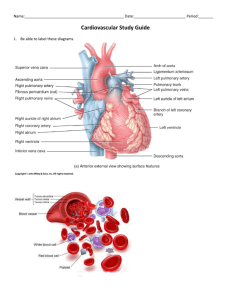
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
advertisement

MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PRACTICE TEST #3 (Ch 7,8,9) Select the best answer. 1. The term pruritus means: a. inflammation b. clumping c. extreme itching d. infection e. coagulation 2. The term for removal of a blood clot is: a. embolism b. catheterization c. thrombectomy d. valvotomy 3. The pulse point located on the side of your neck is called the: a. brachial artery b. radial artery c. temporal artery d. popliteal artery e. carotid artery 4. The coronary arteries supply blood to: a. the lungs b. the brain c. the kidneys d. the myocardium e. the liver 5. The suffix meaning formation or production is: a. -phoresis b. -poiesis c. -pathy d. -penia e. -pnea 6. The combining form for dust is: a. sphygm/o b. steth/o c. coni/o d. orth/o e. spir/o 7. The suffix –phoresis means: a. decrease b. formation c. attraction d. protein formation e. carrying, transmission 8. Drawing in or out by suction is called: a. transfusion b. transplantation c. aspiration d. contraction e. aeration 9. Suffocating chest pain associated with coronary artery disease is called: a. ischemia b. hyperalgia c. angina d. angiodynia e. pectorodynia 10. The term that means head cold or URI is: a. epistaxis b. coryza c. cephalodynia d. ascites e. empyema 11. The blood cell that carries hemoglobin is called a(an): a. leukocyte b. erythrocyte c. thrombocyte d. platelet 12. The exchange of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) in body tissue is called: a. coryza b. metabolism c. external respiration d. internal respiration e. catabolism 13. The valve between the right atrium and right ventricle is: a. mitral valve b. pulmonary valve c. aortic valve d. bicuspid valve e. tricuspid valve 14. The presence of pus and air in the pleural cavity is called: a. pyothorax b. pyemia c. pyopneumothorax d. empyosis 15. The abnormal accumulation of fluid in intercellular space of the body is called: a. uremia b. pallor c. osmosis d. edema 16. The type of blood cell responsible for immunity is a : a. neutrophil b. lymphocyte c. thrombocyte d. granulocyte e. erythrocyte 17. The term for absence of the sense of smell is: a. epistaxis b. siderosis c. anosmia d. ascites e. anoxia 18. The combining form for “windpipe” is: a. trache/o b. bronch/o c. pneumon/o d. steth/o e. thorac/o 19. Which of the following represents the sequence of structures through which blood travels through the heart? a. left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle b. right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle c. right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle d. right ventricle, left ventricle, right atrium, left atrium e. left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, right ventricle 20. The pacemaker of the heart is: a. the Bundle of His b. the Purkinje fibers c. the sinoatrial (SA) node d. the conduction myofibers e. the AV node 21. Antihypertensive medications are used to: a. lower blood pressure b. relieve angina pectoris c. lower cholesterol d. remove clots e. test cholesterol levels 22. Histamines and heparin are released by: a. monocytes b. erythrocytes c. macrophages d. neutrophils e. basophils 23. The liquid medium of the blood is: a. plasma b. myeloid tissue c. hemoglobin d. heparin e. fibrinogen 24. An excess of CO2 in the blood is: a. hypoxia b. hypoxemia c. hypercapnia d. hyperoxia e. hypocapnia 25. An inability of the valves to close properly: a. stenosis b. insufficiency c. commissurotomy d. varices e. coarctation 26. The sac containing the heart is called: a. the epicardium b. the cardiac membrane c. the pericardium d. the coronary membrane e. the epicoronary membrane 27. The structure that covers the larynx is the a. cilia b. uvula c. hypopharynx d. epiglottis e. laryngopharynx 28. A blood vessel that contains valves is: a. a capillary b. a vein c. the coronary artery d. the pulmonary artery e. the abdominal aorta 29. The destruction of old RBCs is a function of the: a. bone marrow b. spleen c. tonsils d. thymus e. lymph nodes 30. The primary function of platelets is: a. phagocytosis b. plasma formation c. cellular immunity d. antigen formation e. blood clotting 31. The combining form phren/o means: a. lung b. chest c. respiration d. diaphragm e. pleura 32. Narrowing of any vessel, especially the aorta: a. coarctation b. patency c. fibrillation d. ischemia e. thrombosis 33. The term epistaxis means: a. coughing b. abnormal respiratory sound c. shallow breathing d. nosebleed e. insufficient O2 34. The inability of alveoli to contract because of a loss of alveolar elasticity is characteristic of: a. emphysema b. empyema c. atelectasis d. bronchiectasis e. asthma 35. The suffix that means standing still is: a. -phoresis b. -stasis c. -poiesis d. -emia e. -blast 36. Destruction