review first exam - University of San Diego Home Pages
advertisement

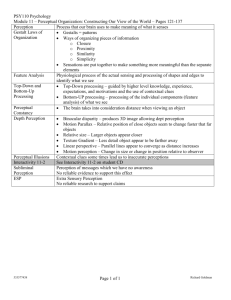
Consumer Behavior Spring 2005 Exam 1 Study Guide Introduction to Consumer Behavior and Consumer Studies Chapter 1 (pp 1-20 and 34-41) Consumer Behavior Definition and Components (Decisions, consumption, offering, decision making units). Who studies CB and why? Perceptual map and positioning Consumer Research – Qualitative/ Quantitative Consumer Research Process Consumer Research Methods Marketing Implications of Consumer Behavior and research Primary Data Qualitative research In-Depth interview Projective techniques Perceptual Map Secondary Data Quantitative research Focus group Reliability Positioning Validity Marketing decisions Motivation Chapter 4 (pp 112-131) and Chapter 6 (pp 187-198) Motivation Model of Motivation Process Drive (intensity and direction) Wants Needs Needs Classification Biogenic vs. Psychogenic Needs Innate vs. Acquired Needs Maslow's hierarchy of human needs Goals Approach vs. Avoidance conflicts. Involvement (types and role) Perceived Risk Psychoanalytical Theory (Freud’s)( Id, Ego, Super Ego) Motivational research Challenges of understanding motivation 1 Perception Chapter 2 Perception definition Perception process Exposure Sensation (receptors) Sensory Threshold Just Noticeable difference Weber’s Law Attention Attention features and influencers Internal and external factors influencing attention Interpretation Gestalt Psychology Figure and ground Closure (Zeigernik effect) Grouping, Similarity, Proximity Marketing and Perception Customer’s defense mechanisms Selective attention selective exposure perceptual distorsion Subliminal Perception (advertising) Learning and Memory Chapter 3 Importance of learning Behavioral school of learning theories classical conditioning Unconditioned, conditioned stimulus unconditioned, conditioned response. Stimulus generalization, discrimination and repetition. Comparative advertising Instrumental (operant) conditioning Positive and negative reinforcement. Punishment. Shaping Loyalty Observational learning. Cognitive learning theory Role of memory Sensory store short term memory Long term memory Rehearsal Recirculation Chunking Mnemonic Network Retrieval Retrieval failures Primacy and Recency effect Decay Interference Recognition Recall How Retrieval is enhanced 2