BCC Math 206 Course Outline
advertisement
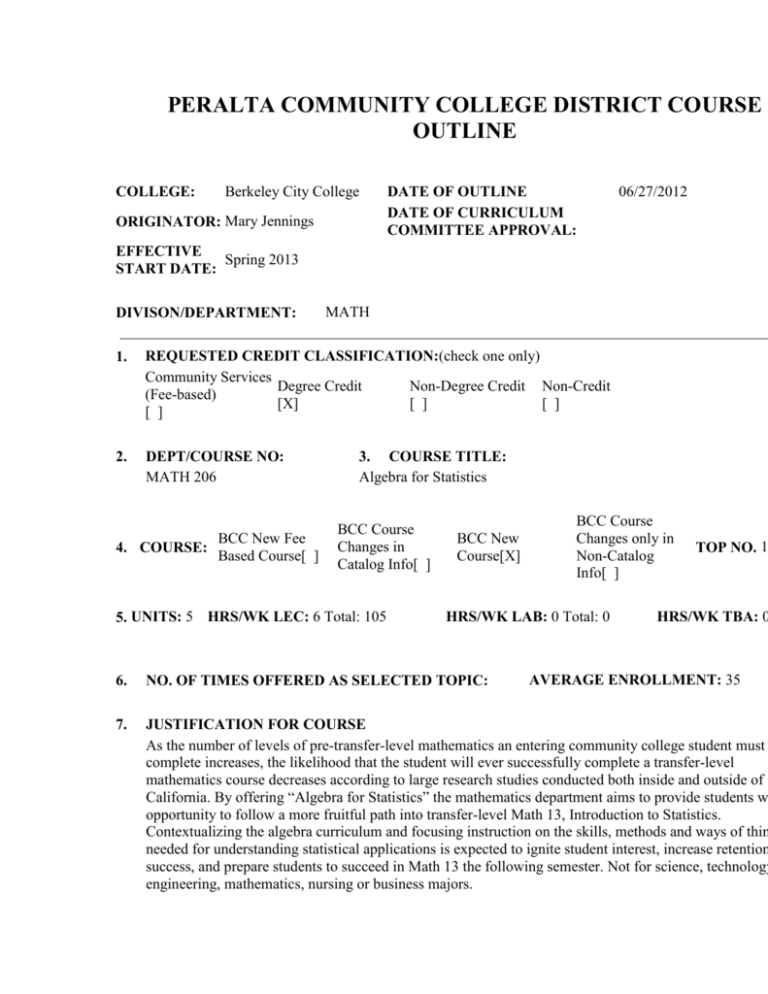
PERALTA COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT COURSE OUTLINE COLLEGE: Berkeley City College ORIGINATOR: Mary Jennings DATE OF OUTLINE DATE OF CURRICULUM COMMITTEE APPROVAL: 06/27/2012 EFFECTIVE Spring 2013 START DATE: DIVISON/DEPARTMENT: MATH 1. REQUESTED CREDIT CLASSIFICATION:(check one only) Community Services Degree Credit Non-Degree Credit Non-Credit (Fee-based) [X] [ ] [ ] [ ] 2. DEPT/COURSE NO: MATH 206 4. COURSE: BCC New Fee Based Course[ ] 3. COURSE TITLE: Algebra for Statistics BCC Course Changes in Catalog Info[ ] 5. UNITS: 5 HRS/WK LEC: 6 Total: 105 BCC New Course[X] BCC Course Changes only in Non-Catalog Info[ ] HRS/WK LAB: 0 Total: 0 TOP NO. 1 HRS/WK TBA: 0 AVERAGE ENROLLMENT: 35 6. NO. OF TIMES OFFERED AS SELECTED TOPIC: 7. JUSTIFICATION FOR COURSE As the number of levels of pre-transfer-level mathematics an entering community college student must complete increases, the likelihood that the student will ever successfully complete a transfer-level mathematics course decreases according to large research studies conducted both inside and outside of California. By offering “Algebra for Statistics” the mathematics department aims to provide students w opportunity to follow a more fruitful path into transfer-level Math 13, Introduction to Statistics. Contextualizing the algebra curriculum and focusing instruction on the skills, methods and ways of thin needed for understanding statistical applications is expected to ignite student interest, increase retention success, and prepare students to succeed in Math 13 the following semester. Not for science, technology engineering, mathematics, nursing or business majors. 8. COURSE/CATALOG DESCRIPTION Integrated mathematics for statistics: Exploratory data analysis and principles of data collection and calculation; ratios, rates, and proportional reasoning; fractions, decimals and percents; evaluating expre analyzing algebraic expressions of statistical measures; modeling bivariate data with linear and exponen functions; graphical and numerical descriptive statistics for quantitative and categorical data. Not for sc technology, engineering, mathematics, nursing or business majors. 9. OTHER CATALOG INFORMATION: a. Modular: Yes [ ] No [X] If yes, how many modules: b. Open entry/open exit: Yes [ ] No [X] c. Grading Policy: Both Letter Grade or Pass/No Pass [ ] Pass/No Pass [ ] Letter Grade Only [ d. Eligible for credit by Exam: Yes [ ] No [X] e. Repeatable according to state guidelines: Yes [ ] No [X] If yes, number of allowable repeats: f. Required for degree/certificate (specify): g. Meets GE/Transfer requirements (specify): h. Are there prerequisites/corequisites/recommended preparation for this course? Yes [X] No [ ] Date of last prereq/coreq validation: 06/27/2012 LIST STUDENT PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES (EXIT SKILLS): (Objectives must define the e skills required of students and include criteria identified in Items 12, 14, and 15 - critical thinking, essay 10. writing, problem solving, written/verbal communications, computational skills, working with others, workplace needs, SCANS competencies, all aspects of the industry, etc.)(See SCANS/All Aspects of Industry Worksheet.) Students will be able to: 1. formulate questions that can be addressed with data, then collect, organize, display, and analyze relevant data to address these questions and communicate findings. 2. use the properties of algebra to simplify expressions, solve equations and answer questio context. 3. apply numerical, algebraic and geometric reasoning skills to statistical analysis. 4. construct, use, and interpret mathematical models, including linear and exponential funct that represent relationships in quantitative data. COURSE CONTENT: (List major topics in sequence; address objectives listed in #11 above. Degree applicable course must be taught at college level; see definition. List percent of time spent on each topi 11A. Also, differentiate content of each level, when levels are assigned.) Lecture and lab content are to be lis separately. LECTURE CONTENT: 10% Review of Relevant Arithmetic A. Recognizing and finding equivalent forms of fractions, decimals and percents B. Comparing fractions, decimals and percents D. Graphing fractions, decimals and signed numbers on a number line E. Unit measure and conversion between units F. Ratios and rates G. Operations with real numbers H. Absolute values I. Exponents and roots J. Scientific notation 20% Introduction to Algebra A. Variables and formulas B. Summation notation, including subscripts C. Sketching and interpreting graphs in the Cartesian plane including those of points, lines and probab distributions D. Finding the equation of a line given its graph or its slope and one point on the line or two points on line. E. Solving systems of linear equations in two