File
advertisement

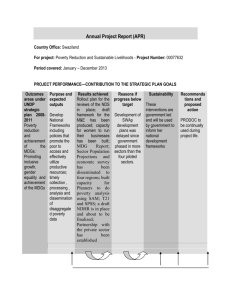
ERADICATION OF POVERTY AND HUNGER: POST-2015 AGENDA SURVIVAL GUIDE UN General Assembly Source: http://www.un.org/ Background The General Assembly (GA) is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the UN Established in 1945 under the Charter of the United Nations Comprising all 193 Members of the UN, allowing it to provide a unique forum for multilateral discussion on international Each country has one vote Current president is Sam Kahamba Kutesa Functions Makes recommendations on international issues Oversees all other UN bodies which must report to the GA annually Approves the UN budget and apportions UN expenses Elects the Secretary-General Holds authority to admit and expel Member States Millennium Development Goals Source: http://www.unmillenniumproject.org/goals/ Creation of the MDGs Millennium Summit Took place September 2000 Largest gathering of world leaders in history Adopted the UN Millennium Declaration, committing nations to a new global partnership to reduce extreme poverty and setting out a series of time-bound targets Deadline of 2015 MDGs are the world's time-bound and quantified targets for addressing extreme poverty in its many dimensions MDGs also basic human rights-the rights of each person on the planet to health, education, shelter, and security Goals 1. Eradicate Extreme Hunger and Poverty 2. Achieve Universal Primary Education 3. Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women 4. Reduce Child Mortality 5. Improve Maternal Health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, Malaria, and other diseases 7. Ensure Environmental Sustainability 8. Develop a Global Partnership for Development 1 Millennium Development Goal 1 Targets of Millennium Development Goal 1 Source: http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals//pdf/Goal_1_fs.pdf 1. Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the proportion of people whose income is less than $1 a day (In 2008, this was changed to $1.25 per day) 2. Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all, including women and young people 3. Halve, between 1990 and 2015, the proportion of people who suffer from hunger Poverty & Definitions Source: vhttp://www.poverty.ac.uk/definitions-poverty/absolute-and-overall-poverty Absolute poverty: characterized by severe deprivation of basic human needs, including food, safe drinking water, sanitation facilities, health, shelter, education and information. Depends not only on income but also on access to services. Overall poverty: Includes all characteristics of absolute poverty. Also characterized by lack of participation in decision-making and in civil, social and cultural life. Prevalence of Poverty Sources: http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/poverty/overview, http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals//pdf/Goal_1_fs.pdf According to most recent estimates, in 2011, 17% of people in developing world lived at or below $1.25 a day Despite progress, some 1.2 billion people will still live in extreme poverty in 2015 Additionally, 2.2 billion people lived on less than $2 a day in 2011, the average poverty line in developing countries 2103 estimates showed that 60.9 per cent of workers in the developing world still lived on less than $4 a day. Progress Report Source: http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals//pdf/Goal_1_fs.pdf 1. The proportion of people living in extreme poverty declined by half at the global level. 2. In developing regions, the proportion of people living on less than $1.25 a day fell from 47 per cent in 1990 to 22 per cent in 2010, five years ahead of schedule. 3. While the proportion of undernourished people globally decreased from 23.2 per cent in 1990-1992 to 14.9 per cent in 2010-2012, this still leaves 870 million people—one in eight worldwide—going hungry. 2 Moving Forwards: Sustainable Development Goals Sources: http://www.un.org/en/sustainablefuture/, https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/ Background: Rio+20 conference UN conference on sustainable development Took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in June 2012 Biggest UN conference ever Agreement by member States to launch a process to develop a set of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which will build upon the Millennium Development Goals and converge with the post 2015 development agenda Outcome document: The Future We Want Proposed SDGs Goal 1 End poverty in all its forms everywhere (Continuation of MDG1) Goal 2 End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture (Continuation of MDG 1) Goal 3 Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages Goal 4 Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all (Continuation of MDG 2) Goal 5 Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls (Continuation of MDG 3) Goal 6 Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all (Continuation of MDG 7) Goal 7 Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all (Continuation of MDG 7) Goal 8 Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all (Continuation of MDG 1) Goal 9 Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation Goal 10 Reduce inequality within and among countries Goal 11 Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable Goal 12 Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns (Continuation of MDG 7) Goal 13 Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts* Goal 14 Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development Goal 15 Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss Goal 16 Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels Goal 17 Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development 3 Programs Working to Eradicate Poverty and Hunger UNDP (http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/operations/about_us.html) Since 1966 UNDP partners with people at all levels of society to help build nations that can withstand crisis, and drive and sustain the kind of growth that improves the quality of life for everyone. On the ground in more than 170 countries and territories, we offer global perspective and local insight to help empower lives and build resilient nations. We focus on helping countries build and share solutions in three main areas: 1. Sustainable development 2. Democratic governance and peace building 3. Climate and disaster resilience In all our activities, we encourage the protection of human rights and the empowerment of women, minorities and the poorest and most vulnerable. In each country office, the UNDP Resident Representative normally also serves as the Resident Coordinator of development activities for the United Nations system as a whole. Through such coordination, UNDP seeks to ensure the most effective use of UN and international aid resources. Homework – Visit your country’s UNDP website and write a one paragraph summary on one UNDP program including the “who, what, where, when, why and how.” Australia (none) Guatemala (http://www.gt.undp.org/) Madagascar (http://www.td.undp.org/content/madagascar/fr/home.html#) Sri Lanka (http://www.lk.undp.org/) Viet Nam (http://www.vn.undp.org/) UNICEF (http://www.unicef.org/about/who/index_introduction.html) 1. We believe that nurturing and caring for children are the cornerstones of human progress. UNICEF was created with this purpose in mind – to work with others to overcome the obstacles that poverty, violence, disease and discrimination place in a child’s path. 2. We promote girls’ education. Girls who are educated grow up to become better thinkers, better citizens, and better parents to their own children. 3. We act so that all children are immunized against common childhood diseases, and are well nourished, because it is wrong for a child to suffer or die from a preventable illness. 4. We work to prevent the spread of HIV/AIDS among young people 5. We involve everyone in creating protective environments for children. We are present to relieve suffering during emergencies, and wherever children are threatened, because no child should be exposed to violence, abuse or exploitation. 6. UNICEF upholds the Convention on the Rights of the Child. We work to assure equality for those who are discriminated against, girls and women in particular. 7. We are active in more than 190 countries and territories through country programs and National Committees. Homework – Visit your country’s UNICEF website and write a one paragraph summary on one UNICEF program including the “who, what, where, when, why and how.” 4 Australia (http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/australia.html) Guatemala (http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/guatemala.html) Madagascar (http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/madagascar.html) Sri Lanka (http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/sri_lanka.html) Viet Nam (http://www.unicef.org/infobycountry/vietnam.html) Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (http://www.fao.org/about/en/) Achieving food security for all is at the heart of FAO's efforts – to make sure people have regular access to enough high-quality food to lead active, healthy lives. Our three main goals are: 1. The eradication of hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition 2. The elimination of poverty and the driving forward of economic and social progress for all 3. The sustainable management and utilization of natural resources, including land, water, air, climate and genetic resources for the benefit of present and future generations. Homework – Visit your country’s FAO website and write a one paragraph summary on one FAO program including the “who, what, where, when, why and how.” Australia (http://www.fao.org/countryprofiles/index/en/?iso3=AUS) Guatemala (http://www.fao.org/countryprofiles/index/en/?iso3=GTM) Madagascar (http://www.fao.org/countryprofiles/index/en/?iso3=MDG) Sri Lanka (http://www.fao.org/countryprofiles/index/en/?iso3=LKA) Viet Nam (http://www.fao.org/countryprofiles/index/en/?iso3=VNM) United Nations World Food Programme (WFP) (http://www.wfp.org/about/mission-statement) WFP