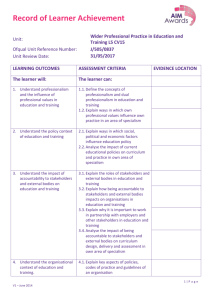
HA Units listed on website – unit summaries
advertisement

HA Units listed on website – unit summaries Compulsory Units 1. Understanding the Retail Environment In this unit, learners will be required to: Analyse the key social and economic external factors which are impacting on retailing Explain the impact of technology, current legislation, and the current environmental agenda are on retailing practice Analyse the response of their own retail outlet to the current external environment Describe the internal factors that can influence the continued success of a retail outlet Analyse the impact of internal factors upon the success of their own retail outlet Explain how the manager of a retail outlet affects the continued success of the store by their management of its internal environment 2. Understanding Customer Service in Retail In this unit, learners will be required to: analyse the contribution customer service makes to organisational goals, and evaluate the influence of customer perception and expectations on service levels Explain how to determine the resources needed to meet customers expectations, how to ensure resources are available to deliver Assess the staff management issues that affect the delivery of customer service Compare the methods available for monitoring and evaluating customer service performance explaining the benefits and drawbacks of each method Analyse information about customer service problems, identify the causes of customer service problems, evaluate possible solutions to customer service problems and how to monitor the effectiveness of solutions to customer service problems Explore ways in which retail organisations can implement and drive continuous improvement in customer service Evaluate methods for making use of technology to improve customer service delivery Management Skills 1. Managing Staff Performance The learner will be able to: Explain the impact of the organisational context on the setting of objectives Set work objectives for staff communicate work objectives to staff Monitor work activities against organisational requirements Explain the methods that can be used to improve achievement of objectives Evaluate quality systems in an organisation Assess the performance of staff against work objectives Provide constructive feedback to staff Agree performance improvements with staff Evaluate options for dealing with underperformance of staff 2. Managing Risk The learner will be able to: Identify potential risks in current and planned activities within own area of responsibility Assess the nature of identified risks and potential consequences Evaluate the probability of identified risks occurring Identify ways and means of minimising the impact and likelihood of potential risks Provide information on identified risks to relevant stakeholders 3. Principles of Management and Leadership The learner will be able to: Explain the relationship between management and leadership Analyse how management and leadership style impacts on the achievement of organisational objectives Explain the personal and professional skills required for effective management Compare the skills and styles of successful leaders Assess the expected impact of own leadership styles on work groups Select appropriate theories of management and leadership to identify management and leadership requirements in given situations Report on the usefulness of using theories for gaining insights into leadership requirements in given situations Use appropriate methods to assess the skills needed by a leader in a given situation Plan the development of management and leadership skills for a given job role Make justified evaluations of the management and leadership development methods selected 4. Developing Successful Business Teams The learner will be able to: Describe the characteristics of successful business teams Assess the importance of team roles in successful business teams Analyse the value of using theoretical models when building successful business teams Explain the stages of team development Plan how to motivate team members to achieve given objectives Encourage open communication between team members to support team development Evaluate ways of resolving conflict between team members Monitor the performance of a team against given objectives recommend how to improve performance against given objectives 5. Management Decision Making The learner will be able to: Explain how current information and knowledge needs for management decision making can be analysed Describe sources of information and knowledge that can support management decision making Evaluate the importance of information and knowledge in the management decision making process Identify the ICT systems that can provide information to support management decision making Assess the benefits of using information from ICT systems when making management decisions Explain how data protection legislation affects the use of information from ICT systems in the management decision process Analyse stakeholder needs and expectations Use current information and knowledge to identify an issue where a proactive decision is required Establish the outcomes that need to be achieved when making a management decision Justify the basis for making a management decision Take a management decision Communicate a management decision to stakeholders Review a management decision making system Analyse the strengths and weaknesses of a management decision making system Plan justified improvements to a management decision making system 6. Addressing Performance problems The learner will be able to: Identify legal requirements, industry regulations, organisational policies and professional codes concerning performance Explain limits of own authority relating to performance problems Assess team member’s performance against performance criteria Evaluate causes of identified performance problems Identify performance problems to the attention of the team member concerned Explain an organisation’s policies for managing performance problems to the team member concerned Develop a confidential