1 - Database on Indian Economy
advertisement
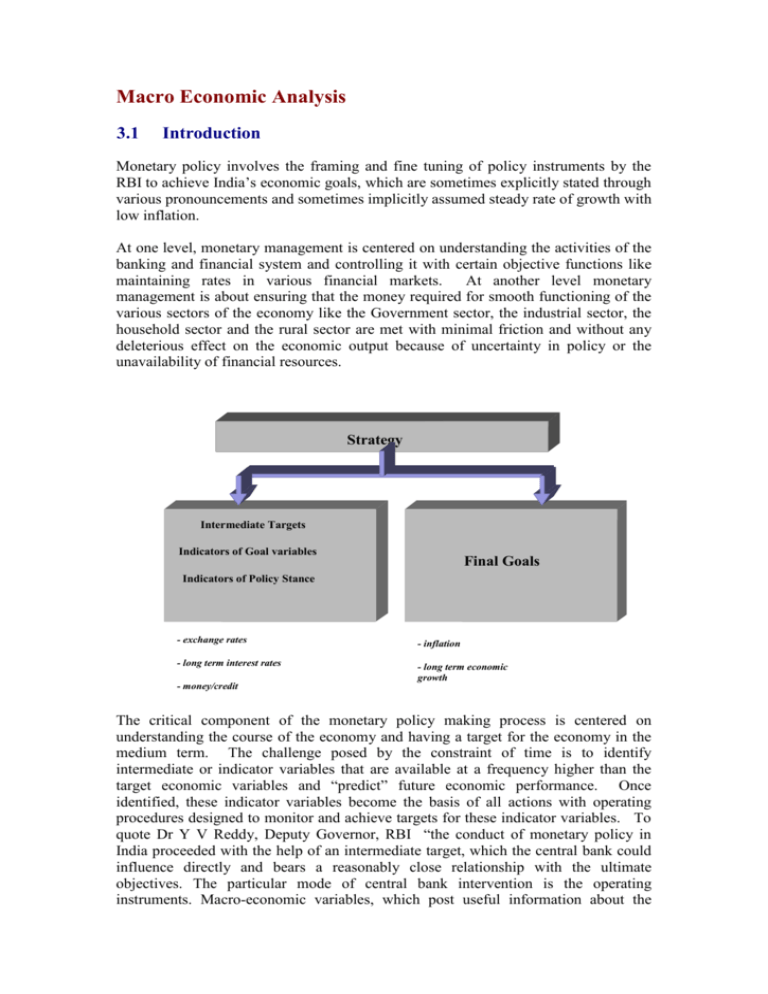
Macro Economic Analysis 3.1 Introduction Monetary policy involves the framing and fine tuning of policy instruments by the RBI to achieve India’s economic goals, which are sometimes explicitly stated through various pronouncements and sometimes implicitly assumed steady rate of growth with low inflation. At one level, monetary management is centered on understanding the activities of the banking and financial system and controlling it with certain objective functions like maintaining rates in various financial markets. At another level monetary management is about ensuring that the money required for smooth functioning of the various sectors of the economy like the Government sector, the industrial sector, the household sector and the rural sector are met with minimal friction and without any deleterious effect on the economic output because of uncertainty in policy or the unavailability of financial resources. Strategy Intermediate Targets Indicators of Goal variables Final Goals Indicators of Policy Stance - exchange rates - inflation - long term interest rates - long term economic growth - money/credit The critical component of the monetary policy making process is centered on understanding the course of the economy and having a target for the economy in the medium term. The challenge posed by the constraint of time is to identify intermediate or indicator variables that are available at a frequency higher than the target economic variables and “predict” future economic performance. Once identified, these indicator variables become the basis of all actions with operating procedures designed to monitor and achieve targets for these indicator variables. To quote Dr Y V Reddy, Deputy Governor, RBI “the conduct of monetary policy in India proceeded with the help of an intermediate target, which the central bank could influence directly and bears a reasonably close relationship with the ultimate objectives. The particular mode of central bank intervention is the operating instruments. Macro-economic variables, which post useful information about the objectives of monetary policy, although they may not in themselves be amenable to central bank targeting, are ‘indicators’ or ‘information’ variables.”1 3.2 Scope and Objective The subject area “Macro Economic Aggregates” covers analysis and understanding of the economy as a whole and its sectoral trends. The scope of the subject area encompasses tracking and explaining strategic (long term perspective) issues whereas the tactical issues (current perspective) are analysed from the time series data of the same variables taken at higher frequency. The analysis of the economy and trends in different sectors is carried out at DEAP and DESACS. While the focus of DEAP is to analyse sectoral trends and the factors influencing the growth of the sectors in detail, DESACS undertakes statistical analysis of economic variables and forecast of key macro economic variables. The context diagram given below outlines flow of information from various sources for performing the analysis: 1 Monetary Policy in India: Objectives, Instruments, Operating Procedures and Dilemmas- A lecture at the Fourth Securities Industry Summit, May 26, 1999. EE Financial Markets FDI,ECB,NRI Deposit and Foreign Liabilities EE ECD and DEIO Equity market, Money market and Foreign Exchange market monsoon EE RPCD,UBD, EE SIDBI,Mercha nt Bankers,Com panies EE CSO National Accounts Statistics, IIP and WPI EE Ministry of Labour EE Ministry of Agriculture EE Minstry of Programme Implementatio n EE IMD Rural Credit Small Scale Industry, Capital Issues DEAP DESACS CPI EE DGCIS Merchandise Trade Agricultural Production Infrastructure Industries Research Findings Publications Notes to Top management EE - Some of the departments of RBI mentioned as EE refers to those external to DEAP & DESACS 3.3 Business Functions The important business functions relating to this subject area are: 1. Collection and compilation of information from various sources. The sources are mostly Government agencies, banks, financial institutions, and other key departments of RBI. 2. Analysis of time series data and preparation of research findings for apprising the top management. 