ACTIVITY AND HALF-LIFE
advertisement
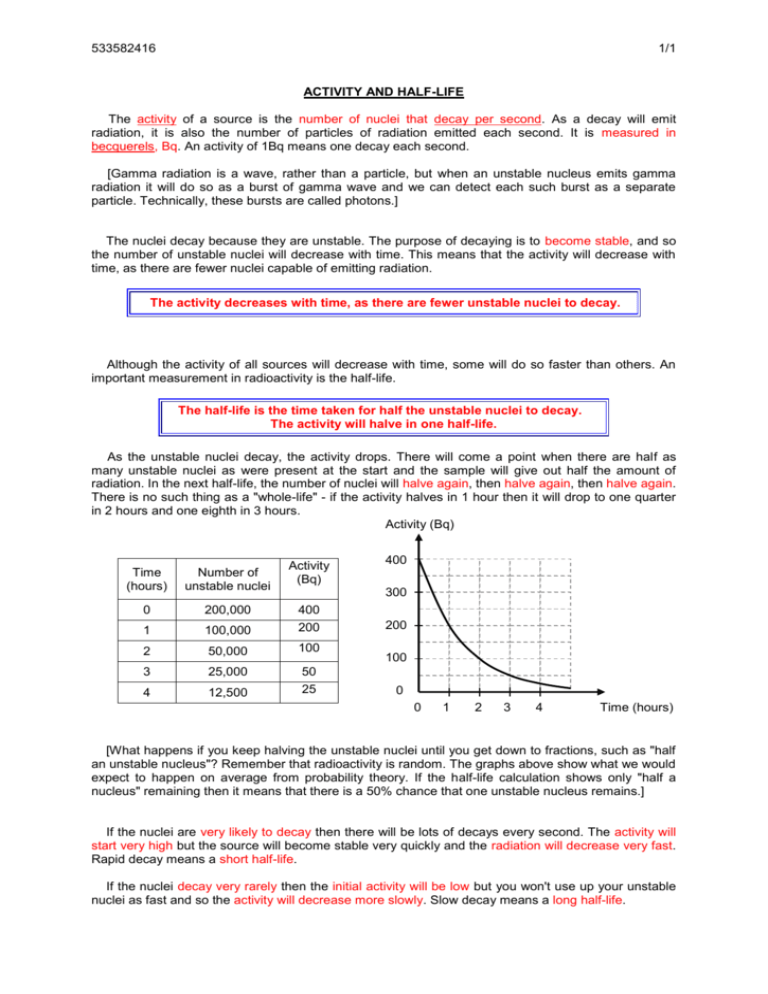
533582416 1/1 ACTIVITY AND HALF-LIFE The activity of a source is the number of nuclei that decay per second. As a decay will emit radiation, it is also the number of particles of radiation emitted each second. It is measured in becquerels, Bq. An activity of 1Bq means one decay each second. [Gamma radiation is a wave, rather than a particle, but when an unstable nucleus emits gamma radiation it will do so as a burst of gamma wave and we can detect each such burst as a separate particle. Technically, these bursts are called photons.] The nuclei decay because they are unstable. The purpose of decaying is to become stable, and so the number of unstable nuclei will decrease with time. This means that the activity will decrease with time, as there are fewer nuclei capable of emitting radiation. The activity decreases with time, as there are fewer unstable nuclei to decay. Although the activity of all sources will decrease with time, some will do so faster than others. An important measurement in radioactivity is the half-life. The half-life is the time taken for half the unstable nuclei to decay. The activity will halve in one half-life. s As the unstable nuclei decay, the activity drops. There will come a point when there are half as many unstable nuclei as were present at the start and the sample will give out half the amount of radiation. In the next half-life, the number of nuclei will halve again, then halve again, then halve again. There is no such thing as a "whole-life" - if the activity halves in 1 hour then it will drop to one quarter in 2 hours and one eighth in 3 hours. Activity (Bq) Activity (Bq) Time (hours) Number of unstable nuclei 0 200,000 1 100,000 400 200 2 50,000 100 3 25,000 4 12,500 50 25 400 300 200 100 0 0 1 2 3 4 Time (hours) [What happens if you keep halving the unstable nuclei until you get down to fractions, such as "half an unstable nucleus"? Remember that radioactivity is random. The graphs above show what we would expect to happen on average from probability theory. If the half-life calculation shows only "half a nucleus" remaining then it means that there is a 50% chance that one unstable nucleus remains.] If the nuclei are very likely to decay then there will be lots of decays every second. The activity will start very high but the source will become stable very quickly and the radiation will decrease very fast. Rapid decay means a short half-life. If the nuclei decay very rarely then the initial activity will be low but you won't use up your unstable nuclei as fast and so the activity will decrease more slowly. Slow decay means a long half-life.