record of discussions with team members about problems affecting their performance Explain and discuss alternative courses of action with the team member concerned Identify the course of action with the team member concerned Review and revise confidential records of discussions with team members about problems affecting their performance Visual Merchandising 1. The Installation of Window Displays for Successful Retailing The learner will be able to: Explain the importance of effective window displays for a retail business Evaluate the characteristics of effective window displays to include the use of o colour o aesthetics o lighting o props o balance o drama o impact o commerciality o themes and schemes Analyse the use of the above to support creative developments Evaluate the effectiveness of 3 window displays in supporting o the intended merchandise o the intended brand 2. Understanding In-Store Visual Merchandising The learner will be able to: Explain the importance of effective in-store merchandising for a retail business Evaluate the characteristics of effective creative display solutions and techniques to include the use of o fixtures o floor layouts o selling space o product adjacencies Analyse the use of the above to support in-store merchandising and brand identity Assess the significance of product and brand adjacencies upon o customer store navigation o potential and add-on sales o brand relationships Evaluate the ambience and theatre created within at least 3 retail outlets Evaluate the effectiveness of the following in creating an attractive retail experience o displays o point of sale o hotshops o general outlet ambience Marketing 1. Marketing Intelligence The learner will be able to: Describe the main stages of the purchase decision-making process Explain theories of buyer behaviour in terms of individuals and markets Explain the factors that affect buyer behaviour Evaluate the relationship between brand loyalty, corporate image and repeat purchasing Evaluate different types of market research techniques Use sources of secondary data to achieve marketing research objectives Assess the validity and reliability of market research findings Prepare a marketing research plan to obtain information in a given situation Assess market size trends within a given market Plan and carry out a competitor analysis for a given organisation Evaluate an organisation’s opportunities and threats for a given product or service Evaluate techniques of assessing customer response Design and complete a customer satisfaction survey Review the success of a completed survey 2. Internet Marketing in Business The learner will be able to: Describe the role internet marketing has in a marketing context Describe how selected organisations use internet marketing Explain the benefits to customers of a business using internet marketing Describe the benefits and opportunities to the business of using internet marketing within the marketing mix of a selected business Explain how internet marketing has made a selected business more efficient, effective and successful Explain the challenges of globalisation facing a selected business when using the internet as a marketing tool 3. Using Digital Channels & Social Networks to Deliver Marketing Communications The learner will be able to: Confirm the objectives, budget, creative strategy and response rate for online engagement activity Analyse benefits, limitations and differences between online engagement and email marketing communications (advertising) Explain how online engagement and email marketing communications work together Analyse the implications of differences between programmes aimed at retention, acquisition and conversion when identifying suitable marketing communications channels and platforms Review factors for consideration when balancing added value with the potential for exploiting customer relationships Evaluate methods for testing and gauging the likely impact of digital and electronic channels and platforms programmes Identify how to access specific target audience groups Assess the benefits and risks of electronic tools and platforms Identify electronic tools and platforms suitable for communicating with a target audience Create marketing communications (advertising) messages which o make appropriate use of selected channels and platforms o build audience engagement o convey propositions clearly Identify how to access specific target audience groups Assess the benefits and risks of electronic tools and platforms Identify electronic tools and platforms suitable for communicating with a target audience Create marketing communications (advertising) messages which o make appropriate use of selected channels and platforms o build audience engagement o convey propositions clearly Confirm that the content of messages is o accurate o justifiable o generates interest in products and services Confirm that clear links o allow recipients to access further relevant information o take relevant action Develop and implement responses to negative messages and comments relating to campaigns and associated products and service Confirm that content complies with data protection and privacy legislation Confirm that activity is o in line with creative strategy o integrates with other associated marketing communications activities Include response devices with coding to identify the source of responses Create data collection and reporting systems to fulfil agreed monitoring and quality assurance requirements Liaise with system specialists and marketing communications colleagues as required Deliver a marketing campaign within agreed timescales and budget Use digital channels and platforms to amplify reach and facilitate growth of social and online content Manage and measure undelivered messages amending related records accordingly 4. Doing Business Globally The learner will be able to: Analyse the impact of the following on entering a Global market o company branding o web site design and functionality in a new market o product design for a specific market Evaluate methods of breaking into Global Markets through o consultation with