Westward Settlement Notes - - APUSHistory
advertisement

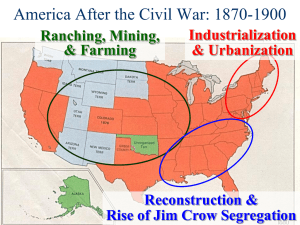
AP U.S. History Notes: Western Settlement – Railroads, Mining, Cattle and Farming I. Railroads A. Transcontinental RR – Central Pacific (Leland Stanford), Union Pacific B. Labor – Chinese, Irish C. Government Land Grants D. Standard Gauge E. Time Zones F. Four Transcontinental Lines by 1890 G. Great Northern RR. – James J. Hill, only RR built w/o Federal assistance II. Mining – fostered westward movement more than any other activity A. Boomtowns (Helldorados) Ghost towns B. Vigilantes C. California Gold Rush -1848 population = 14,000, 1852 population = 223,856 D. Bonanza Kings – large operators using hydraulics and hydroelectric power 1. Comstock Lode (Silver City, NV), Anaconda Copper Mining Co. (Butte MT) D. Western Labor Movement began in mining towns. E. Environmental Impacts III. Mormon Settlements A. Brigham Young - Mormon Trek 1846-47 B. Communal Society C. 1879 U.S. vs Reynolds – Polygamy case D. Edmunds-Tucker Act – Gov’t confiscated Mormon assets, disenfranchised anyone practicing polygamy E. Forty-niners – Gold Rush F. 1890 Mormons abandon polygamy G. Utah statehood 1896 IV. Cattle Industry – feed the miners and RR workers A. Joseph McCoy B. Longhorns C. Cattle Trails – The Long Drive: South Texas to Kansas D. RR and refrigerator cars – Chicago, Kansas City = meatpacking industry E. Cowboys – rugged individualist, Indians, African-Amer. and Mexican about 1/3 F. Cowtowns – Abilene, Dodge City, wild and crazy places: saloons, prostitution, gambling, violence(sin city) G. Open Range gives in to the Fenced Ranches – barbed wire (Joseph Glidden) and windmills H. Range Wars: Cattlemen vs Sheepherders and Cattlemen vs. Farmers I. Overgrazing and drought and harsh winters of 1885-87 V. Great Plains Farmers – Homestead Act and sale of RR lands provided opportunity for land ownership A. Problems: 1. Lack of trees for building and fuel and fencing 2. Arid climate, little rainfall, droughts 3. Extreme season- hot summers, cold winters, lots of wind year round. 4. Locusts, floods B. Solutions: 1. Sod homes and buffalo chips 2. Barbed Wire 3. Deep wells and windmills 4. Dry farming – 5. New breeds of wheat, corn more resistant to drought, insects. 6. Mechanization allows for large scale farming (Bonanza Farms) – reaper (Cyrus McCormick), steel plow (John Deere), irrigation systems, later tractors. 7. RR provided important transportation link with markets C. Ethnic settlement 1. Germans largest- settled in Missouri, Iowa, Wisconsin, Nebraska 2. Scandinavians – Swedes in Minn., Norwegians in Dakotas 3. Tight-knit groups helped to maintain cultural identity 4. Religion was important – 70% were church goers D. Family life– everyone worked 1. One room school house 2. Harsh conditions, isolation led to communal work – barn raising, harvesting, clearing land 3. Start up costs resulted in high rate of farmer debt 4. Low yields, severe weather, low crop prices all added to many farmers unable to turn a profit. E. Legislation 1. Homestead Act 1862 – sparked the largest migration in U.S. History 2. Morrill Land Grant Act 1862 3. Dept. of Agriculture 1889 4. Hatch Act – created experimental agricultural stations