of a blood clot is called: a. thrombectomy b. hematocyte c. hemoblast d. thrombolysis 37. The cell that becomes infected by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a: a. memory T-cell b. helper T-cell c. plasma cell d. macrophage 38. Sickle cell anemia is classified as a/an: a. autoimmune disease b. bleeder’s disease c. hemoglobinopathy d. metabolic disorder e. coagulopathy 39. Heparin is a/an: a. anticoagulant b. antifibrinolytic c. antimicrobial d. thrombolytic e. antiviral 40. The space in the chest between the lungs is the: a. pleural cavity b. diaphragm c. alveolus d. sinus cavity e. mediastimum 41.. The prefix tachy- means: a. straight b. rapid c. many d. breathing e. slow 42. The presence of pus in the pleural cavity is: a. empyema b. pyosis c. pyemia d. pyothoracosis e. empyosis 43. A “bronchodilator” is used to: a. constrict the airways b. lubricate the airways c. open up the airways d. thicken the mucus in the airways 44. A term that means sudden and violent is: a. chronic b. expectoration c. paroxysm d. purulent e. coryza 45. Blockage of a vessel is called: a. occlusion b. infarction c. anastomosis d. angina 46. The inability of alveoli to contract because of their decreased elasticity is: a. emphysema b. empyema c. atelectasis d. bronchiectasis e. asthma 47. The passage of a balloon catheter through the lumen of an occluded coronary vessel in order to compress plaque against the arterial wall is: a. bypass surgery b. angioplasty c. cardiac catheterization d. cardioplasty e. arterioplasty 48. When blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg; 80 indicates: a. systolic pressure b. pulse rate c. respiration rate d. diastolic pressure e. hemoglobin count 49. The term “septal” refers to: a. the wall between the heart chambers b. the atrium c. the muscle of the heart d. the outer layer of the heart e. the inner layer of the heart 50. Vessels that carry blood away from the heart are: a. capillaries b. veins c. lymphatics d. venae cavae e. arteries 51. The term that means head cold is: a. epistaxis b. coryza c. cephalodynia d. ascites e. empyema 52. The suffix for voice is: a. –osmia b. –phasia c. –capnia d. –ptysis e. –phonia 53. An abnormal respiratory sound heard on auscultation is a/an: a. rale b. coryza c. anosmia d. paroxysm e. epistaxis 54. The term cardiomegaly means: a. spasm of the heart b. rupture of the heart c. disease of the heart d. enlargement of the heart e. narrowing of the heart 55. The expelling of carbon dioxide from the lungs is: a. external respiration b. inspiration c. cellular respiration d. internal respiration e. anabolism 56. The combining form ather/o means: a. artery b. vessel c. fatty plaque d. hardening e. vein 57. The suffix for voice is: a. -osmia b. -phasia c. -capnia d. -ptysis e. -phonia 58. The incision of a vein to withdraw blood is: a. venolysis b. venipuncture c. phlebolith d. phleboplasty e. phlebocentesis 59. Gently tapping the chest with fingers to determine the position, size, or consistency of underlying structure is called: a. palpation b. auscultation c. inspection d. provision e. percussion 60. Reye syndrome is associated with: a. antihistamines b. antitussives c. aspirin d. decongestants e. expectorants 61. The term “incompetent” means: a. valves of veins function properly b. valves of veins collect blood clots c. valves of veins deteriorate d. valves of veins do not prevent backflow of blood 62. Excess carbon dioxide in blood is: a. hypoxia b. hypoxemia c. hypercapnia d. hyperoxia e. hypocapnia 63. Olfactory means pertaining to: a. the sense of taste b. the process of respiration c. the sense of smell d. phonation e. the sense of touch 64. The classification of drugs that suppresses coughing by blocking the cough reflex in the medulla is: a. antihistamines b. bronchodilators c. antibitics d. antitussives e. decongestants 66. the visual examination of the heart, trachea, esophagus, bronchus, and thymus is: a. mediastinoscopy b. tracheoscopy c. thoroscopy d. pneumonoscopy e. bronchoscopy 67. The combining form vas/o means: a. fatty plaque b. blood flow c. plug d. vessels e. pressure 68. Oxygen deficiency in surrounding tissues is called: a. infarction b. malnutrition c. dystrophy d. anemia e. ischemia 69. A mass of undissolved matter circulating in blood or lymphatic channels until it becomes lodged in a vessel is a/an: a. clot b. embolus c. thrombus d. coagulant e. occlusion 70. The combining form for vein is: a. angi/o b. phleb/o c. sphygm/o d. thromb/o e. vas/o 71. The suffix –sphyxia means: a. pain b. narrowing c. breathe d. beat e. pulse 72. The pacemaker of the heart: a. bundle of His b. Purkinje fibers c. SA node d. conduction myofibers e. AV node 73. The highest O2 concentration is found in the blood of the: a. superior vena cava b. pulmonary artery c. right ventricle d. coronary arteries e. right atrium 74. A test used to