relevant trade, and government support agencies o the understanding of import/export procedures/ law/ financial costs o the use of agents Analyse the cultural differences in potential markets and consider how this could effect product development Evaluate the important differences in communicating with a range of cultures including o language - non verbal and verbal o translation o dress o social etiquette o managing time Merchandising 1. Merchandising for Retail Success The learner will be able to: Interpret unit and financial information in the planning and trading processes Analyse and report trends and implications for the business Use real or simulated data to plan and manage the retail business, including, for example o sales o financial targets o key events calendar o department sales phasing o options o ratios o open to buy Use available data, including, for example o seasonal reviews o forward trend information o company strategic plan/s o to propose and justify range plan parameters Implement and review strategies to manage stock flow, to include, for example o intake o allocation o distribution o replenishment o mark-down o to achieve agreed KPIs Assess the significance of the following in branch planning o grading, profiling and tiering o allocation and replenishment parameters o strategic and tactical promotional activity Analyse potential short and longer term consequences of proposals to manage stock flow Retail Operations 1. Understanding Retail Concepts and Outlet Design The learner will be able to: Evaluate the characteristics of effective retail architecture to include o aesthetics of outlet design o shopping environment o outlet concept and ambience o space and location Compare and contrast at least 2 retail outlets in terms of o design aesthetics o shopping environment o outlet concept and ambience o space and location Evaluate the effectiveness of each outlet in supporting the brand and customers’ requirements Evaluate the characteristics and significance of ‘concept’ stores/outlets to include o architecture o design aesthetics o product placement o brand image o location 2. Project Management Skills The learner will be able to: Explain the responsibilities of a project manager Assess the techniques available for planning projects Explain techniques used to monitor and review projects Determine the need and scope for the project Develop project plans identifying the following o aims and objectives o full costs of the project o timescale for the whole project o human resources required o physical resources required o individual tasks within the project o documentation and information required o interdependencies involved o milestones and deliverable to be met o possible risks Conduct and manage the project in line with the plan Monitor the progress of the project to ensure that o objectives are met o delivery is on time and on budget o quality standards are met and maintained Communicate effectively with all team members and other stakeholders Report progress to relevant parties at agreed stages Deal promptly and effectively with problems within their control Report problems which they cannot resolve to appropriate personnel Report project completion to relevant stakeholders 3. Finance for Non-Finance Managers The learner will be able to: Analyse and interpret prepared financial statements which include o profit and loss statements o balance sheet o cash flow spreadsheets Assess which business elements are profitable and worthy of development by considering the following o allocation of budgets o establishing pricing o segmental analysis o break even analysis o return on investment (ROI) o risk analysis Identify, evaluate and construct systems to implement the following o setting price o ensure profitability o track cash flow o allocate budgets Determine and identify techniques in order to o calculate pricing o allocate time o collect debt o negotiate discounts Integrate techniques into overall business to o assess financial risks o increase profitability o apply theories and implement within your business 4. Understanding Security and Loss Prevention The learner will be able to: Define the security risks faced by a retail business and distinguish between external and internal threats to security Explain how and why losses can occur in a retail business as a result of crime Explain the implications of criminal loss to retail businesses Explain the role of management and other staff in maintaining the security of a retail business Explain the main ways in which retail businesses use technology to prevent loss Explain how stock control procedures are used to prevent loss Explain how routine stocktaking helps to prevent loss Explain how to apprehend individuals suspected of fraud in accordance with relevant legislation Explain how to apprehend individuals suspected of theft in accordance with relevant legislation Explain common procedures for carrying out searches when theft is suspected Describe common types of situations where threatening and violent behaviour from customers may occur in a retail business Explain the techniques for controlling threatening and violent behaviour and explain why these techniques are effective Explain why it is necessary to assess security risks in a retail business Describe the key stages in the risk assessment process Explain why it is important to identify breaches in security and deal with them promptly 5. Improving Retail Store Operations The learner will be able to: Explain characteristics of the organisation’s brand image, customer base and desired market position Explain the relationship between the agreed performance measures for own area of responsibility and the organisation’s brand image and desired market position Explain how systems and procedures in own area of responsibility are intended to support the achievement of organisational performance measures Explain potential causes of failure to achieve organisational performance measures in the type of retail operations carried out in own area of responsibility Explain why it is important for staff to understand the purpose and intended benefits