Exam 3 Study Guide Biol 13- Marine Biology
advertisement

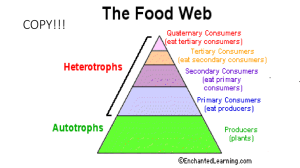
Exam 3 Study Guide Biol 13- Marine Biology Chapters 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. What are the three general swimming “forms” in fish? What are some of the sensory structures in the fishes? Explain the counter-current gas exchange system on the fish gill. What are the types of marine reptiles? What are some of the characteristics of marine birds? Know all the orders in class Mammalia and their characteristics. What are the two types of cetaceans? What, and how, do whales eat? Compare and contrast the feeding strategies of humpbacks, Orcas, and grays. Be able to explain the results of at least two tagging studies. Know the groups of fishes and what makes them all different. How do salts move into and out of freshwater vs. saltwater fish? Explain ecology, biotic, abiotic, and communities. Explain the statement “Character displacement is the ghost of competition past.” What are the main ways that species can interact? Contrast bottom-up vs. top-down ideas of community structure. Know how the littoral zones are defined. Know the various physical factors that define and affect the intertidal. What are several of the adaptations, both physical and behavioral, to desiccation. What are the types of meiofauna? What determine where they live? What are the dominate plants in most coastal estuaries? Describe how wave energy can affect how an organism grows. Understand the classic ecological studies in the intertidal and what they have taught us about the nature of marine communities. What are the two main causes of zonation patterns, be able to explain them? What are five cues that larvae could use to influence their settlement? Explain why there are few large algae in soft bottom communities. What factors defines a beach? How does grain size and sorting determine the livable space and types of organisms found in soft bottoms? What types of organisms make up the meiofauna? What are the four types of estuaries and how do they form? Describe the algal/plant and animal communities in estuaries. Explain the osmoregulation strategies found in estuarine organisms. What are two invasive species we have in our local estuary and what problems do they cause? How do most invasives come into an area? Explain the different subtidal communities. What is so special about kelp forests? Explain how hydrographic conditions (storms, temp, nutrients) influence kelp density and urchin populations.