3. Forecasting of key economic variables based on statistical models 4. Publication of analysis and research work. 3.4 Analytical Perspective The broad analytical framework in which the above objective is addressed can be classified into analysis encompassing both the micro (entity level) and macro (aggregate level) aspects. The various types of analysis that may be considered are: Trend analysis (trends in National Income, IIP etc,) Comparative analysis (comparing the composition of Income across time) Ratio analysis (Debt-GDP ratio, Savings- GDP ratio etc.,) Intra group / sector analysis (i.e. comparing entities like banks, Financial Institutions and NBFCs), Cumulative analysis (average inflation level in the financial year) Top ‘n’ analysis (top 5 contributors in the export earnings) The above analysis helps in drawing important conclusions/generalizations on the basis of which the policy prescriptions may be initiated and/or guidelines formulated. 3.5 Macroeconomic indicators Introduction The various economic indicators that are key to understanding the economy are both on long term and short-term time scales. These issues spread across a wide spectrum of distinct subject areas such as National Income, Savings, Investment, Employment, Agriculture, Industry and Infrastructure, Prices, Corporate Finance, Government Finances and External Sector. Analytical Issues i) National Income, Savings, Investment and Employment What is the long-term trend in country’s economic growth - both in nominal and real terms? What is the forecast for GDP growth by RBI? How does the actual estimate of economic growth compare with the forecasts made at RBI? What is the current trend in the GDP and its sectoral composition? What is the long-term sectoral growth pattern? Is there any structural shift in the composition of GDP over the years? What are the forecasts for sectoral GDP growth by RBI? How is the growth pattern among the States as reflected through the growth in State Domestic Product? How does the per capita income of States compare against each other and with national per capita income? Does it reflect imbalanced growth pattern in the country? How is the trend in savings-investment in the economy? What is the trend in savings and investment ratio? What is the incremental savings and investments ratio? What is the composition of savings across types (physical and financial) and entities (household, private and public sector)? How is the flow of funds taking place within the key entities of the economy (as estimated by RBI)? Is there any shift towards reducing or increasing dependence of other entities on resources coming from household sector? Is there any structural shift in the composition of resources in terms of the instruments of savings and what is the pattern seen across entities? What are the employment levels in private and public sector? ii) Agriculture, Industry and Infrastructure What is the long-term trend in IIP, Agricultural and Food grains productions levels? What is the trend in buffer stock of food grains available? What is the current trend in agriculture, industrial production and index of infrastructure production? How is the current trend in monsoon? How is it varying from long-term monsoon trends in the past? How is the current trend in credit (both direct and institutional) for agriculture compared to last year? What is the current flow of food credit from the banking system? How is the procurement and distribution position of agricultural products and the food grains? iii) Prices What is the year-on-year inflation trend? Which are the commodity groups that contribute substantially to inflation? How is the trend in the core inflation level as compared to past few years? What is the expected level of inflation as estimated by RBI? What is the trend in agricultural and food grain prices, which are having a large bearing on the price indices like WPI and CPI? What is the trend in international oil prices? iv) Corporate Finance v) vi) How is the current flow of credit from banks to corporate sector (non food credit)? Is there a drop in industrial credit from the banking system compared to past years? How is the trend in the resource mobilisation effort by corporate sector through capital issues? What is the mode of fund raising by the corporates through capital market i.e., through public issues or private placements? Whether the capital issues are concentrated with a few mega issues? What is the industry wise profile of capital issues this year? What are the instruments of capital issues? What is the level of sanctions and disbursements from FIs to corporate sector this year compared to last year? What is the type of assistance sanctioned to corporates by Financial Institutions? Financial Markets How are equity market, money market and Forex market moving at present? Government Finances What is the long-term trend in resource mobilisation by the