of improvements to retail operations Explain how own manner when explaining improvements can affect staff’s response to these Explain the importance of encouraging staff to suggest ideas for improvement to retail operations Explain the importance of ensuring that colleagues receive the credit if their ideas are implemented Explain the importance of showing enthusiasm and leading by example when putting improvements into practice Evaluate organisational performance within own area of responsibility using information that is o relevant o reliable o up to date Develop ideas to improve the effectiveness of operations in own area of responsibility Evaluate which ideas for improvements to the effectiveness of operations in own area of responsibility should be put forward to decision makers, based on the extent to which the ideas are o consistent with the organisation’s brand image o consistent with organisational policy o achievable, given the available resources o beneficial to the organisation and its customers Present ideas to decision makers for possible improvements, doing so o with supporting facts o acknowledging any contributions made by other people Explain to decision makers the benefits the recommended improvements could bring Justify to decision makers the resources needed to put improvements into practice Clarify any aspects of the recommended improvements decision makers wish to discuss further Explain planned improvements to staff in ways that attempt to o make clear the benefits of the proposed changes o encourage involvement in implementing proposed changes Ensure that staff have everything they need to implement proposed changes including additional training Seek advice and support to resolve any problems with implementing proposed changes that are not within own authority to resolve Demonstrate to staff own commitment to achieving the benefits of proposed changes through own behaviour 6. Developing Operational Plans The learner will be able to: Identify operational objectives within own area of responsibility Analyse objectives of own area of responsibility in relation to those of own organisation Assess risks associated with operational plans and include contingency arrangements Identify support from relevant stakeholders Implement operational plan within own area of responsibility Monitor procedures within the operational plan Evaluate operational plans and implement any necessary actions 7. Auditing Stock Levels The learner will be able to: Explain the importance of auditing levels of stock and stock inventories Plan an audit of stock that o will ensure accurate, complete and timely auditing o will cause as little disruption as possible to normal work o includes plans for dealing with contingencies Negotiate with colleagues to obtain staff who have the necessary skills to help with the audit Allocate specific responsibilities to each member of the audit team Explain to the audit team what they are expected to do Diagnose and resolve problems that arise when implementing the audit Analyse the findings of a stock audit to identify problems that need resolving Clarify audit findings, including any unresolved problems, in a timely fashion for those who need the information Prioritise problems according to their importance and urgency Investigate and resolve problems o methodically o as far as possible within the scope of the audit and with the resources available Buying 1. Understanding the Sourcing Environment in Retail The learner will be able to: Determine sources of specific manufacture to include country and/or suppliers Assess options available to include, for example working direct with factory using buying agents using buying offices/hubs Analyse the influence and potential impact of contemporary PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal & Environmental) concerns upon sourcing decisions, for example o fair trade o working conditions o environmental protection o sustainability o social and cultural issues o animal testing o trading standards o copyright o legal considerations Determine the terms and conditions that would be negotiated when sourcing product(s) to include, for example o cost price o shipping o import duties o volume and discounts o timescales and/or logistics Determine the skills needed to develop a good working relationship with a supplier Assess the components of a good supply relationship 2. Understanding Buying in Retail The learner will be able to: Compare and contrast 3 of the following buying environments o own label retailer o o o o o high street chain department store branded buying independent store franchise/concession Analyse how the buying environment affects o the role and responsibilities of the buyer o the relationship with other departments, for example merchandising, retail operations, visual merchandising Analyse the significance of the following upon buying o trade shows o buying season o timescales o historical sales patterns Technology 1. Graphics in the Retail Environment The learner will be able to: Analyse how and where different styles of graphics are used in the retail environment Compare and contrast how graphics have been designed and used in two different scenarios Evaluate the effectiveness of each example in promoting the brand and the product Select, design and produce a co-ordinated graphics package to support a brand Select and justify choice of o size o scale o colour o logo o typeface o materials o method o media Evaluate the graphics package in terms of costs, benefits and achievement of intended outcome Analyse feedback from appropriate sources on graphics package and formulate their own response 2. The Internet and E-business The learner will be able to: Describe the environment in which e-business is conducted and business transaction types Explain the benefits and barriers to businesses considering an online presence Assess the security and legislative issues facing an online business organisation State the modes of communication available to an e-business and their applications Explain the internet technologies and their importance in making an e-business successful