assess the volume and airflow rate of the lungs is: a. bronchoscopy b. pulmonary function studies c. arterial blood gases d. sweat test 75. The suffix that means spitting is: a. -pnea b. -ptosis c. -capnia d. -osmia e. -ptysis 76. Suffocating chest pain associated with coronary artery disease is called: a. ischemia b. hyperalgia c. angina d. angiodynia e. pectorodynia 77. Oxygen deficiency in surrounding tissues is: a. infarction b. malnutrition c. dystrophy d. anemia e. ischemia 78. The combining form for incomplete is: a. anthrac/o b. atel/o c. steth/o d. orth/o e. alveol/o 79. The combining form for bone marrow is: a. my/o b. meil/o c. myel/o d. may/o e. mie/o 80. The medical term ”hardening of the arteries” is: a. scleroderma b. atherosclerosis c. hypertension d. arteriosclerosis e. phlebolith 81. An accumulation of fluid in a body cavity is called: a. ascites b. thoracentesis c. hemoptysis d. emphysema 82. The structures through which conduction impulses pass, in sequential order, that cause the heart to contract are: a. SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers b. AV node, SA node, AV bundle, Purkinje fibers c. AV bundle, AV node, SA node, Purkinje fibers d. Purkinje fibers, SA node, AV node, AV bundle 83. A soft blowing sound heard on auscultation that is associated with the movement of blood and/or valvular action is: a. Cheyne-Stokes syndrome b. regurgitation c. a bruit 84. Coronary arteries supply blood to the: a. lungs b. brain c. kidneys d. myocardium e. liver 85. The term for removal of a clot is: a. embolism b. catheterization c. thrombectomy d. valvotomy e. venisection 86. The term that describes “easier to breath when sitting up” is: a. orthopnea b. eupnea c. dyspnea d. bradypnea e. tachypnea 87. The combining form angi/o means: a. angina b. aorta c. pulse d. oxygen e. vessel 88. A traveling blood clot is called a(n): a. ischemia b. thrombosis c. embolism d. occlusion 89. The written record of the electrical activity of the heart is called: a. electrocardiography b. electromyopathy c. electrocardiology d. electrocardiogram e. electrocardiomegaly 90. The term “dysphagia” means: a. difficulty talking b. difficulty eating c. difficulty urinating d. difficulty hearing e. difficulty seeing 91. The sac containing the heart is the: a. epicardium b. cardiac membrane c. pericardium d. coronary membrane 92. The prefix peri- means: a. under b. behind c. around d. between e. above 93. The abbreviation CHF means: a. congestive heart flutter b. congenital heart flutter c. congenital heart failure d. congestive heart failure e. cardiac hypertensive failure 94. Another medical term for heart attack is: a. MVP b. MI c. CCU d. CHF e. CV 95. Doppler echocardiography assesses the type of blood passing through a. different areas of the heart. b. the mitral valve of the heart. c. all the valves of the heart. d. the chambers of the heart. 96. Diuretics are used to: a. expand blood vessels b. regulate the heartbeat c. lower cholesterol d. promote the excretion of urine e. relieve chest pain 97. Quivering or spontaneous muscle contractions, especially of the heart, is called: a. ischemia b. thrombosis c. embolism d. fibrillation e. patency 98. An ECG taken with a small portable recorder capable of storing information for up to 24hrs is a/an: a. stress test b. nuclear stress test c. electrocardiogram d. cardiac monitor test e. Holter monitor test 99. The term “prophylactic” mean: a. helper b. guarding c. destruction d. treatment e. open up 100. The abbreviation HTN means: a. hypertension b. hypotension 101. A condition where clots form due to inflammation of the linings in deep veins is called: a. b. c. d. atherosclerosis edema diaphoresis thrombophlebitis 102. The term “lumen” means: a. available b. opening c. tip d. vessel e. softening 103. The abbreviation DVT means: a. deep vein thrombosis b. deep valve threadiness c. determine vein thickness d. determine valve thrombosis e. deep valve thrombosis 104. The abbreviation MVP means: a. b. c. d. e. most valuable patient mitral valve progress mitral valve prolapse most valvular prolapse mean valvular progression 105. Excessive fluid in the lungs that induces cough and dyspnea; common in left heart failure: a. pulmonary edema b. pulmonary embolus c. pulmonary thrombosis d. pneumoconiosis e. pneumonitis 106. A heart valve with three cusps is called: a. b. c. d. 107. bicuspid valve pulmonary valve tricuspid valve mitral valve The combing form for voice box is: a. b. c. d. e. laryng/o pharyng/o cheil/o pleur/o pulmon/o 108. The instrument used to determine hypertension is a/an: a. electrocardiograph b. sphymomanometer c. sphygmomanometer d. electrocardiogram e. spirometer 109. The pulse point located on the inner aspect of your arm in the antecubital space is called the: a. radial artery b. brachial artery c. carotid artery d. femoral artery e. apical artery