WorkSheet - MeasuringStars_HRDiag KEY
advertisement

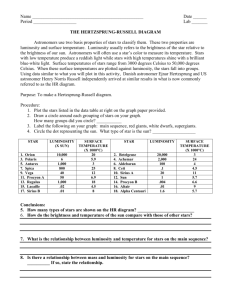
Measuring the Stars and the HR Diagram 19 points Chapter 25 Please use a separate sheet of paper to do the following assignment. A) Define the following terms using your book: 1) Fusion_At high temperatures, hydrogen nuclei collide, bond, release energy and create a new element, Helium. 2) Apparent magnitude_ How bright a star looks in the sky. 3) Absolute magnitude :a star’s actual brightness- the amount of light it gives off. 4) Luminosity—How bright a star is 5) Spectral Class—The temperature of a star. 6) Astronomical Unit (AU) a unit om measure is space = 93 million miles and is the distance from earth to sun. 7) Light Year (ly)- the distance light travels in one year= 9.5 trillion km or 5.9 trillion miles. Part 1: 7 points Part 2: 12 points B) Answer the following questions using full sentences using the book and your notes: 1) What is the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? This diagram shows the life cycle of stars using a graph with spectral class (temperature) along the X axis and brightness (luminosity) along the Y axis. It shows stars along a main sequence and some stars off of a main sequence. Size of stars indicates relative mass on the diagram. 2) What are the specific properties of stars that are depicted on the HertzsprungRussell diagram? The properties depicted on the the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram are luminosity, spectral class, relative mass, relative color and relative size. 3) On the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, which way does mass decrease? Along the main sequence, mass decreases to the lower right part of the diagram. The smallest stars, white dwarfs, appear on the lower left portion of the diagram. 4) On the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram which way does Luminosity increase? On the H-R diagram, luminosity increase in an upward direction or towards the top of the graph. 5) What are the general properties of stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram in the following locations on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? Use complete senteces!!!! a. Upper Left: Stars in the upper left portion of the H/R diagram will be hot and bright. b. Upper Right Stars in the upper right portion of the H/R diagram will be cool and bright. c. Lower Left Stars in the lower left portion of the H/R diagram will be hot but not so bright. d. Lower Right Stars in the lower right portion of the H/R diagram will be cool and not so bright. 6) Describe the life cycle of a low-mass star from start to finish. A low mass star like the sun is born from a nebula of gases that contracts due to the shock wave from a nearby dying star. As the nebula contracts, fusion begins at the core when temperature reaches 15 mill. Degrees. Throughout its life, the star fuses hydrogen into helium. When hydrogen runs out, the core of the star will begin to collapse on itself while throwing of its outer, atmospheric layers. The appearance of the star in this state is called a planetary nebula—it looks larger –some call it a red giant. After the outer layers are completely thrown off, the hot small core of the star is left. This hot, small, not so bright star is known as a white dwarf. Extra Credit: 7) If the speed of light is 3.156 * 108 m/s, how many meters are there in a light year? How many miles? (1 in. = 2.54 cm) Show all your math from start to finish including all units!