Solutions to Problems in Chapter 1
advertisement
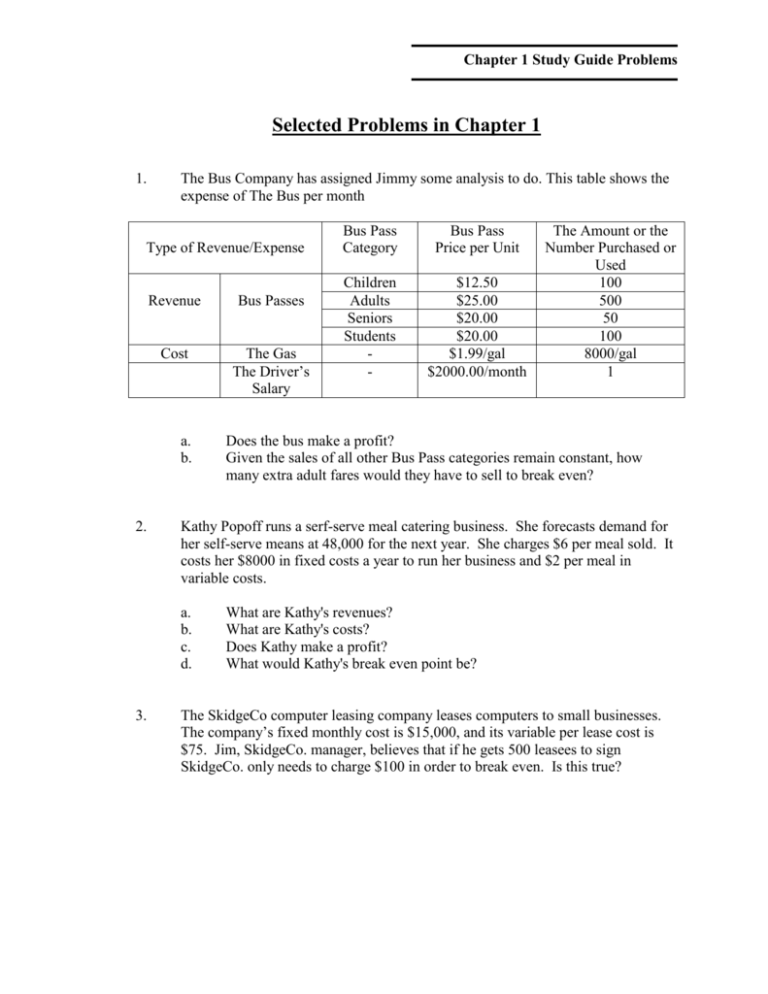
Chapter 1 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 1 1. The Bus Company has assigned Jimmy some analysis to do. This table shows the expense of The Bus per month Type of Revenue/Expense Revenue Bus Passes Cost The Gas The Driver’s Salary a. b. 2. Bus Pass Price per Unit Children Adults Seniors Students - $12.50 $25.00 $20.00 $20.00 $1.99/gal $2000.00/month The Amount or the Number Purchased or Used 100 500 50 100 8000/gal 1 Does the bus make a profit? Given the sales of all other Bus Pass categories remain constant, how many extra adult fares would they have to sell to break even? Kathy Popoff runs a serf-serve meal catering business. She forecasts demand for her self-serve means at 48,000 for the next year. She charges $6 per meal sold. It costs her $8000 in fixed costs a year to run her business and $2 per meal in variable costs. a. b. c. d. 3. Bus Pass Category What are Kathy's revenues? What are Kathy's costs? Does Kathy make a profit? What would Kathy's break even point be? The SkidgeCo computer leasing company leases computers to small businesses. The company’s fixed monthly cost is $15,000, and its variable per lease cost is $75. Jim, SkidgeCo. manager, believes that if he gets 500 leasees to sign SkidgeCo. only needs to charge $100 in order to break even. Is this true? Chapter 1 Study Guide Problems 4. Jennifer must hire temporary workers for the call center she manages each month. It costs her $2000 a worker in fixed costs to hire. She knows that each worker hired costs around $500 a month in variable costs. She estimates she will have on average 10 workers a month that must be hired for the next year. Each temp employee hired adds around $1500 in revenue per month. a. b. c. 5. What are Jennifer's first month's revenues from the temp employees? What are Jennifer's first month's average costs from the temp employees? Does Jennifer make a marginal profit in the first month from the temp employees? Referring back to Jennifer's temporary employee problem, answer the following questions a. b. c. What are Jennifer's second month's revenues from the temp employees? What are Jennifer's second month's average costs from the temp employees? Does Jennifer make a marginal profit in the second month from the temp employees? 6. A man owns a hot dog stand. He sells 700 hot dogs per month at a $3.25 each making the total revenue $2,275. Each hot dog, bun, and condiments costs the man $0.70 and he has fixed costs of $1,800, making his total costs $2,290. Therefore, he realizes a loss of $15 a month. Help him determine what his break even point is. 7. Referring back to the hot dog stand problem, answer the following questions a. b. c. d. At the current sales levels, what price does the man need to charge in order to break even? If the man reduces his variable costs from $0.70 to $0.60 and all else stays constant, what is his new break even point? If the man reduces his fixed costs from $1,700 and all else stays constant, what is his new break even point? Which of these two cost reductions lowers his break even point the most? Chapter 2 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 2 1. Create a simple spreadsheet to calculate break-even points. Create a key that includes fixed costs, variable costs, and price. Create and label a cell that contains the break-even calculation for any values of fixed costs, variable costs, or price. 2. Stevie knows the following information regarding sales at the convenience mart he works at (see Table 1.1). He notices that sales have appeared to rise over time. a. b. c. d. Fit a linear curve to the data using Excel or another spreadsheet application. Fit an exponential curve to the data. Which curve fits better? Use your answer from d to predict the sales for year 2002. Year 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 3. Table 1.1 Sales ($000) 10 12 16 22 30 40 Nora can earn 1% every six months (biannually) on any money she saves in her credit union account. She wants to know how much she will accumulate over five years if she starts with $1,000. Build a spreadsheet that displays this information. Use the simple equation “principle*(1+interest rate)” to calculate the yearly totals in Excel or another spreadsheet application. Does Excel or another spreadsheet application have a function that does this calculation automatically? If so use it and compare your answers. Chapter 2 Study Guide Problems 4. Copy the information from Table 1.2 into a spreadsheet. Multiple the two columns together using a spreadsheet function such as * or the product command in Excel. Table 1.2 Column A Column B 1 2 3 4 5 8 7 16 9 32 12 64 5. Graph the numbers presented in Table 1.2 and your answer to Problem 4. Compare the graphs. Are the graphs similar or different? Why would they be similar or different? Chapter 3 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 3 1. Given the following data set: 21, 45, 34, 25, 61, 45, 6, 12, 49, 58, 38, 41, 9 a. b. c. d. 2. Calculate the simple mean. Calculate