Chapter Three (Part 2): Tissues Notes
advertisement

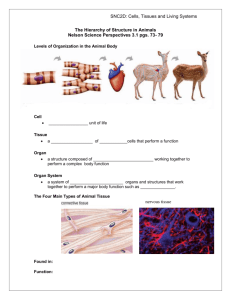
Name: ____________________________________________ PD ________ Chapter Three: Tissues Notes I. Cells & Tissues Cells are specialized for _________________________________ Tissues - ___________________________________________________________ o Four primary types of Tissues 1. Epithelium tissue - ______________________ 3. Nervous tissue – ______________________ 2. Connective tissue - ______________________ 4. Muscle tissue – _______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Overview of Tissues & Functions 1. Epithelial Tissues Functions 3. Muscular Tissues Functions Covers ___________________ ____________________ passages •Specialized for __________________ Forms _____________ •Skeletal muscle, _______ muscle, and Provide ______________ protection _________________________ organs Control _____________________ Provide _____________________ Produce specialized ______________ 4. Neural Tissues Functions 2. Connective Tissues Functions • • • • •Carries _______________________ from 1 part of __________________ spaces the _________ to another Supports other tissues _________________ materials Stores _____________ ________________________________________________________________________ II. EPITHELIAL TISSUE Found in Different Areas: *Body ___________ *Body ___________ *__________ Tissue Functions: * * * * Characteristics: *Cells fit _________________ *_____________ (have no blood supply) *Regenerate easily if ____________ Classification of Epithelium I. Number of cell layers II. Shape of cells 1. ___________– One Layer 1. Squamous – ________________ 2. ___________– More Than One Layer 2. Cuboidal – _________________ 3. Columnar – _________________ Simple Epithelium Tissue • __________ layer of cells: Usually forms ___________ or lines ____________ – Examples: Simple Squamous, _________________, Simple columnar Glandular Epithelium Tissue • Gland – _________________________________________________ • Two major Gland Types – 1. _____________ gland - 2. _________________ gland • Ductless * Empty through ducts to the _______ surface • Secretions are hormones * Include: ________________________ Into interstitial fluid III. CONNECTIVE TISSUE Found: * ____________ in the body Includes: * The _____ abundant and widely distributed tissues Functions o Binds __________________ together * _________________ the body o Provides ___________________ * Store ______________ (fat) o Have _______________ with environment * Provide _______________ (bone) o Connect epithelium to the _________________ o ___________________ materials (blood) Provides ______________ Characteristics of Connective Tissues * Variations in blood supply: - Some tissue types are well __________________________ - Some have _________________ or are avascular * Extracellular matrix - The extracellular components of _____________________ (fibers & ground substance) - __________________ of cell volume - determines specialized ___________________ - Non-living material that __________________________________ - Two Main Elements: 1. _________________ - Mostly water along with adhesion proteins and polysaccharide molecules 2. _________________ - Produced by the cells - Three types 1. _________________ fibers 2. Elastic ______________ 3. _________________ fibers * Fibroblast: The ____________________ cell type: -secrete proteins and hyaluronan (cellular cement) Classification of Connective Tissues: 1. Connective __________ Proper: 2. Fluid _______________ Tissues: 3. ____________ Connective Tissues: __________ and Protect _____________ Structural strength Fibers in Connective Tissue Proper •Collagen fibers: –_________________ fibers in CTP –long, straight, and ______________ –strong and ________________ –resists force in ______ direction –e.g., tendons and ______________ •Elastic fibers: Reticular fibers: - network of ____________________ fibers - ____________ and flexible - resists force in ____________ directions - stabilizes functional _________ and structures - e.g., ____________ around organs –contain _____________ –_______________ and wavy –return to _____________ length after stretching –e.g., ________________________ of vertebrae * Connective Tissue Types (4) BONE TYPE: (Osseous Tissue) * For weight ____________ * Made up of bone cells in cavities * Hard Matrix of Traits _____________________ _____ * Large # of collagen fibers * Resists Shattering (flexible) *___________ Functions ____________ ___________ Cartilage * Gel-type substance * For ________ absorption & ____________ Dense Connective Tissue * Main matrix element is collagen fibers *__________________ ________ surrounded by fluid matrix * Cells are ____________ *Fibers are ____________ during clotting * Elastic * Supports _______ _________ and body weight *Provides __________ Blood Tendon: attach __________________ ______ Ligament: attach __________________ ______ *Functions as the transport vehicle _______ ______________ Bones: Bone Cells: Osetocytes Bone Surface: Periosteum: - arranged around central canals within matrix - covers bone surfaces - small __________ through matrix (canaliculi) access blood supply IV. MUSCLE TISSUE Function: Produce __________________________________________________________________ Type of Muscle Tissue Characteristics ________ body muscles responsible for movement Can be __________________________ Usually called Muscle Fibers Cells attach to ____________________tissue These cells do not divide Cells are ___________________ Cells have ____________________ nucleus Found only in ______________________ Function is ____________________ (involuntary) Cells are ________________________ __________ nucleus per cell _________________ muscle Surrounds _________ organs Attached to _________________________ cells No visible striations & __________ nucleus per cell 1. ___________ Muscle 2. ___________ Muscle Cells are called cardiocytes 3. ___________ Muscle These cells can divide and regenerate! V. NERVOUS TISSUE Functions: to send __________________________________ - Rapidly senses ________________________________ environment a. _____________ - ability to respond to stimuli b. Conductivity – ability to ______________________________ Location: Neural tissue is concentrated in the ________________________ system: Brain and _________________ Cord _______________________________________________________________________________________ VI. Tissues Injury and Repair Cells restore homeostasis with 2 processes: 1. Inflammation (1): the tissue’s ________ response to ______________ –Signs: Swelling, ___________, heat, __________ –Triggered by: Inflammation or _________________ –Chemicals released –White blood cells __________________ 1. Regeneration (2) begins when the injury or infection is cleaned up, or ______________ •_______________ move into necrotic area: –lay down ___________________ fibers –to ____________________ together (____________ tissue) •New cells _________________ to area Tissue Repair (wound healing): Determination of method - Type of ______________________________ - Severity of the injury a. Regeneration - __________________________________ b. _________________- Repair by dense fibrous connective tissue (scar tissue) A. Regeneration of Tissues a. Tissues that regenerate easily i. __________________________________ ii. Fibrous connective tissue and bone b. Tissues that regenerate ____________ i. Skeletal muscle c. Tissues that are replaced largely with ________ tissue (*Do not regenerate) i. ____________________ ii. ____________________ within the brain and spinal cord Developmental Aspects of Tissue With old age there is a _________________ in mass and viability in most tissues Speed & _________________ of tissue repair ______________________, due to: slower rate of ________________________________ (metabolism) ____________________ alterations reduced ______________________________ Chemical and structural tissue changes: thinning _______________ and __________________ tissues ________________ bruising and ________ brittleness joint _________ and ________________ bones cardiovascular ____________ ____________ deterioration Ch 3 Tissues Review Questions: Directions: Use your notes and the book to answer the following questions. I. TISSUES INTRODUCTION QUESTIONS 1. Define Tissues. 2. List the four major types of tissues along with two functions. 3. Which type of tissue is the most widely distributed in the body? II. EPITHELIAL TISSUE QUESTIONS 4. Describe the general characteristics of epithelial tissues. 5. List the most important functions of epithelial tissues, and give examples of each. (Use your book). 6. How are epithelial tissues classified? 7. How do the endocrine and exocrine glands differ in structure and function? III. CONNECTIVE TISSUE QUESTIONS 8. What are the general structural characteristics of connective tissues? 9. List four functions of connective tissues. 10. Name which connective tissues have (a) a stony hard matrix and (b) a less hard, more flexible matrix. 11. Describe the characteristics and function of a fibroblast. 12. What is the classification of connective tissues & their basic functions? 13. Which type of tissue is composed of tendons and ligaments? What is the difference between Tendons and Ligaments? 14. What are the two main elements in the Extracellular matrix? 15. a) What are bone cells called? b) What is the bone surface called? IV. MUSCLE TISSUE QUESTIONS 16. What is the function of muscle tissue? 17. Name the three types of muscle tissue, and tell where each would be found in the body. 18. What does it mean, “smooth muscles are involuntary in action”? (Page 97) 19. Which muscle type is be voluntary in action? V. NERVOUS TISSUE QUESTIONS 20. What is the difference between irritability and conductivity? 21. Describe the function of the nervous tissues. 22. Where are neurons most heavily located? Why? VI. TISSUE REPAIR (WOUND HEALING) 23. Describe the process of wound healing-- Inflammation? 24. Describe the process of wound healing-- Regeneration? 25. What is the difference between regeneration and fibrosis? 26. What types of regeneration occurs easily and which occurs poorly? 27. Which type of tissue is replaced with scar tissue?