is the food aid arm of the United Nations system. Food aid is one of the many instruments that can help to promote food security, which is defined as access of all people at all times to the food needed for an active and healthy life. The policies governing the use of World Food Programme food aid must be oriented towards the objective of eradicating hunger and poverty. The ultimate objective of food aid should be the elimination of the need for food aid. Targeted interventions are needed to help to improve the lives of the poorest people people who, either permanently or during crisis periods, are unable to produce enough food or do not have the resources to otherwise obtain the food that they and their households require for active and healthy lives. Consistent with its mandate, which also reflects the principle of universality, WFP will continue to: 1. Use food aid to support economic and social development; 2. Meet refugee and other emergency food needs, and the associated logistics support; and 3. Promote world food security in accordance with the recommendations of the United Nations and FAO. 4. The core policies and strategies that govern WFP activities are to provide food aid: 5. To save lives in refugee and other emergency situations; 6. To improve the nutrition and quality of life of the most vulnerable people at critical times in their lives; and 5 7. To help build assets and promote the self-reliance of poor people and communities, particularly through labor-intensive works programs. Homework – Visit your country’s WFP website and write a one paragraph summary on one WFP program including the “who, what, where, when, why and how.” Australia (http://www.wfp.org/about/funding/governments/australia and https://www.wfp.org/news/news-release/australia-and-world-food-programme-unitedagainst-global-hunger) Guatemala (https://www.wfp.org/countries/guatemala) Madagascar (https://www.wfp.org/countries/madagascar) Sri Lanka (https://www.wfp.org/countries/sri-lanka) Viet Nam (http://reliefweb.int/report/viet-nam/economic-success-vietnam-allows-wfpclose-doors) Oxfam (http://www.oxfam.org/en/our-purpose-and-beliefs) Our vision is a just world without poverty. We want a world where people are valued and treated equally, enjoy their rights as full citizens, and can influence decisions affecting their lives. Our purpose is to help create lasting solutions to the injustice of poverty. We are part of a global movement for change, empowering people to create a future that is secure, just, and free from poverty. We use a combination of rights-based sustainable development programs, public education, campaigns, advocacy, and humanitarian assistance in disasters and conflicts. We challenge the structural causes of the injustice of poverty, and work with allies and partners locally and globally. Homework – Visit your country’s Oxfam website and write the “who, what, where, when, why and how” of one the Oxfam programs. Australia (https://www.oxfam.org.au/) Guatemala (http://www.oxfam.org/en/countries/guatemala) Madagascar (none) Sri Lanka (http://www.oxfam.org/en/countries/sri-lanka) Viet Nam (http://www.oxfam.org/en/countries/vietnam) World Bank (http://www.worldbank.org/en/about/what-we-do) The World Bank Group has set two goals for the world to achieve by 2030: 1. End extreme poverty by decreasing the percentage of people living on less than $1.25 a day to no more than 3% 2. Promote shared prosperity by fostering the income growth of the bottom 40% for every country We are not a bank in the ordinary sense, but a unique partnership to reduce poverty and support development. Established in 1944, the World Bank Group is headquartered in Washington, D.C. We provide low-interest loans, zero to low-interest credits, and grants to developing countries. These support a wide array of investments in such areas as education, health, public administration, infrastructure, financial and private sector development, agriculture, and environmental and natural resource management. 6 Homework: Country profile Find the following information 1. Type of Government 2. Leader (ex. President) 3. Gross Domestic Product: 4. Public Debt: 5. External Debt 6. Unemployment, youth ages 15-24 7. Children under the age of 5 years underweight 8. Population below poverty line 9. Unemployment rate 10. Transnational Issues 11. Has your country achieved MDG 1? 7 Sources http://www.un.org/ http://www.unmillenniumproject.org/goals/ http://www.un.org/en/sustainablefuture/ https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/ http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals//pdf/Goal_1_fs.pdf http://www.poverty.ac.uk/definitions-poverty/absolute-and-overall-poverty http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/poverty/overview http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/operations/about_us.html http://www.unicef.org/about/who/index_introduction.html http://www.fao.org/about/en/ http://www.wfp.org/about/mission-statement http://www.oxfam.org/en/our-purpose-and-beliefs http://www.worldbank.org/en/about/what-we-do 8