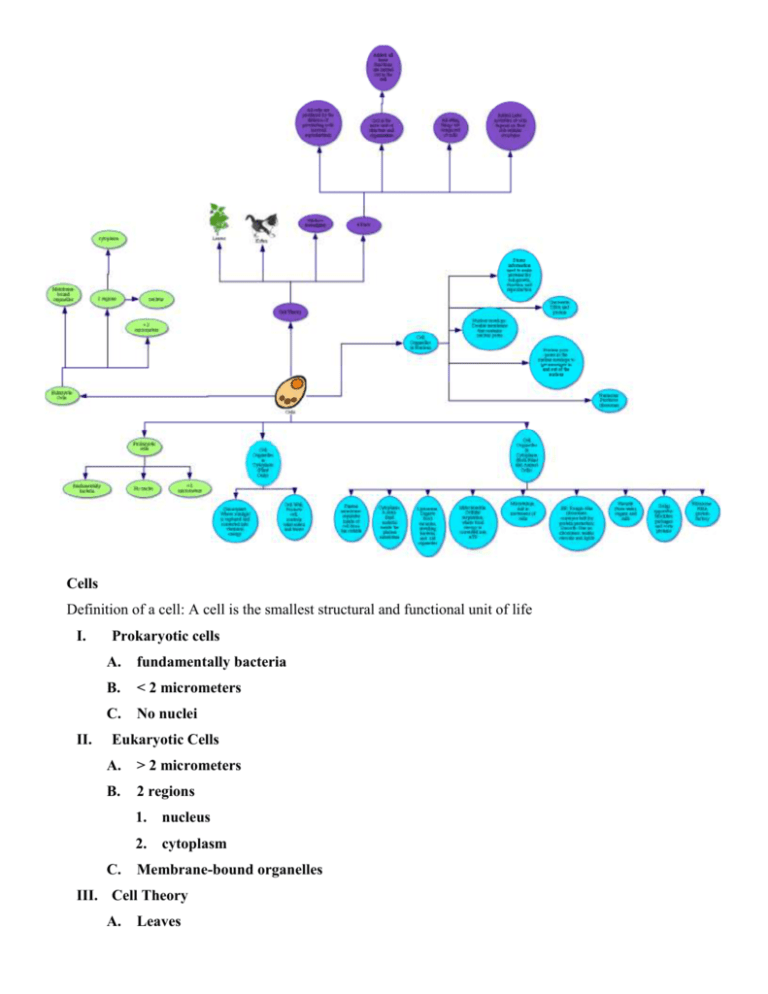
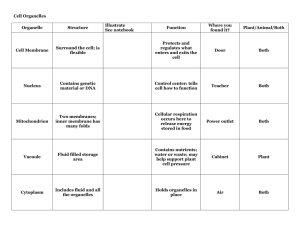
Cells Definition of a cell: A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life I. II. Prokaryotic cells A. fundamentally bacteria B. < 2 micrometers C. No nuclei Eukaryotic Cells A. > 2 micrometers B. 2 regions C. 1. nucleus 2. cytoplasm Membrane-bound organelles III. Cell Theory A. Leaves Schleiden: all plants are composed of cells B. Kitten Schwann: all animals are composed of cells C. Virchow formalized D. 4 Parts 1. Added Later: Activities of cells depend on their sub-cellular structures 2. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells (asexual reproduction) 3. Cell is the basic unit of structure and organization a. 4. Added: all basic functions are carried out in the cell All living things are composed of cells IV. Cell Organelles in Cytoplasm (Both Plant and Animal Cells) A. Plasma membrane: separates inside of cell from the outside B. Cytoplasm: A semi-fluid material inside the plasma membrane C. Lysosome: Digests food vacuoles, invading bacteria, and old organelles D. Mitochondria: Cellular respiration; where food energy is converted into ATP E. Microtubule: Aid in movement of cells F. ER: Rough: Has ribosomes; conveyor belt for protein protection; Smooth: Has no ribosomes; makes steroids and lipids G. Vacuole: Store water, sugars, and salts H. Golgi apparatus: Modifies, packages, and sorts proteins I. V. Ribosome: RNA protein factory Cell Organelles in Cytoplasm (Plant Only) A. Cell Wall: Protects cell, controls what enters and leaves B. Chloroplast: Where sunlight is captured and converted into chemical energy VI. Cell Organelles in Nucleus A. Stores information used to make proteins for cell growth, function, and reproduction B. Nuclear envelope: Double membrane that contains nuclear pores C. Nuclear pore: pores in the nuclear envelope to get messages in and out of the nucleus D. Nucleolus: Produces ribosomes E. Chromatin: DNA and protein