or three variables F. Solving quadratic equations G. Solving simple rational and square root equations H. Introduction to functions I. Linear functions J. Exponential and logarithmic functions 10% Introduction to Logic A. Venn diagrams B. The scientific method 15% Categorical Variables A. Constructing and reading graphs of distributions of categorical data: bar graphs, line graphs and pie charts B. Analyzing two-way tables; rules of probability; mutually exclusive and independent events; calcula joint, marginal and conditional probabilities 15% Quantitative Variables A. Graphs of univariate distributions of quantitative data: histograms and boxplots B. Measures of central tendency: mean, median and mode C. Descriptions and measures of spread: variance, standard deviation, quartiles, percentiles D. Measure of symmetry: skewness 10% Geometric and Graphical Interpretation of Algebraic Structures A. Signed distance from the mean B. Geometric interpretation of standard deviation C. Symmetry 10% Bivariate Distributions of Quantitative Variables A. Creating and analyzing scatterplots B. Intuitive introduction to least squares regression using linear and exponential models C. Intuitive and graphical introduction to correlation coefficient r 10% Data Collection A. Sample surveys B. Observation vs. experiment 11B. LAB CONTENT: 12. METHODS OF INSTRUCTION (List methods used to present course content.) 1. Lecture 2. Discussion 3. Projects 13. ASSIGNMENTS: 10 hours/week. (List all assignments, including library assignments. Requires two (2 hours of independent work outside of class for each unit/weekly lecture hour. Outside assignments are n required for lab-only courses, although they can be given.) Out-of-class Assignments: Problem sets including problems equivalent to those covered in lectures and original problems which require the synthesizing of various concepts. Research project and paper summarizing statistical findings. ASSIGNMENTS ARE: (Check one. See definition of college level): [X] Primarily college level [ ] NOT primarily college level STUDENT ASSESSMENT: (Grades are based on): (Check as many boxes as are applicable. Note: Fo 14. degree credit, AT LEAST ONE of the first three boxes must be checked. If "ESSAY" is not checked, pl explain why here.) ESSAY (Includes "blue book" exams and any written assignment of sufficient length and [X] complexity to require students to select and organize ideas, to explain and support the ideas, demonstrate critical thinking skills.) Why "ESSAY" is not checked: [X] COMPUTATION SKILLS NON-COMPUTATIONAL PROBLEM SOLVING (Critical thinking should be demonstrat [X] solving unfamiliar problems via various strategies.) [X] SKILL DEMONSTRATION [X] MULTIPLE CHOICE [ ] OTHER (Describe) 15. TEXTS, READINGS, AND MATERIALS: A. Textbooks: Date of Publicatio Utts, Jessica M Seeing Through Statistics (3rd/e). Brooks Cole, (2009). Additional class activities and materials for this course are currently under development by BCC Mathemati department faculty in collaboration with colleagues at other Bay Area community colleges and a 2011-2012 consortium organized by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. Author Title and Edition Publisher *Date is required: Transfer institutions require current publication date(s) within 5 years of outline addition/u B. Additional Resources: Library/LRC Materials and Services: 1. The instructor, in consultation with a librarian, has reviewed the materials and se of the College Library/LRC in the subject areas related to the proposed new cour Are print materials adequate? Yes [X] No [ ] Are nonprint materials adequate? Yes [X] No [ ] Are electronic/online resources available? Yes [X] No [ ] Are services adequate? Yes [X] No [ ] Specific materials and/or services needed have been identified and discussed. Librarian comments: Joshua Boatright. Action: Reviewed 09/13/2011 2. C. Other Resources: Identify types, location, and availability of other resources and materials required for this course. Readings listed in A and B above are: (Check one. See definition of college level): [X] Primarily college level [ ] NOT primarily college level 16. Designate Occupational Code (check ONE only): [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [X] A B C D E Apprenticeship Advance Occupational Occupational Possible Occupational Non-Occupational SUPPLEMENTAL PAGE Use only if additional space is needed. (Type the item number which is to be continued, followed by "contin Show the page number in the blank at the bottom of the page. If the item being continued is on page 2 of the the first supplemental page will be "2a." If additional supplemental pages are required for page 2, they are numbered as 2b, 2c, etc.) 1a. Prerequisites/Corequisites/Recommended Preparation: PREREQUISITE(S): MATH 253: Pre-Algebra or appropriate placement through multiple measures assessment process Subject course and pre/corequisite is:




