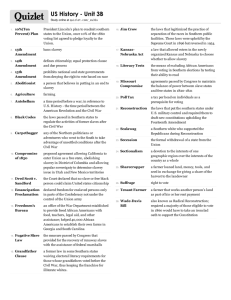
American History Regents Prep
advertisement
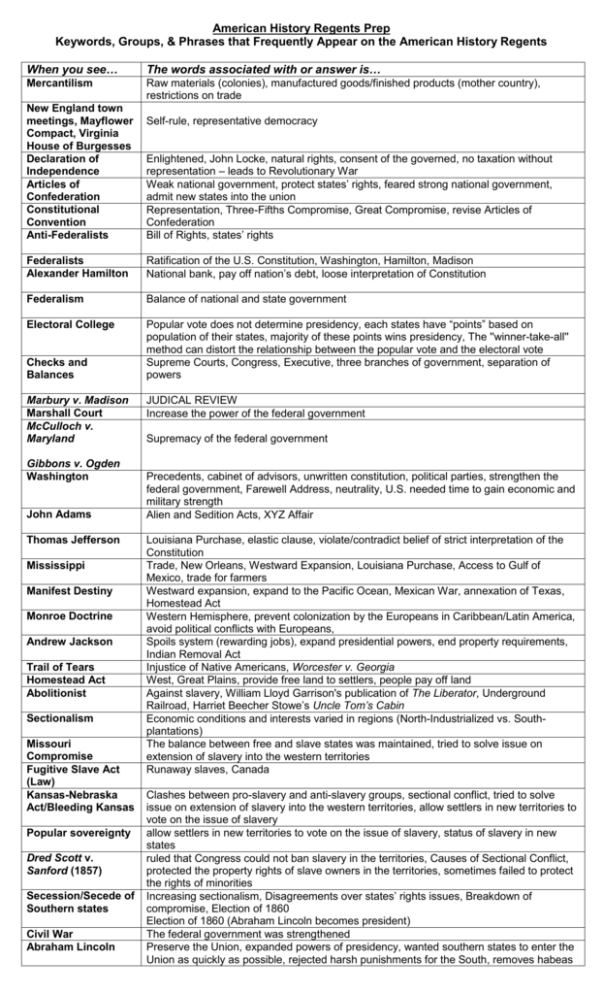
American History Regents Prep Keywords, Groups, & Phrases that Frequently Appear on the American History Regents When you see… The words associated with or answer is… Mercantilism Raw materials (colonies), manufactured goods/finished products (mother country), restrictions on trade New England town meetings, Mayflower Compact, Virginia House of Burgesses Declaration of Independence Articles of Confederation Constitutional Convention Anti-Federalists Self-rule, representative democracy Enlightened, John Locke, natural rights, consent of the governed, no taxation without representation – leads to Revolutionary War Weak national government, protect states’ rights, feared strong national government, admit new states into the union Representation, Three-Fifths Compromise, Great Compromise, revise Articles of Confederation Bill of Rights, states’ rights Federalists Alexander Hamilton Ratification of the U.S. Constitution, Washington, Hamilton, Madison National bank, pay off nation’s debt, loose interpretation of Constitution Federalism Balance of national and state government Electoral College Popular vote does not determine presidency, each states have “points” based on population of their states, majority of these points wins presidency, The ''winner-take-all'' method can distort the relationship between the popular vote and the electoral vote Supreme Courts, Congress, Executive, three branches of government, separation of powers Checks and Balances Marbury v. Madison Marshall Court McCulloch v. Maryland Gibbons v. Ogden Washington John Adams Thomas Jefferson Mississippi Manifest Destiny Monroe Doctrine Andrew Jackson Trail of Tears Homestead Act Abolitionist Sectionalism Missouri Compromise Fugitive Slave Act (Law) Kansas-Nebraska Act/Bleeding Kansas Popular sovereignty Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857) Secession/Secede of Southern states Civil War Abraham Lincoln JUDICAL REVIEW Increase the power of the federal government Supremacy of the federal government Precedents, cabinet of advisors, unwritten constitution, political parties, strengthen the federal government, Farewell Address, neutrality, U.S. needed time to gain economic and military strength Alien and Sedition Acts, XYZ Affair Louisiana Purchase, elastic clause, violate/contradict belief of strict interpretation of the Constitution Trade, New Orleans, Westward Expansion, Louisiana Purchase, Access to Gulf of Mexico, trade for farmers Westward expansion, expand to the Pacific Ocean, Mexican War, annexation of Texas, Homestead Act Western Hemisphere, prevent colonization by the Europeans in Caribbean/Latin America, avoid political conflicts with Europeans, Spoils system (rewarding jobs), expand presidential powers, end property requirements, Indian Removal Act Injustice of Native Americans, Worcester v. Georgia West, Great Plains, provide free land to settlers, people pay off land Against slavery, William Lloyd Garrison's publication of The Liberator, Underground Railroad, Harriet Beecher Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin Economic conditions and interests varied in regions (North-Industrialized vs. Southplantations) The balance between free and slave states was maintained, tried to solve issue on extension of slavery into the western territories Runaway slaves, Canada Clashes between pro-slavery and anti-slavery groups, sectional conflict, tried to solve issue on extension of slavery into the western territories, allow settlers in new territories to vote on the issue of slavery allow settlers in new territories to vote on the issue of slavery, status of slavery in new states ruled that Congress could not ban slavery in the territories, Causes of Sectional Conflict, protected the property rights of slave owners in the territories, sometimes failed to protect the rights of minorities Increasing sectionalism, Disagreements over states’ rights issues, Breakdown of compromise, Election of 1860 Election of 1860 (Abraham Lincoln becomes president) The federal government was strengthened Preserve the Union, expanded powers of presidency, wanted southern states to enter the Union as quickly as possible, rejected harsh punishments for the South, removes habeas Andrew Johnson corpus, Emancipation Proclamation (frees slaves) allow the Southern States to reenter the nation as quickly as possible, a power struggle with Congress over Reconstruction, impeachment increased individual rights for African Americans, Radical (Congressional) Reconstruction, legal and political rights to African Americans Former slaves earned a living, economically dependent deny equal rights to African Americans limits voting rights of African Americans 13th, 14th, 15th Amendments Sharecropping Black Codes Poll tax, grandfather clause, literacy tests, Jim Crow Laws Segregation of public facilities, limit effects of Radical Reconstruction, state and local governments to restrict the freedoms Plessy v. Ferguson Racial segregation, “separate but equal” based on race, separate public facilities were (1896) constitutional (allowed), failed to protect rights of minorities Booker T. African Americans should achieve equality by expanding their opportunities for vocational Washington education, difference than that of W.E.B. Dubois on how racial equality should be achieved W.E.B. Dubois African Americans should demand immediate participation in American society, Formal education (science and literature), difference than that of Booker T. Washington on how racial equality should be achieved Dawes Act (1887) Native Americans to give up their culture, assimilation of Native Americans Homestead Act Great Plains, settle West, decline the Plains Indians Industrialization Urbanization (cities), increased immigration, growth of the middle class, job opportunities, expansion of the railroads, Gospel of Wealth, Social Darwinism (justified big business and the rich) Monopolies/Trusts Limit competition, big businesses, furthered gap between rich and poor Yellow Journalism Start of Spanish American War, exaggerate events Laissez faire Government should not intervene (get involved) in business Progressives Reform, social and economic changes, limit power of big business, Government regulation (control) in business, Prohibition, Suffrage, income tax, direct election of senators, Theodore Roosevelt, Woodrow Wilson Women’s Suffrage Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Seneca Falls Convention, WWI working in (Voting Rights) war industries (factories), 19th Amendment Theodore Roosevelt Good and bad trusts, trustbuster limit power of monopolies, imperialism, Big Stick Policy, international police, Western Hemisphere, Latin America, Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, Panama Canal, Square Deal, Food and Drug Administration, Meat Inspection Act Anti-trust (Against Encouraged/increased competition, Sherman Anti-trust Act, Clayton Anti-trust Act, U.S. v. big businesses) and Standard Oil (breaks up Rockefeller’s oil monopoly) trust busting, protect small Business Regulation businesses and farmers (control) Labor Unions Collectively bargain, higher wages (pay), improved hours, American Federation of Labor (skilled workers), Knights of Labor, Haymarket Riots, Homestead Strike, Pullman Strike (government is anti-unions) Big Business John D. Rockefeller (Standard Oil, railroads), Andrew Carnegie (Carnegie Steel), J.P. Leaders Morgan, Cornelius Vanderbilt, robber barons (ruthless business tactics against competitors), captains of industry, philanthropic activities (did good things for society— Rockefeller Foundation, Carnegie Hall, J.P. Morgan Library) Muckrakers Make America aware of problems in society, expose the evils in American society, expose the abuses of the government and industry Poor, urban slums: Jacob Riis (How the Other Half Lives), Jane Addams (Hull House) Meatpacking Industry: Upton Sinclair (The Jungle) Political Corruption: Lincoln Steffens (The Shame of Cities) Standard Oil: Ida Tarbell (History of Standard Oil Company) Populism & Granger Farmers, social and political problems Movement Entrance to WWI Sinking of The Lusitania, submarine warfare, freedom of the seas, world safe for democracy, Zimmerman Telegram, Russian Revolution (1917) Schenck v. U.S. “clear and present danger”, don’t shout fire in a crowded theater, civil liberties limited for national security, limits freedom of speech Results of WWI Wilson’s Fourteen Points (avoid future wars/conflicts), Treaty of Versailles, League of Nations (U.S. Senate does not join—goes back to neutrality) Roaring 20s Consumerism (people spending $), Henry Ford’s assembly line, flappers, social and economic changes/improvements, Harlem Renaissance, Coolidge, Harding, & Hoover (President that practiced trickledown (tax cuts) economics—give money to rich to stimulate economy) Harlem Renaissance African American culture, music (jazz), literature (poetry—Langston Hughes) Intolerance—1920s Prohibition (18th Amendment), Temperance (no drinking) Movement, Red Scare & Palmer Raids (scared of Communist; arrest and deport), KKK revival, The Scopes Monkey Trial (science v. religion), anti-immigration (Sacco and Vanzetti trial) Causes of the Great Overproduction and under consumption, buying stocks on margin (borrowing), banks Depression giving too much credit, banks crash, Stock Market Crash (October 1929—all stocks lose value), Dust Bowl (Great Plains, severe drought and overproduction of farming) Life During the Hoovervilles/Hoover blankets (people blamed President Hoover for not helping them), Depression High unemployment, racism (African Americans can’t get jobs) Hoover FDR WWII Korematsu v. U.S. After WWII (1945): Early Cold War JFK Cold War Life During the 1950s Civil Rights Movement (late 1950s to 1960s) Rugged individualism (people should rely on themselves not the government) New Deal relief (CCC, WPA, PWA—give people jobs), recovery (AAA, NIRA—regulate prices), reform (Social Security Act, bank holiday, SEC—regulate stock market), pump and prime, Court Packing (tries to add supreme court justices when they declare part of New Deal unconstitutional (Butler v. U.S., and Schechter Poultry v. U.S.—Congress says “no”),12 years as president, greater involvement of federal government Lend Lease, cash and carry (U.S. helps England), Pearl Harbor attacked by Japanese (1941)—Congress declares war, D-Day, atomic bomb (Hiroshima and Nagasaki) – used to save American lives, women work in factories, Nuremberg Trials (crimes against humanity) Internment camps for Japanese in U.S., “clear and present danger” (JUST LIKE SCHENCK CASE), national security is more important than civil liberties Potsdam Conference sets up Cold War, Superpowers (U.S. and U.S.S.R), Containment (stop Communism from spreading-Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan ($ to Greece and Turkey), NATO (collective security), domino theory, Korean War (Congress did not officially declare war, outcome—Korean stays divided at 38th parallel), Berlin Blockade, Berlin Airlift Bay of Pigs Invasion (try to overthrow Fidel Castro), Cuban Missile Crisis, early involvement in Vietnam Baby boom, suburbs (automobile and Interstate Highway Act), social conformity, consumerism, technology, McCarthyism (similar to Palmer Raids—fear of Communism in the U.S. and spies), Cold War fear (bomb shelters, fear nuclear attack) Brown v. Board of Ed (1954)—(separate, but equal is INEQUAL, overturns Plessy v. Ferguson case), Rosa Parks (Montgomery Bus boycott) Martin Luther King (civil disobedience), Greensborough sit-ins, freedom riders, Selma March (Voting Rights), Million Man March, NAACP, Malcolm X, Black Panthers and Black Power Warren Court Achieved Civil Rights Act 1964 (racial and gender equality) and Voting Rights Act (1965) Rights of the accused, Miranda v. Arizona, Mapp v. Ohio, Escobedo v. Illinois, Gideon v. Wainright New Frontier (JFK) No religions in public schools—Engel v. Vitale Peace Corps, Space Program (fear of Sputnik satellite in Russia), tries to get economic and civil rights programs, but dies Great Society (LBJ) Vietnam War Richard Nixon Jimmy Carter Ronald Reagan George Bush Sr. Bill Clinton George W. Bush Financial Crisis Barack Obama Globalization and Global Issues War on Poverty (help poor people), Medicare and Medicaid, Civil Rights Programs, similar to FDR’s New Deal Program and Teddy Roosevelt’s Square Deal, greater involvement of federal government Domino Theory, Congress did not officially declare war (just like Korean War), Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, LBJ becomes an unpopular president, Vietnam War takes away money from Great Society, war protests (Vietnam veterans against the war), counter culture (hippies), draft, Kent State Massacre, Tinker v. Des Moines (freedom of speech/arm bands allowed in school), guerrilla warfare, Tet Offensive, riots at the Democratic National Convention Ends Vietnam War (vietnamization and Nixon Doctrine—peace with honor),détente (easing of tension--USSR), SALT Agreement, Visits China to ease tensions (Ping Pong Diplomacy), Watergate Scandal (Nixon resigns)--*President is not above the LAW* (U.S. v. Nixon, Nixon v. NY Times—limit executive power) Camp David Accords (Peace with Israel and Egypt), OPEC Crisis (gas), SALT Domestic: Reagonomics--Trickle down (tax cuts), supply side economic (like Hoover, give businesses money to stimulate economy) Foreign: Increase spending on military (federal deficit), puts pressure on Russia (tension increase again), Reagan Doctrine (support people who want to be free in Communist countries). ALL OF THIS LEADS TO FALL OF THE BERLIN WALL AND END OF COLD WAR! Persian Gulf War (protects Kuwait and prevent Iraq from getting oil), third party costs him election, New World Order NAFTA (free trade), Impeachment Trial (vote him not guilty), adopts Republican platforms (welfare reform), good economy=high approval ratings, policing overseas for human rights (Bosnia, Kosovo, Haiti) War on Terror as reaction to September 11, 2001—War in Afghanistan and war in Iraq, Patriot Acts (limits rights for national security), department of Homeland Security, trickle down (tax cuts)/supply side Stocks and banks crash (like Hoover’s Great Depression) Stimulus plan (like New Deal), federal deficit, government involvement, Osama Bin Laden killed Global warming, free trade, outsourcing (giving jobs overseas),