Course Syllabus - Magoffin County Schools
advertisement

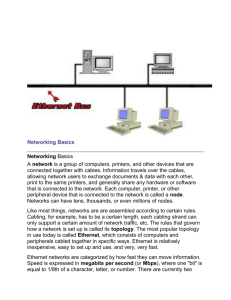
Course Syllabus Networking + Teacher: Location: Length: Prerequisite: Mrs. Traci Prater Magoffin County Career & Technical Center 1 year CompTIA A+: PC Maintenance & Repair Course Description: This course is designed to provide students with the skills necessary to perform tasks relating to networking. Curriculum: Will be accessed through an e-learning environment developed by Cisco Academy; CCNA Discovery: Networking for Home or Small Businesses. Course Objectives: Upon completion of the sequence of courses and based on the Program of Studies, students will be able to: 1. Analysis Design a. Gather data to identify customer requirements b. Identify, interpret and evaluate systems and network requirements based on OSI model c. Review network architecture, media (cabling), topology, interdependencies and constraints d. Research technical alternatives & analyze technical options participate in design reviews e. Prepare overall design and integration plan for new processes, protocols and equipment f. Recommend selection of architecture, topology, hardware & software 2. Configuration Implementation a. Plan & document system configuration including addressing b. Implement new system configuration c. Perform workstation configuration & software loading d. Perform network device configuration & software loading e. Support, track and document change implementation f. Assist in development of deployment plan and methods g. Develop and implement security procedures 3. System Testing a. Define and document test specifications b. Develop test plan and procedures c. Schedule and perform testing d. Document, interpret and report test results 4. Monitoring & Management a. Analyze system performance to baseline b. Monitor and report component security and connectivity problems c. Perform functional verifications and system audits d. Make recommendations for system optimization/improvement e. Generate and present reports 5. Administrative & Maintenance a. Set up & maintain user accounts b. Develop maintenance and upgrade plans c. Schedule and coordinate network maintenance d. Apply maintenance, upgrades and process changes e. Coordinate, communicate & document changes f. Perform system backups & restore data g. Manage inventory h. Document maintenance activities Course Approach: Instructional methods of this course include lecture, discussion, group activities, independent research, field research projects, examinations, and presentations and interaction of curriculum through an e-learning (web-based) environment. Course Content: Course Introduction – Focuses on the goals of the course and introduce students to an elearning environment. Chapter 1 – Personal Computer Hardware o Personal Computers & Applications How & Where Computers Are Used Local & Network Applications o Types of Computers Classes of Computers Servers, Desktops & Workstations Portable Devices o Binary Representation of Data Representing Information Digitally Measuring Data Storage Capacity Measuring Speed, Resolution & Frequency o Computer Components & Peripherals Computer Systems Motherboard, CPU, & RAM Adapter Cards Storage Devices Cases & Power Supplies o Computer System Components Safety & Best Practices Installing Components & Verifying Operation Installing Peripherals & Verifying Operation Chapter 2 – Operating Systems o Maintaining the Operating System Why & When to Apply Patches Applying Operating System Patches Application Patches & Updates Chapter 3 – Connecting to the Network o Introduction to Networking What is a Network? Benefits of Networking Basic Network Components Computer Roles in a Network Peer-to-Peer Networks Network Topologies o Principles of Communication Source, Channel, & Destination Rules of Communication Message Encoding Message Formatting Message Size Message timing Message Patterns Protocol Use in Communication o Communicating on a Local Wired Network Importance of Protocols Standardization of Protocols Physical Addressing Ethernet Communication Hierarchical Design of Ethernet Networks Logical Addressing Access & Distribution Layers and Devices o Building the Access Layer of an Ethernet Network Access Layer Function of Hubs Function of Switches Broadcast Messaging Switch Behavior MAC & IP Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) o Building the Distribution Layer of Networks Distribution Layer Function of Routers Default Gateway Tables Maintained by Router Local Area Network (LAN) Adding Hosts to Local & Remote Networks Learn to Use Packet Tracer o Plan & Connect a Local Network Plan & Document an Ethernet Prototypes Multi-Function Device Connecting the Linksys Router Sharing Resources Chapter 4 – OSI Transport Layer o Explain the need for the Transport layer. o Identify the role of the Transport layer as it provides the end-to-end transfer of data between applications. o Describe the role of two TCP/IP Transport layer protocols: TCP and UDP. o Explain the key functions of the Transport layer, including reliability, port addressing, and segmentation. o Explain how TCP and UDP each handle key functions. o Identify when it is appropriate to use TCP or UDP and provide examples of applications that use each protocol. Chapter 5 – OSI Network Layer o Identify the role of the Network layer as it describes communication from one end device to another end device. o Examine the most common Network layer protocol, Internet Protocol (IP), and its features for providing connectionless and best-effort service. o Understand the principles used to guide the division, or grouping, of devices into networks. o Understand the hierarchical addressing of devices and how this allows communication between networks. o Understand the fundamentals of routes, next-hop addresses, and packet forwarding to a destination network. Chapter 6 – Addressing the Network – Ipv4 o Explain the structure IP addressing and demonstrate the ability to convert between 8-bit binary and decimal numbers. o Given an IPv4 address, classify by type and describe how it is used in the network. o Explain how addresses are assigned to networks by ISPs and within networks by administrators. o Determine the network portion of the host address and explain the role of the subnet mask in dividing networks. o Given IPv4 addressing information and design criteria, calculate the appropriate addressing components. o Use common testing utilities to verify and test network connectivity and operational status of the IP protocol stack on a host. Chapter 7 – Data Link Layer o Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission. o Describe how the Data Link layer prepares data for transmission on network media. o Describe the different types of media access control methods. o Identify several common logical network topologies and describe how the logical topology determines the media access control method for that network. o Explain the purpose of encapsulating packets into frames to facilitate media access. o Describe the Layer 2 frame structure and identify generic fields. o Explain the role of key frame header and trailer fields, including addressing, QoS, type of protocol, and Frame Check Sequence. Chapter 8 – OSI Physical Layer o Explain the role of Physical layer protocols and services in supporting communication across data networks. o Describe the purpose of Physical layer signaling and encoding as they are used in networks. o Describe the role of signals used to represent bits as a frame is transported across the local media. o Identify the basic characteristics of copper, fiber, and wireless network media. o Describe common uses of copper, fiber, and wireless network media. Chapter 9 – Ethernet o Describe the evolution of Ethernet o Explain the fields of the Ethernet Frame o Describe the function and characteristics of the media access control method used by Ethernet protocol o Describe the Physical and Data Link layer features of Ethernet o Compare and contrast Ethernet hubs and switches o Explain the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Chapter 10 – Planning & Cabling Networks o Identify the basic network media required to make a LAN connection. o Identify the types of connections for intermediate and end device connections in a LAN. o Identify the pinout configurations for straight-through and crossover cables. o Identify the different cabling types, standards, and ports used for WAN connections. o Define the role of device management connections when using Cisco equipment. o Design an addressing scheme for an internetwork and assign ranges for hosts, network devices, and the router interface. o Compare and contrast the importance of network designs. Chapter 11 – Configuring and Testing Your Network o Define the role of the Internetwork Operating System (IOS). o Define the purpose of a configuration file. o Identify several classes of devices that have the IOS embedded. o Identify the factors contributing to the set of IOS commands available to a device. o Identify the IOS modes of operation. o Identify the basic IOS commands. o Compare and contrast the basic show commands. Grading Scale: A = B = C = D = F = 90-100% 80-89% 70-79% 60-69% 59% or less