the standard deviation. Calculate the median? Is the median equal to the mean? Why or why not? The following data was collected from a quantitative methods class at a major university regarding quiz #1 grades: % Grade 94 81 75 92 51 3. Letter Grade & Grade Points A = 4.0 B- = 2.7 C = 3.0 A- = 3.7 F = 0.0 % Grade 75 77 65 88 85 Letter Grade & Grade Points C = 2.0 C+ = 2.3 D = 1.0 B+ = 3.3 B = 3.0 Note: Standard grading scale is as follows - 94-100=A, 90-93 =A-, 87-89=B+, 84-86=B, 8083=B-, 77-79=C+, 74-76=C, 70-73=C-, 60-69=D, all else F a. b. c. d. e. f. What is the mean % grade for the class? What is the mean letter grade points for the class? What is the median % grade for the class? What is the median letter grade points for the class? Are the mean and median % grades equal? Why or why not? Are the mean and median letter grade points equal? Why or why not? The following data was collected regarding miles per gallon (MPG) for the YUGO1 new sports car. MPG 23 24 16 26 22 21 26 17 15 MPG 22 26 24 21 20 26 25 24 14 Chapter 3 Study Guide Problems a. b. c. 4. What is the mean of the data set for YUGO MPG? What is the standard deviation of the data set for YUGO MPG? Construct a histogram for the speed data set using 2 MPG as your class width starting with 14 as your lowest class. The following data was collected regarding scores out of 100 for a pre-test in Quantitative Methods Scores 99 88 10 a. b. 94 89 10 21 18 87 11 97 100 88 5 10 What is the mean of the data set for pre-test scores? What is the median of the data set for the scores on the pre-test? Is there a difference or similarity between the mean and the median? Explain the similarity or difference. What is the standard deviation of the data set for speed on H1? Construct a histogram for the pre-test score data set using 5 as your class width starting with 0 as your lowest class. Relate the standard deviation you calculated in part c to your histogram in part d. c. d. e. 5. 12 2 5 The following data was collected regarding scores out of 100 for a pre-test in Quantitative Methods Arrivals 95 102 99 88 100 a. b. c. Data Set #1 75 67 87 120 71 68 65 94 81 104 45 62 49 48 50 Data Set #2 25 17 37 70 21 18 15 54 31 54 What are the means for the two data sets? What are the medians for the two data sets? Is there a difference or similarity between the mean and the median? Explain the similarity or difference. What are the standard deviations for each of the data sets? Chapter 3 Study Guide Problems d. e. Construct a histogram for each data set using 5 as your class width starting with 60 as your lowest class for Data Set #1 and 10 for Data Set #2. Relate the standard deviation you calculated in part c to your histograms in part d. Chapter 3 Study Guide Problems 6. In a university, if a student is a graduate, then there is 60% chance that he/she is from Asia. And if a student is in undergraduate, then there is a 35% chance that he/she is from Asia. We also know that there 20% of students are in graduate school and 80% of students are in undergraduate school. What is the probability of that a student who is a graduate given he/she is from Asia? 7. For the safety and health reasons, Japan Airliner Company is considering moving all flights to nonsmoking flights. However, the Board of Directors is going to take a vote and most of them are smokers. The Board of Directors consists of 40 nonsmokers and 60 of smokers. 70% of the nonsmokers and 35% of the smokers favor the nonsmoking policy. a. b. c. 8. Construct a probability tree for this problem. Construct a probability table for this problem. Determine the probability given that a Board of Director member opposes the nonsmoking policy that that Board of Director member is a nonsmoker. When the service station owner gets tires delivered from two sources of plant A & B. There is a probability of 60% that the order consists of tires from plant A. According to the case, 20% of all tires produced at plant A are defective and only 10% of the tires from plant B are defective. a. b. c. d. Construct a probability tree for this problem. Construct a probability table for this problem. Find the probability that a tire comes from plant A and is defective. Given that you have a defective tire, what is the probability that it came from plant B? Chapter 3 Study Guide Problems 9. One hundred college males play varsity football for the University of Free Shoes. Thirty of the players are from local high schools and 70 went to high out of state. Those players from Florida high schools have a 25% chance of being arrested and charged with a crime while in college and those from out of state have a 15% chance of being arrested and charged while in college. a. b. c. d. Construct a probability tree for this problem. Construct a probability table for this problem. What is the probability that a randomly selected University of Free Shoes football player will arrested and charged while in college? Given a player was arrested and charged while in college, what is the probability that they came from a local high school? 