Chapter 9 - 2profs.net
advertisement

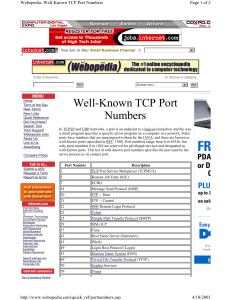
Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition 9-1 Chapter 9 Performing Vulnerability Assessments Additional Resources 1. SATAN - Security Administrator's Tool for Analyzing Networks http://www.swtech.com/net/security/satan/ 2. Storing Passwords - done right! http://www.aspheute.com/english/20040105.asp 3. Rainbow table http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rainbow_table 4. RFC792 - Internet Control Message Protocol http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc792.html 5. Attack tree http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attack_tree Key Terms Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE) The expected monetary loss that can be expected for an asset due to a risk over a one year period. Annualized Rate of Occurrence (ARO) The probability that a risk will occur in a particular year. asset identification The process of inventorying and managing items of value. attack tree A visual image of the attacks that may occur against an asset. blocked port A TCP/IP port in which the host system does not reply to any inquiries. closed port A TCP/IP port in which no process is listening at the port. Exposure Factor (EF) The proportion of an asset’s value that is likely to be destroyed by a particular risk (expressed as a percentage). Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) A TCP/IP protocol that provides support to IP in the form of ICMP messages that allow different types of communication to occur between IP devices. network mappers Software tools that can identify all the systems connected to a network. open port A TCP/IP port in which an application or service assigned to that port is listening. Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language (OVAL) An international information security standard to promote open and publicly available security content, and to standardize the transfer of this information across the spectrum of security tools and services. Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals, Third Edition 9-2 outsourcing Contracting with an outside company to provide a service or product instead of providing it from within the organization. password cracker A program that uses the file of hashed passwords and then attempts to break the hashed passwords offline. penetration testing A method of evaluating the security of a computer system or network by simulating an attack by a malicious hacker instead of just scanning for vulnerabilities. ping An Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packet. port number A numeric value used as an identifier to applications and services on TCP/IP systems. port scanner Software used to search a system for port vulnerabilities that could be used in an attack. process A program running on a device. promiscuous mode A mode on an interface card (NIC) adapter that does not ignore packets intended for other systems but shows all network traffic. retained risk The potential loss that exceeds the amount covered by insurance. risk assessment Determining the damage that would result from an attack and the likelihood that the vulnerability is a risk to the organization. risk management A systematic and structured approach to managing the potential for loss that is related to a threat. risk retention pool A means of spreading risk over a group. No premium is paid by members of the group but losses are assessed across all members of the group. shadow password A defense against password cracker programs for UNIX and Linux systems by creating a second file without password hashes. Single Loss Expectancy (SLE) The expected monetary loss every time a risk occurs. threat modeling A process for constructing scenarios of the types of threats that assets can face. vulnerability appraisal A current snapshot of the security of an organization. vulnerability scanner A generic term that refers to products that look for vulnerabilities in networks or systems.