Central/State Governments? What is the long-term trend in the Plan and non-plan expenditure of the Central/ State Governments? vii) What is the trend in the major budget deficit indicators of the Central/State Governments? What is the Central Government’s dis-investment plan as indicated in the budget document? External Sector How are the long-term trend and the current position of Balance of Payment (BOP) situation as reflected through the current and capital accounts of the BOP? What is the trend in key indicators like Current Account deficit, Trade-GDP ratio, export-GDP ratio and import-GDP ratio, both in long term and short term? What is the trend in export-import ratio, which reflects proportion of imports that can be financed through export earnings? Has the trend in this ratio improved or deteriorated over time, reflecting pressure on BOP? What is the extent of India’s openness with the rest the world as reflected in the trend in India’s trade to world trade? What is the share of imports to world imports and share of exports to world exports? What is the long-term trend in the composition of trade in terms of commodity, area and currency? Is there a trend towards increasing use of US Dollar for financing of trade of the country? What has been the change in the commodity composition of exports and imports of the country during the year? What is the level of oil imports and its variation from long-term trends? What is the forecast for imports, exports and oil imports as estimated by DESACS and its comparison with the recent trend? Is there any major shift in India’s trading partners and whether this change in trading partnership has impacted on the value of rupee as against other major currencies? What are the new areas of foreign exchange earners such as InfoTech services or rice exports? What is the trend in movement of Foreign exchange reserves? What is the quantum of capital flows into the country? Is there any slackening of the Capital flows? What is the country wise or mode of Foreign Investments (direct or portfolio) coming into India? Which are the industries where higher FDI is coming? What is the profile of External Commercial Borrowings in terms of volume and tenor of the borrowing? Is there any shift towards medium and long-term borrowing? What is the total flow of deposits from NRIs? Is there a shift towards long-term deposits? What is the trend in the Trade weighted exchange values (NEER and REER) of Indian rupee? The variables that are tracked to understand the strategic issues can be drawn from: National Account Statistics (Annually and quarterly) Forecast of GDP and sectoral GDP (Annually and quarterly) State Domestic Product (Annually) Population Statistics (Once in ten years) Savings and Investments from National Income Statistics (Annually) Flow of Funds Statement (Annually) Employment Statistics (Annually) WPI, CPI and forecasts of WPI (Weekly, Monthly and Monthly respectively) Agricultural Production and food grains production and stock (quarterly) Index on Industrial Production (IIP) and Production estimates from Annual Survey of Industries (Monthly) Index of Infrastructure Industries- Monthly Rainfall data- weekly Rural Credit from Cooperative Sector, Scheduled Commercial BanksAnnually Food procurement and distribution data- Monthly Food Credit from Banks-Fortnightly Food grain procurement, food stock and distribution- Monthly Agricultural commodity and food article Prices- Weekly Non food credit- Fortnightly Banks’ credit to Commercial Sector-Fortnightly Scheduled Commercial Banks’ investment in Commercial PaperFortnightly Capital Issues by the corporate sector (both private placement and public issue)-Quarterly Financial Institutions’ sanctions and disbursements to corporate sector (Annually) Budget items at the most granular level (Annually) DGCIS trade statistics at the commodity level and also at the aggregate level (Monthly) BOP statement at the top headline level and at its most granular level (Quarterly) IMF Statistics on world trade (Annually) The variables, which are available at detailed granular level, can be aggregated to its top headline level to see the trend and variations over a longer time frame. The above variables may be plotted against each other to see correlation or cause-effect relationship. Constraints Faced Most of the data pertaining to macro economic aggregates are available in the excel sheets at aggregated level that too for the past 3-4 years only. Disaggregated data is available in hard copies and the same needs to be transformed to a soft format before uploading to the Data Warehouse.





