W. History Ch. 14 Review
advertisement

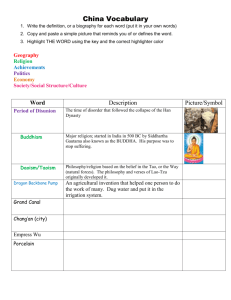
World History Study Guide Ch. 14 Name: ___________________________________ 1. During the Period of Disunion, cultures in China became ____________________. (410) 2. During the Period of Disunion, many people turned to _____________________, because to offered an escape from suffering & achievement of peace. (412) 3. Buddhism is one of the world’s major religions, originating in _______________ around 500 B.C. (412) 4. The __________________ _____________________ _______________ allowed farmers to scoop up water & pour it into irrigation canals. (414) 5. China’s capital & largest city of the Tang dynasty was ____________________________. (416) 6. The Grand Canal was primarily built to allow the Chinese to move _________________ and _________________ from distant agricultural areas into cities. (416) 7. Chinese kept the silk-making process a secret, giving them control of the trade. 8. __________________________ ___________________ could copy drawings or text quickly, much faster than they could be copied by hand. (418) 9. _______ ____________________ is perhaps China’s greatest female poet. (417) 10. _____________________ _____________ is a set of letters or characters that can be reused and rearranged to create new lines of text & different pages. (419) 11. Confucius taught that people should live by 2 life principles: ________________ for others & appropriate _______________________. (421) 12. Unlike ___________________________, which stressed ethical behavior, _______________________ stressed a more spiritual outlook that promised escape from suffering. (421) 13. During the Song dynasty, its official policy became _____________-Cunfucianism. (422) 14. Neo- Cunfunianism is similar to Cunfucianism for it taught proper behavior but it also emphasized _______________________ matter. (422) 15. The bureaucracy of scholar- officials, during the Song dynasty, created ____________________ and an efficient government. (423) 16. During the Han dynasty, __________________________ became the official state philosophy. (421) 17. What does Genghis Khan mean? ___________________ ______________ (424) 18. _________ ___________________________ became China’s emperor, finding the Ming dynasty. (427) 19. ______________ _____________ became ruler of the Mongol Empire in 1260. (425) 20. What city was the Forbidden City built in? (428)________________________ 21. What dynasty was the Forbidden City built? (428) _____________________ 22. The Great Wall of China is how long? (429) _________________miles 23. In the 1430s a new Ming emperor banned foreign trade creating a period of ___________________________. (430) 24. Essay: How did the Forbidden City get its name? (428) Definitions: Zhu Yuanzhang – a former monk who led a rebellion against the Yuan emperor Zheng He – the greatest sailor of the Ming dynasty Li Bo – Great poet of the Tang dynasty Yuan dynasty – a period in Chinese history also known as the Mongol Ascendancy Great Wall of China – building project that was completed during the Ming dynasty Mongols – nomadic people who came from the plains north of China Porcelain – Compass – Civil Service – Isolationism – Period of Disunion – Dragon backbone pump – Bureaucracy – Confucius -