2010 Study Guide for Quiz 6
advertisement

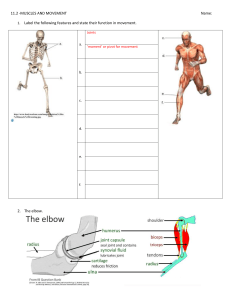
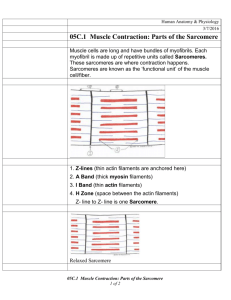
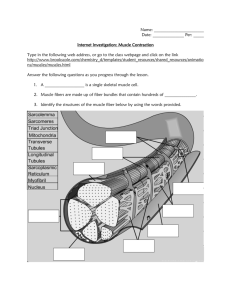
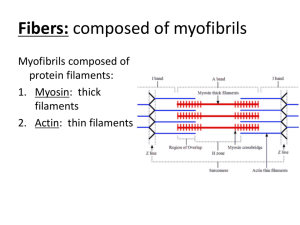
Quiz 6 Study Guide - Fall 2010 1. When ATP supplies first become depleted in a muscle cell, the ADP + P may be rapidly converted to ATP using a. the creatine phosphate system. b. myoglobin. c. anaerobic respiration. d. acetyl choline. 2. In a muscle, a single stimulus/contraction/relaxation sequence is called a ___________________________________. 3. If a muscle is stimulated continuously at a high frequency, (generally greater than 20/sec.) the muscle will respond with a contraction called _____________________________. 4. Before a sarcomere may initiate a contraction a. the t-tube releases calcium (Ca+2) b. the sarcomere becomes permeable to Na+ c. cross bridges form between the z-lines and the filaments d. the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca+2 into the sarcomere 5. The portion of the sarcomere which actually generates the force of contraction is the a. myosin heads b. myoglobin c. z-lines d. actin 6. What is a neuromuscular junction and what happens in the junction? Briefly explain. 7. The organelle of a muscle cell that carries an action potential from the surface membrane to the sarcoplasmic reticulum is the ___________________________________________. 8. The banding patterns on skeletal muscle are called ______________________________. 9. During contraction of a muscle, b. the actin filaments slide over the myosin. d. the actin shortens rapidly. a. both the actin and myosin shorten. c. the myosin binds to the z-bands. 10. Acetyl choline is a. released into the neuromuscular junction. b. released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. c. carried by the transverse tubules. d. a waste product of lactic acid metabolism at the liver. 11. Acetyl choline esterase (cholinesterase) a. stimulates the muscle membrane. b. is a neurotransmitter released by motor neurons. c. degrades neurotransmitters in the synapse. d. initiates muscle contraction at the sarcomere. 12. Arrange the following terms from largest structure to smallest structure. myofibril muscle bundle fascicle actin and myosin sarcomere muscle fiber 13. The diagram given below represents a sarcomere from a myofibril. I. Label the actin, myosin and z-line protein. II. Describe how this sarcomere will look differently following a contraction. 14. The graph given below represents the response of a muscle being stimulated with shocks from an electronic stimulator. The experiment is similar to one of the experiments we performed in lab. C B Force (g) A Time (seconds) I. The response known as "treppe" (summation) would be represented by the data beneath A. B. C. II. Which region of the curve cooresponds to "tetanus" and what type of stimulus is required to cause this response? 15. (4 points) An action potential a. is an electric impulse caused by ions crossing the cell membrane. b. is carried from the muscle cell surface to the sarcoplasmic reticulum by the transverse tubules (T-tubes). c. may occur in both nerve and muscle cells. d. all of the above.