10. The grade of midterm for class 6010 is normally distributed with a mean of 76 and a standard deviation of 9. What percentage of the students will have a grade of midterm of 80 or greater? 11. The cost per month of a renting a two-bedroom apartment in Honolulu is normally distributed with a mean of $800 and a standard deviation of $150. What is the probability of finding a two-bedroom apartment renting for $700 a month or less? 12. Masami is a student from Japan. Her monthly telephone bill is normally distributed with a mean of $67.69 and a standard deviation of $3. Masami is considering a calling plan that has a great benefit for a customer who often uses international call and whose phone bill is more than $75/month, however, the plan also requires an extra basic fee for the service. What is the probability that Masami's phone bill is going to be more than $75? 13. A spaceship is in orbit around the earth. The time it takes to complete one revolution around the earth is normally distributed with a mean of 15 hours and standard deviation of 7. What is the probability that the spaceship will complete one revolution around the earth in more than 20 hours? Chapter 3 Study Guide Problems 14. The table below gives the number of computer breakdowns experienced by MTC at HPU every week. It further shows the probability of each number of computer breakdowns. Determine the expected value of the number of computer breakdowns in given week. Table 14.1 Number of computer breakdowns (xi) 1 2 3 4 5 a. b. c. 15. Calculate the expected number of breakdowns per week. Find the standard deviation for the distribution. If the MTC has one tech on duty at all times and one tech can fix 2 computers a week, does the MTC need to staff more techs? Steven Li has a small software company. Every week the company acquires revenues, the following table contains the past business records. Compute the expected revenue for this week. Revenue $(xi) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 a. b. . Probability p(xi) 0.15 0.10 0.25 0.30 0.20 Probability p(xi) 0.30 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.10 Calculate the expected revenues. Find the standard deviation for the distribution. Chapter 4 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 4 1. Kelly is contemplating on returning to graduate school to earn her MBA. She knows from experience, that she can get a well paying job after undergraduate school. The probability of getting a job with a salary of $20,000/year is 75% and a job with a salary of $30,000/year is 25%. However, if she chooses to attend and finish graduate school, her salary would likely increase. The probability of getting a job with a salary of $40,000/year is 75% and getting a job with a salary of $50,000/year is 25%. Knowing that tuition cost and years spent on schooling is not a concern to Kelly, should Kelly find a job or return to graduate school? Find the best decision using the following: a. b. c. 2. Develop a payoff table for the above situation. Find the following: 1. Maximax 2. Maximin 3. Equal Likelihood 4. Minimax Regret Create a sensitivity graph comparing the different alternatives as the probability of getting a job changes. Steven is thinking about two investments. One is a grocery store, which can make $10,000 in good economic condition or $6,000 in bad economic condition. Another is a clothes store, which can make $15,000 in good economic condition or $1,000 in bad economic condition. The decision depends on the economic conditions. What is the probability of good and bad economic conditions that equate the decisions? a. b. c. Develop a payoff table for the above situation. Find the following: 1. Maximax 2. Maximin 3. Equal Likelihood 4. Minimax Regret Create a sensitivity graph comparing the different alternatives as the probability of economic conditions changes. Chapter 4 Study Guide Problems 3. JLM Enterprises is expanding into Hawaii. They must select one location where they can establish a store to sell their widgets. The table below lists the expected profits for stores in three locations and the expected probabilities of the two possible situations: high numbers of tourists visiting Hawaii or low numbers of tourists visiting Hawaii. Location Waikiki High (0.75) $150,000 Mililani $95,000 North Shore $120,000 Low (0.25) $60,000 $90,000 $20,000 Find the best decision using the following: a. b. c. 5. Develop a payoff table for the above situation. Find the following: 1. Maximax 2. Maximin 3. Equal Likelihood 4. Minimax Regret Create a sensitivity graph comparing the different alternatives as the probability of high numbers of tourists changes. A developer is planning to open a Sesame Street Toyshop at Waikiki, Ala Moana, or Aloha Tower. There is a 60% chance that Japanese tourists come to Hawaii will increase in the near future, a 25% chance that the number will remain the same, and a 15% chance that the number will decrease. The developer estimates the following profits will result from each decision given each set of economic conditions. Location Increase (0.60) Same (0.25) Waikiki $551,000 $428,000 Ala Moana $360,000 $320,000 Aloha Tower $400,000 $351,000 Decrease (0.15) $251,000 $301,000 $110,000 Find the best decision using the following: a. b. Develop a payoff table for the above situation. Find the following: 1. Maximax 2. Maximin 3. Equal Likelihood 4. Minimax Regret Chapter 4 Study Guide Problems c. 6. Can you create a sensitivity graph comparing the different alternatives as the probability of increase, decrease, and same changes? Why or why not? The Adams Company is deciding whether to bid a new contract to supply computers. Such bids are confidential and the lowest bid entered wins the contract. Adams estimates it costs $1,000 to prepare for the bid and $15,000 for the computers if it wins the contract. The table below shows the probabilities of Adams winning the bid given the bids they submit. Probability of winning 40% 30% 20% 10% Value of bid $25,000 $30,000 $35,000 $40,000 Set up a decision tree to find the bid that gives Adams the highest chances of winning. 7. Jessie and James are currently renting an apartment in Waikiki for $2000 per month. They are deciding on whether to buy a house now or to continue renting their apartment for a year and buy a house then. They recently saw an advertisement for a new development in Kailua stating the price to be $280,000. The current interest rate for a 20-year loan is 7% per annum. They believe there is a 40% chance that this interest rate will fall to 5% per annum in a years time. They also believe that the house they are interested in will still be available in a years time at a discounted price of $250,000. Jessie and James have to decide if they should buy the house now or in a year’s time. Interest payments will be made on the loan at the end of each year. a. b. Develop a decision tree that will aid Jessie and James in their home purchasing decision. Fold back the tree and find the expected value. Chapter 4 Study Guide Problems 8. Gerard is currently a director for an established consulting company making $150,000 in base pay p.a. He is also eligible for a bonus at the end of the year of 5% of all revenues if the company makes above $800,000 and 10% of all revenues if above $1.5 million. He is debating whether to leave his lucrative job to set up his own company. Although he has established client relationships, he believes only 65% of all existing clients will follow him if he sets up his own business. Based on previous years performance he believes there is a 25% chance the contracts would be worth $600,000; a 45% chance the contracts would be worth $1 million and a 30% chance the contracts will be worth $1.5 million. He estimates that the total cost of operating his own company would be $350,000. a. b. Develop a decision tree to help Gerard decide whether he should set up his own company. Fold back the tree and find the expected value 9. Valencia is deciding which hotel she will stay in on her next business trip to New York. What variables will affect her choice of hotel? Draw an influence diagram to assist Valencia in figuring out which hotel she will stay in. 10. Convert problem 1 into an influence diagram. 11. Sadie has completed her business plan for a Restaurant to be named “A Fine City” selling Singaporean cuisine. She wants to run a survey to assess the market viability for her restaurant. She estimates that if she runs the survey, there is a 50-50 chance the test will be successful. If she chose to open the restaurant with positive survey results, she expects there is a 60% chance she will make $50,000 a month, a 30% chance she will break even and a 10% chance she will lose $10,000 a month. She has been quoted by the market research company that the cost of a survey is $5000. However if she should skip the survey, the chances she will make $50,000 drops to 30%, with a 60% chance she will break-even and still a 10% chance she will lose $10,000 a month. Develop a decision tree to help Sadie decide what she should do. Chapter 5 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 5 1. In July 2000, a Polex watch dealer in Waikiki has to place his 2001 stock order for his watch boutique. The cost of each watch ordered in July 2000 is $1,000 and he can sell each Polex watch for $2,500 in 2001. The 2001 demand for Polex watches follows the probability distribution shown in Table 6.1. If the number of watches he orders exceeds demand, he can sell the excess back to the factory for $500 each. Table 5.1 2001 Demand for watches 200 250 300 350 400 a. b. Probability 0.3 0.15 0.15 0.2 0.2 Use simulation to determine the number of Polex watches the dealer should order. For your optimal order quantity, find a 95% confidence interval for expected profit. 2. Redo Question 1 with the following condition: If the number of watches he orders is not enough to meet demand, he will have to reorder his watches at a premium and the cost would be $2,000. 3. Redo Question 1 if Polex watch demand is believed to be normally distributed with a mean of 290 and a standard deviation of 48. 