Explain the main features of HTML Analyse the functions of client servers and browsers, and the role of the search engine Evaluate the use of intranets and extranets within business communication Illustrate the different e-business models that can be used to generate revenue for a business Analyse each model in terms of its capacity to generate revenue Report on future developments in e-business models Use the key elements of good web design structure Evaluate the impact of a well designed website to an e-business Report on the issues concerning website usability 3. Promote the Use of Technology within an Organisation The learner will be able to: Examine current use of technology in meeting customer needs within an organisation Identify good practice in the use of technology through benchmarking activities Assess opportunities to increase productivity through the use of technology Develop a technology strategy to increase productivity through the promotion of technology in line with organisational values and customer needs Develop criteria to evaluate the success of the technology strategy Communicate a technological strategy across an organisation Ensure resources and support are provided across an organisation to implement the strategy Monitor the implementation of a technology strategy across an organisation Evaluate the success of a technology strategy against success criteria 4. Social Networking Management for a Business The learner will be able to: Define social networking Identify current external social networking tools for the geographical location of a business Compare the functionality and features of different external social networking tools Describe the limitations of different external social networking tools Select external social networking tools for a business Justify the selection of social networking tools for a business Explain the potential uses of grouping people in social networking tools Identify the audience groups for social networking for a business Explain the importance of evaluating the need for brand ambassadors in social networking for a business Explain how to recognise brand ambassadors Explain how to ensure the validity and credibility of brand ambassadors Explain how to manage brand ambassadors Explain the importance of evaluating the need for influencers in social networking for a business Explain how to recognise influencers Explain how to ensure the validity and credibility of influencers Explain how to manage influencers Compare brand ambassadors and influencers Define the term ‘social media management tool’ Explain the importance of using social media management tools in relation to social networking Explain the disadvantages of using social media management tools Use a social media management tool to group an audience relevant to a business Use a social media management tool to schedule content relevant to a business Use a social media management tool to share content relevant to a business Explain the benefits of using short-URLs within content Use a social media management tool to listen to content relevant to a business Use a social media tool to have ongoing dialogue with an audience relevant to a business Compare risk analysis and digital crisis management Explain the importance of monitoring for risk Carry out a risk analysis in relation to social networking for a business Create a digital crisis management plan in relation to social networking for a business Define the term social networking measurement and monitoring Identify social networking measurement and monitoring tools Explain the potential uses of social networking measurement and monitoring tools Explain the limitations of social networking measurement and monitoring tools Measure the amount of engagement and amplification on social networking for a business Analyse changes in sentiment to social networking for a business Recommend improvements to social networking for a business 5. Principle of Social Media Within a Business The learner will be able to: Describe a business and its type, vision, aims, objectives and goals Identify the brand and values of a business and how these are portrayed to the audience of a business Describe the marketing tools available to a business Explain the consequences of using Social Media on the budget of different sizes and types of business Explain the benefits and consequences of encouraging amplification Explain the benefits and consequences of encouraging engagement Explain the factors to consider when identifying a Social Media plan for a business Explain how Social Media could fit into the marketing plan of a business Describe the different tools and channels that can be used for Social Media Describe the features and benefits of the different tools and channels that can be used for Social Media Identify the potential type of audience for each different tool and channel that can be used for Social Media Explain the factors to consider when selecting different tools and channels for Social Media Evaluate different tools and channels for Social Media for business use Understand how to measure the success of using social media tools and channels Explain why SMARTER targets should be set for different Social Media tools and channels Describe the methods a business can use to measure and identify success of different Social Media tools and channels Describe what success could look like when using different Social Media tools and channels for different types and sizes of business Describe the components of a business’s social media policy and guidelines Explain the importance of having a social media policy and guidelines Explain the importance of having a reputation management policy Describe the benefits of managing perception changes in a business’s reputation Describe how to manage perception changes in a business’s reputation Explain the importance of knowing how similar businesses or industries are using Social Media Explain how to monitor the ways similar businesses or industries are using Social Media Monitor how a business is using Social Media Identify improvements to a business’s use of Social Media