optics_unit_review 2D - East Northumberland Secondary School
advertisement

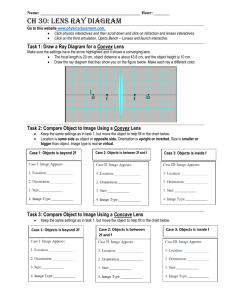
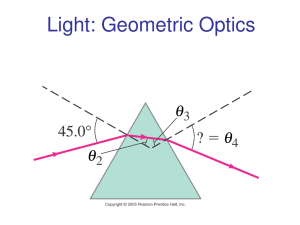
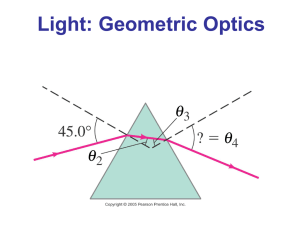
SNC 2D LIGHT AND GEOMETRIC OPTICS UNIT REVIEW 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. What is light? Why is light unique? What is visible light? List the 7 distinct colours identified as the visible spectrum in order of increasing energy. List them in order of increasing wavelength. Using the electromagnetic spectrum, name the 7 different types of magnetic waves. Provide at least 1 example of how each is important. What is the difference between incandescence and luminescence? Provide examples of each. Explain and give examples of the different methods of producing light: phosphorescence, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, triboluminescence. Why are objects transparent, translucent and opaque? Give examples of objects that are each. Compare and contrast incandescent, compact fluorescent, and LED (light-emitting diode) light sources. Describe the properties of LASERS. Using a diagram, label the angle of incidence, incident ray, normal, reflected ray, angle of reflection, and plane mirror. What are the laws of reflection? If you were wearing a t-shirt with the words SCIENCE on it, what would it look like to you in a mirror? What is the difference between specular and diffuse reflection? Name the 4 characteristics we use to describe images. What is the difference between a real and virtual image? Complete the ray diagrams on page 495, Apply and Extend, section j, a through g. Label the centre of curvature, principal axis, vertex and focus for curved mirrors on a ray diagram. To locate the image in a converging (concave) mirror, what 4 rules can be used when drawing ray diagrams? To locate the image in a diverging (convex) mirror, what 3 rules can be used when drawing ray diagrams? Do questions 8 a-c on page 501. Describe the SALT characteristics of each image. Define refraction. Why does refraction occur? Light bends _____________ the normal when the speed of light in the 2nd medium is less than the speed of light in the 1st medium. Light bends _____________ the normal when the speed of light in the 2 nd medium is more than the speed of light in the 1st medium. Define index of refraction and name the variables. What is the unit? Define critical angle and total internal reflection. Describe an example of something where humans have taken advantage of total internal reflection. When does partial refraction occur? Give a practical example. The speed of light in carbon disulfide is 1.84 x 108 m/s. Calculate the index of refraction for carbon disulfide. What is fibre optics? What are they used for? Describe how refraction is happening in the phenomena of: apparent depth, mirage, shimmering, and a rainbow. What is a lens? Describe the difference between a converging and diverging lens. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Label the optical centre, principal focus, secondary principal focus, and principal axis for lenses on ray diagrams. To locate the image in a converging lens, what 3 rules can be used when drawing ray diagrams? To locate the image in a diverging lens, what 3 rules can be used when drawing ray diagrams? Do questions 2 and 3 on p. 561. Describe the SALT characteristics of each image. Do questions 1, 2 and 5 on p. 566. Describe applications where humans have taken advantage of lenses and their properties. Trace the path that light would follow as it enters your eye. What parts does it touch? What is the difference between hyperopia and myopia? What is presbyopia? Note that there is a Unit Review section on page 590 to 597. The following information will be provided in writing your test. n=c v Table 1 – The Index of Refraction For Various Media Medium Index of refraction (n) air/vacuum 1.00 ice 1.31 pure water 1.33 ethyl alcohol 1.36 quartz 1.46 soybean oil 1.47 olive oil 1.48 acrylic 1.49 glass 1.52 zircon 1.92 diamond 2.42 1+1=1 do di f M = hi = - di ho do Table 2 – Sign Conventions for Lenses Variable Positive Negative (object distance) do (image distance) di (height of object) ho always real image when measured upward when measured upward converging lens upright image never virtual image when measured downward when measured downward diverging lens inverted image (height of image) hi (focal length) f (magnification) M Study hard and good luck!