4. Adeline wants to analyze her spending habits and make better budgeting decisions. Adeline puts all her monthly savings in a bank, and her parents help her pay off her debts via her credit card on a monthly basis. Her parents believe that she is overspending and want to take away her credit card. Adeline’s income and expenses are not fixed the only fixed expense is her rent of $500. Adeline knows that the tips she receives as a waitress is most likely to be $900, but it varies from $700 to $1100. Her expenses can go up to $520 and can go as low as $280, but on average it is $400. Use simulation to give Adeline an indication of her current spending profile. Chapter 5 Study Guide Problems 5. Use a range of discrete expenses and simulate her budget. With the results provide her guidance on her spending habits so that she will ‘live within her means’. Adeline believes that if she can show her parents that she is able to build savings and only incur a debt 25% of the time, they would maintain her credit card. Chapter 6 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 6 1. Jeannie's brother tells her that it takes him the same time to get to work as it does her. Jeannie doesn't believe him and wants to test her brother's hypothesis. The data on the average time it takes Jeannie and her brother are listed below, all times are in minutes. Jeannie's Average Commute Time 10 12 9 7 15 11 7 9 6 8 5 15 8 3 a. b. Jeannie's Brother's Average Commute Time 10 18 15 12 17 11 14 11 12 14 6 12 9 5 Use a test of two means to assist Jeannie. What is your conclusion? Chapter 6 Study Guide Problems 2. Frank is testing how fast two computers are. His tech department told him that the two computers completed commands at the same rate. Frank though has done his own tests and found the following data, times are in seconds. Table 2.1 Computer A Computer B 100 210 120 180 90 150 70 212 110 117 111 211 170 114 125 150 130 130 144 140 288 299 100 150 210 200 220 250 a. b. Use a test of two means to assist Frank. What is your conclusion? 3. The following is Sabine’s weekly expenditure for the last six months: 67, 53, 89, 101, 85, 44, 56, 59, 63, 67, 91, 56, 66, 79, 90, 110, 47, 48, 49, 55, 50, 88, 54, 66 a. b. c. Develop forecasts for periods 1-24 using a trend line. What is the Mean Square Error for your model. Calculate an R statistic and interpret it. 4. Gryphon is a high-end hi-fi stereo shop and has increased its US client base over the last 8 months: 13, 25, 39, 42, 27, 32, 35, 50. a. b. Develop a trend equation and use it to forecast Gryphon’s client base next month. What is the MSE for your model. Chapter 6 Study Guide Problems 5. Tom and Sadie wanted to forecast the property values in the Bay Area given the value of similar homes in the last 12 months. Table 5.1 Month January February March April May June July August September October November December a. b. c. Property Values $133,890 $135,000 $135,790 $137,300 $138,130 $139,100 $139,900 $141,120 $141,890 $143,230 $144,000 $145,290 How much will properties be worth in July the following year? Calculate the MSE and MAD for your model. Calculate a R statistic and interpret it. 6. An InVogue writer is doing a study for her latest article to be titled “Brain or Brawn”. The writer found 10 female volunteers of the same age and above average looks to observe how many times a woman is invited on a date in a month. The different qualities tested are intelligence (GPA) and weight. The results of 10 women are as follows. Help InVogue understand if there is a relationship in this data using Multiple Linear Regression. Woman 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Date invitations 7 1 8 11 5 0 10 2 5 10 GPA 3.75 2.5 2.9 4.0 3.8 3.1 1.8 2.5 3.5 3.9 Weight 115 145 110 112 129.5 150 98 120 120 98 Chapter 7 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 7 1. The number of cans of soft drinks sold in a machine each week is recorded below. Develop forecasts for periods 1-11 using a three period moving average using the following soft drink sales numbers: 122, 85, 92, 98, 110, 108, 115, 102, 95, 98. 2. The number of cans of soft drinks sold in a machine each week is recorded below. Calculate the mean square error for a three period moving average using the following soft drink sales numbers: 122, 85, 92, 98, 110, 108, 115, 102, 95, 98. 3. Use a four period moving average to forecast attendance at baseball games for period 11. Historical records show: 2863, 2481, 3239, 3519, 3349, 3637, 3501, 3892, 3732, 3526. 4. Use a four period moving average to calculate mean square error for attendance at baseball games. Historical records show: 2863, 2481, 3239, 3519, 3349, 3637, 3501, 3892, 3732, 3526. 5. A hospital records the number of floral deliveries its patients receive each day. For a two week period, the records show: 25, 30, 32, 38, 42, 37, 39, 34, 31, 36, 33, 29, 31, 28. Use exponential smoothing with a smoothing constant of 0.4 to forecast the number of deliveries for periods 2-15. 6. A hospital records the number of floral deliveries its patients receive each day. For a two week period, the records show: 25, 30, 32, 38, 42, 37, 39, 34, 31, 36, 33, 29, 31, 28. Use exponential smoothing with a smoothing constant of 0.4 to calculate the mean square error. 