Muscular System Test
advertisement
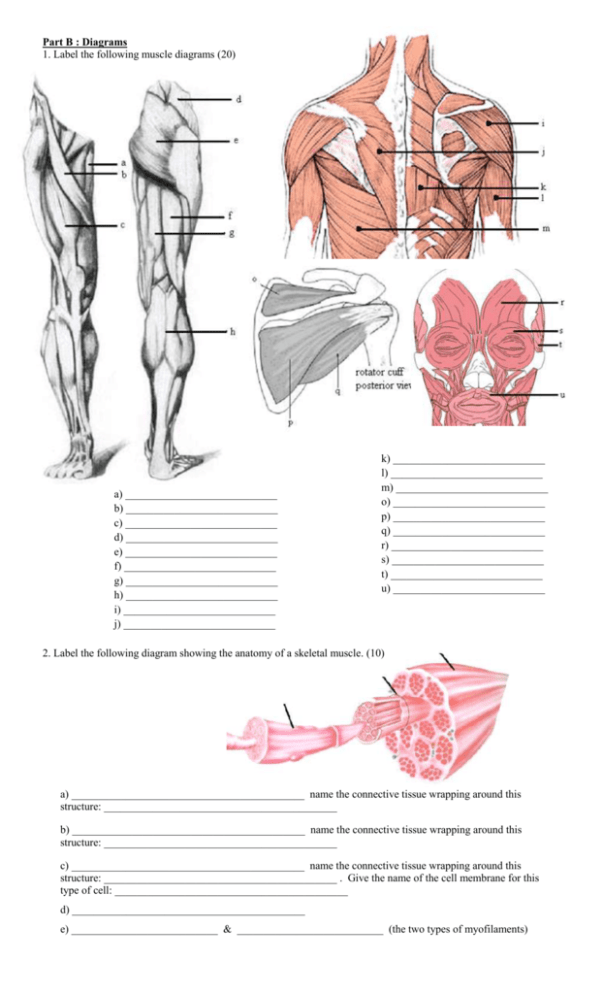
Part B : Diagrams 1. Label the following muscle diagrams (20) a) ____________________________ b) ____________________________ c) ____________________________ d) ____________________________ e) ____________________________ f) ____________________________ g) ____________________________ h) ____________________________ i) ____________________________ j) ____________________________ k) ____________________________ l) ____________________________ m) ____________________________ o) ____________________________ p) ____________________________ q) ____________________________ r) ____________________________ s) ____________________________ t) ____________________________ u) ____________________________ 2. Label the following diagram showing the anatomy of a skeletal muscle. (10) a) ___________________________________________ name the connective tissue wrapping around this structure: ___________________________________________ b) ___________________________________________ name the connective tissue wrapping around this structure: ___________________________________________ c) ___________________________________________ name the connective tissue wrapping around this structure: ___________________________________________ . Give the name of the cell membrane for this type of cell: ___________________________________________ d) ___________________________________________ e) ___________________________ & ___________________________ (the two types of myofilaments) Name: __________________________________ PSE 4U Total: _______ / _______ Muscular System Test Part A: Short Answer Answer the following questions on lined paper. Communication: _______ 1. Three types of muscle tissue exist: skeletal, cardiac and smooth. a) Explain why skeletal and cardiac muscles both have a striated appearance (meaning they both contain sarcomeres). Consider speed and type of contraction. (2) b) Explain what is meant when a muscle is said to be excitable. (1) 2. What are the main functions of skeletal muscles (briefly explain each function) (4) 3. Choose two of the following names of muscles, for each one, explain the ‘system’ used to name it (refer to the example if you’re confused). Muscles: Transverse abdonminus, serratus anterior, frontalis. (2) Example: rectus femoris Rectus refers to the direction in which the muscle runs (vertically along the body) Femoris refers to the location of the muscle over the femur 4. For each of the following examples name the type of contraction described, and provide reasoning for your choice. (6) a) You dorsi flex your foot (bring your toe towards your shin) b) You lower yourself down after completing a pull up. c) Your leg muscles work to keep you upright while you balance on one foot 5. You’ve just suffered a nasty injury to the back of your lower leg….it seems that you’ve severed your Achilles tendon, but luckily you have not injured your gastrocnemius (phewf!). Given that your muscle is unhurt, why are you unable to point your toe? (2) 6. Sad Sally Anne Lumpkin is at the gym trying to complete a set of dumbbell curls. Being a scrawny little thing (5’8” and 100 lbs) she is struggling to generate enough force to lift the dumbbell for the final time. a) Suggest several ways that Sally could increase the amount of force she could generate. (2) b) What other factors, outside of Sally’s control, influence the amount of force generated by a contraction. (2) 7. Explain why you remove your hand from a hot stove before you feel pain from the heat. (2) 8. The force generated when a muscle contracts is due to the simultaneous action of thousands of sarcomeres. a) Label the diagram of a sarcomere shown below. (4) Include the following terms: actin, myosin, z-disk, H-zone b) Explain the process of events that occur when a sarcomere shortens during muscular contraction (5) c) Why does sarcomere shortening end – provide 2 possible reasons (2) d) Why is this model referred to as the ‘sliding filament model’ (1) 9. Compare the following terms (4) a) Fast twitch fiber (Type II) vs. Slow twitch fiber b) Intermuscular coordination vs. intramuscular coordination 10. Over time we can train our muscles to achieve different tasks. a) Provide an overview of several adjustments our muscular system can make given enough training. (2) b) Even with excellent training over a long duration, some things cannot be trained. What are some characteristics of muscle over which we have little to no control. (1)