7. The number of girls who attend a summer basketball camp has been recorded for the seven years the camp has been offered. Use exponential smoothing with a smoothing constant of 0.8 to forecast attendance for the eighth year. The number of girls attending camp are: 95, 110, 163, 147, 172, 175, 183. 8. The number of girls who attend a summer basketball camp has been recorded for the seven years the camp has been offered. Use exponential smoothing with a smoothing constant of 0.8 to calculate the mean square error. The number of girls attending camp is: 95, 110, 163, 147, 172, 175, 183. Chapter 7 Study Guide Problems 9. Quarterly billing for water usage is shown below. Seasonal Irregular Component Values Winter 0.971, 0.918. 0.908 Spring 0.840, 0.839, 0.834 Summer 1.096, 1.075, 1.109 Fall 1.133, 1.156, 1.141 What is the seasonal index for the Spring season? 10. Quarterly billing for water usage is shown below. Seasonal Irregular Component Values Winter 0.971, 0.918. 0.908 Spring 0.840, 0.839, 0.834 Summer 1.096, 1.075, 1.109 Fall 1.133, 1.156, 1.141 Seasonal Indexes 0.93 0.84 1.09 1.14 Given the above information and new Winter sales number of 100, what is the deseasonalized sales forecast? Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 8 1. A local company manufactures two lines of rocking chairs called type a and b. Each rocking chair requires hand-assembled materials, which totals the amount of 3,000 pounds of wood and 800 pounds of nails. Type A requires 500 pounds of wood and 40 pounds of nails. Further each A chair is worth $450. Type B requires 150 pounds of wood, 50 pounds of nails, and each B chair is worth $350. These chairs are handmade with a high quality. The company would like to maximize their profit, help them to find the best combination of rocking chairs. Lbs per Lbs per Chair A Chair B Availability Wood 500 150 3,000 Nails 40 50 800 Profit $450 $350 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 2. A small manufacturer, which produces 2 types of new perfumes labeled A and B in the table below, needs to decide how much of each perfume to produce to maximize profit. The profit earned from the sales of perfume A is $30, and the profit earned from the sales of perfume B is $50. The maximum Filling capacity is 180 and the maximum Boxing capacity is 75. The perfume must go through two steps: Filling and Boxing. Perfume A takes 30 units of Filling capacity per bottle of perfume processed, whereas Perfume B only takes 20 units of Filling capacity per bottle processed. Perfume A takes 15 units of Boxing capacity per bottle of perfume processed, whereas Perfume B only takes 5 units of Boxing capacity per bottle processed. The table below summarizes the findings. Process Units per Units per Perfume A Perfume B Maximum available capacity Filling 30 20 180 Boxing 15 5 75 Unit Profit $30 $50 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 3. Mark owns one-acre farmland in Waimanalo for the production of strawberries and tomatoes. To make sure the plants grow properly and that he will make a profit, Mark has invested in fertilizers. Help Mark find the most profitable combination of Strawberries and Tomatoes. Units per Units per Availability Strawberries Tomatoes Labor 10 6 50 Fertilizer 5 2 20 Profit $5 $3 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 4. The read-a-lot book company is facing difficulties in deciding on how to best manufacture their books for maximum profit. They produce two type of books, hardcover and paperback. It requires 10 pounds of corrugated paper to make one paperback and 240 pounds to produce one hard cover. The books also need a special solution for preserving the books. Hard cover books require 30 gallon and paperbacks use 20 gallons. Each hardcover brings in a profit of $35 dollars and each paperback brings in $19 dollars. We currently have on-hand 12,000 pounds of corrugated paper and 1,300 gallons of solution. We need you help to find the best production mix. Units per Units per Available Quantity Paperbacks Hardcover Corrugated Paper 10 240 12,000 Preservation Solution 30 20 1,300 Profit $19 $35 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 5. The LTD Inc is making two types of calculators, the TI-83 and HP-G49. The LTD Inc would like to figure out which combination would be the best solution for them to produce as they would like to see if it is possible to increase sales and profit. The maximum capacity is 500 units per month for plant A and 200 units for operation B. LTD Units per Units per Maximum TI-83 HP-G49 Capacity A 100 60 500 B 50 20 200 $259 $130 Profit Margin a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions?\ e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 6. The following report has been generated in excel using the solver. The company needs some help to have the output explained to them. a) What is the objective function optimal value? b) What are the final values of the decision variables at this optimal value? Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems c) Explain which constraints are binding and not binding and what does that mean? d) What is the maximum increase in the objective coefficient of the first variable that can occur without changing the optimal product mix? e) If you could increase the value of constraint #2 by on unit what would be the effect on the objective function? Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 7. Big Gaming is a company that wishes to produce two new video game consoles to place on the new market. They are a new company and wish to appeal to the public investors with the sales of their first two gaming consoles. They wish to maximize their profit. The two consoles both require a certain number of hours of Assembly and Packaging to ensure that the products are not damaged before reaching consumers. Since all the electronic parts are brought in from other companies. Big Gaming does not have to set aside time for electronics. Since they are a relatively new company their work hours is very limited. There is only a certain amount of hours that can be spent on each gaming system. Also, twice as many A consoles must be produced than B consoles. From the chart below, determine the best combination of the two products that will maximize Big Gaming Profits. Department Units per Units per Console A Console B Available hrs per week Assembly 2 4 200 Packaging 2 2/3 1 200 Profit per unit $210 $290 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 8. Whit’s Appliances produces two products. In order to produce, each product it requires a certain amount of production time from Employee A, grinding, and Employee B, polishing. The chart shows the amount of hours available per employee and the amount of time for production. Units per Units per Available Hrs X Y Employee A-Grinding 2 4 40 Employee B-Polishing 4 3 50 $200 $305 Profit a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 9. A new company is involved in the production of two secret items (S1 and S2) both of which are in liquid form. Each product requires hand mixing and automatic processing. The table below gives the number of hours required a gallon of each item. The company has 40 hours of processing time available in the next working week but only 35 hours of hand mixing time. In addition, the company has signed a contract stating that they must provide at least 5 gallons of S2 to the government. The company would like to maximize its profits. Units per Units per Available Hrs. Gal. S1 Gal. S2 Processing time 1 2 40 Hand mixing time 5 1 35 $150 $290 Profit a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically g) Find the optimal solution. Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 10. In producing their new golf clubs, Knight must utilize rubber for the grips and titanium for the golf heads. The driver set requires 12 inches of rubber material and 3 pounds of titanium. The iron set requires 10 inches of rubber and 2 pounds (lbs) of titanium. Knight must supply a prime customer with at least 10 iron sets. Their profit is $190 for the driver set and $155 for the iron set. What is our best way to maximize profits for the sets of clubs? Units per Units per Available Products Driver set Iron set Titanium 3 2 900 (lbs) Rubber 12 10 400 (inches) $190 $155 Profit a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically. g) Find the optimal solution. Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 11. A carpenter assembles tables and chair sets for a larger company. He can sell each table for a profit of $43 and each chair set for a profit of $20. Each table requires 2 hours of labor and each chair set requires 2 hours of labor. The carpenter also needs screws for producing each item. The carpenter also wishes to produce 1 1/2 times as many chair sets as tables as (he likes to make chair sets more than tables). The chart illustrates the different variables for production. The carpenter would like to know how many of each to assembly to maximize his profit. Units per Table Units per Available Chair Set Labor 20 8 512 Screws 16 24 1,000 Profit $43 $20 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically. g) Find the optimal solution. Chapter 8 Study Guide Problems 12. Firebridge’s new radial tires come in two styles. The Fire Hawk uses 20 pounds of rubber and 6 pounds of steel. The Tiger Claw requires 15 pounds of rubber and 1 pounds of steel. They currently have 3,000 pounds of rubber and 300 pounds of steel. Firebridge is obligated to provide these tires to the government in the following minimum quantities: at least 20 Tiger Claws and at least 10 Fire Hawks. However, the government stipulates that of all the tires provided at least twice as many must be Tiger Claws than Fire Hawks. In addition, Firebridge must provide at least 100 tires total. At a cost of $10 for the fire hawk and $10 for a tiger claw, what is the best solution to minimize cost? Units per Units per Available Fire Hawk Tiger Claw Products Steel 6 Rubber 20 Cost $10 1 300 15 3,000 $10 a) What are the decision variables? b) What is the objective function? c) What are the constraints? d) What are the non-negativity assumptions? e) Write the LP in modified standard form f) Solve the LP graphically. g) Find the optimal solution. Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 9 1. A project network is shown below. The time in weeks for each activity are listed in the table below. Use a forward and a backward pass to determine the critical path. A202 A22 A20 Start A23 A201 A203 A21 A24 A204 Activity A22 5 A23 4 A24 8 A20 4 A21 12 A203 10 A202 3 A204 2 Finish Time in Weeks Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems A201 5 Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems 2. A project network is shown below. The time in weeks for each activity are listed in the table below. Use a forward and a backward pass to determine the critical path. T202 T22 T203 Start T23 T201 T21 Finish T24 Activity Time in Weeks T22 8 T23 2 T24 5 T21 3 T203 7 T202 6 T204 12 T201 10 T204 Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems 3. A senior QM/MS case study project team has developed the following schedule of activities for their project, using their best estimate of completion times. Draw the project network and find the critical path. Can they complete the project in the 38 class days remaining until the end of the semester? Activity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Contact Client Write Proposal Obtain Approval Complete Computer Programming Complete Industry Literature Review Write Final Draft Complete Oral Report Time (in days) 4 2 Immediate Predecessors 1 3 2 9 3 5 - 6 4,5 5 4,5 Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems 4. One of the seniors hears that if they purchase an upgrade for their programming software package, they can complete the final draft in just 3 days and complete the programming in just 5 days. By saving this time the group can cash in on the "deal" offered by Binkos copies and save $10 on the printing for each day earlier the project is completed. One of the group members says they will save $70 total (7 days * $10 day). Is this correct? How does this reduction in time for writing the final draft effect the overall network? Activity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Contact Client Write Proposal Obtain Approval Complete Computer Programming Complete Industry Literature Review Write Final Draft Complete Oral Report Time (in days) 4 2 New Time (in days) 4 2 Immediate Predecessors 1 3 3 2 9 5 3 5 5 - 6 3 4,5 5 5 4,5 Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems 5. Given the following activity times and precedence, create a network and find the critical path. Activity Precedence Time in Weeks A23 --10 A22 A23 4 A20 A22 2 A202 A22 2 A24 A23 6 A21 A23, A20 3 A201 A202 4 A203 A21,A201 6 A205 A202 5 Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems A204 A24 4 Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems 6. A CD-ROM manufacturing guide gives the following numbered steps. 1. Print CD labels 2. Print CD case labels 3. Transfer files to CD software 4. Begin CD burning 5. Stuff CD case labels 6. Attach CD labels 7. Return finished CD into CD case Although the steps are numbered, they do not always reflect immediate precedence relationships. Develop a table that lists the immediate predecessors for each activity. 7. Given the following network with activities and times estimated in days. Activity Optimistic A B C D E F 2 1 6 5 3 8 Most Probable 5 3 7 12 4 9 Pessimistic Precedence 6 7 10 14 5 12 ----A,B C C D,E Create a network that follows the precedence set above. Chapter 9 Study Guide Problems 8. Given the following network with activities and times estimated in days. Activity Optimistic A B C D E F 2 1 6 5 3 8 Most Probable 5 3 7 12 4 9 Pessimistic Precedence 6 7 10 14 5 12 ----A,B C C D,E What are the estimated times and variances for the activities? 9. Given the following network with activities and times estimated in days. Activity Optimistic A B C D E F 2 1 6 5 3 8 Most Probable 5 3 7 12 4 9 Pessimistic Precedence 6 7 10 14 5 12 ----A,B C C D,E a. What are the critical path activities? b. What is the expected time to complete the project? Chapter 10 Study Guide Problems Selected Problems in Chapter 10 1. Using Excel’s macro-recorder, record the VB code for formatting a cell to Times New Roman font, bold type, and the color red. 2. In a new Excel spreadsheet, type 10 in row 1 column A cell location and 10 in row 2 column A cell location. Using Excel’s macro-recorder, record the VB code for adding the cells together in row 3 column A cell location. 3. In a new Excel spreadsheet, type 10 in row 1 column A cell location and 10 in row 1 column B cell location. Using Excel’s macro-recorder, record the VB code for multiplying the cells together in row 1 column C cell location. 4. Rewrite the code in Chapter 12 Figure 12.12 so as to multiply the two numbers together instead of adding them. 5. Create VB code that when given an ordered pair, (x1, x2) and (x3, x4), will construct a slope-intercept equation y = mx + b, find and list the ordered pairs, and then graph the equation on any form.