US History Midterm
advertisement
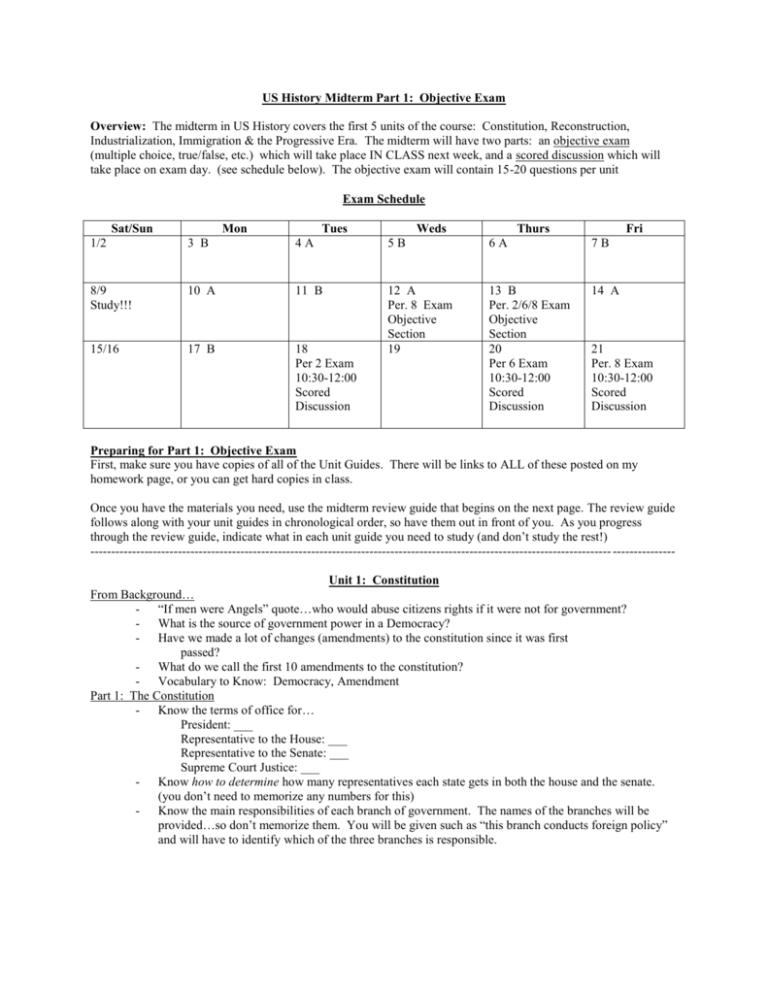
US History Midterm Part 1: Objective Exam Overview: The midterm in US History covers the first 5 units of the course: Constitution, Reconstruction, Industrialization, Immigration & the Progressive Era. The midterm will have two parts: an objective exam (multiple choice, true/false, etc.) which will take place IN CLASS next week, and a scored discussion which will take place on exam day. (see schedule below). The objective exam will contain 15-20 questions per unit Exam Schedule Sat/Sun Mon Tues Weds Thurs Fri 1/2 3 B 4A 5B 6A 7B 8/9 Study!!! 10 A 11 B 17 B 18 Per 2 Exam 10:30-12:00 Scored Discussion 13 B Per. 2/6/8 Exam Objective Section 20 Per 6 Exam 10:30-12:00 Scored Discussion 14 A 15/16 12 A Per. 8 Exam Objective Section 19 21 Per. 8 Exam 10:30-12:00 Scored Discussion Preparing for Part 1: Objective Exam First, make sure you have copies of all of the Unit Guides. There will be links to ALL of these posted on my homework page, or you can get hard copies in class. Once you have the materials you need, use the midterm review guide that begins on the next page. The review guide follows along with your unit guides in chronological order, so have them out in front of you. As you progress through the review guide, indicate what in each unit guide you need to study (and don’t study the rest!) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------------Unit 1: Constitution From Background… - “If men were Angels” quote…who would abuse citizens rights if it were not for government? - What is the source of government power in a Democracy? - Have we made a lot of changes (amendments) to the constitution since it was first passed? - What do we call the first 10 amendments to the constitution? - Vocabulary to Know: Democracy, Amendment Part 1: The Constitution - Know the terms of office for… President: ___ Representative to the House: ___ Representative to the Senate: ___ Supreme Court Justice: ___ - Know how to determine how many representatives each state gets in both the house and the senate. (you don’t need to memorize any numbers for this) - Know the main responsibilities of each branch of government. The names of the branches will be provided…so don’t memorize them. You will be given such as “this branch conducts foreign policy” and will have to identify which of the three branches is responsible. Part 2: The Bill of Rights First Amendment - Limits to freedom of speech/expression: you will be given a list of 5 examples of speech/expression that are illegal, and you will need to identify which one is defamation, obscenity, etc. You basically need to know what each limit means and be able to identify an example of each. - You will be given a scenario of student speech in a school setting and will be asked to determine if the speech is protected under the first amendment, or if it can be limited, according to the Tinker v. Des Moines ruling. - Freedom of Religion is guaranteed by the first amendment …What does the “establishment clause” prohibit Congress (or any government entity) from doing? …The “free exercise clause” prohibits Congress (or any government entity) from passing laws or making rules that would prevent citizens from doing what? Second Amendment - This amendment was passed in recognition of the fact that, back then, it was important for each state to be able to do WHAT quickly?\ 4th Amendment - “Probable cause” is needed to get a warrant. What is this? (Read that language carefully…) - The “exclusionary rule” says that objects seized or knowledge gained during execution of a search cannot be introduced as evidence in court if the search did not follow 4 th Amendment legal procedure. 8th Amendment: What has the Supreme Court ruled about capital punishment? Unit 2: Reconstruction From Overview - What was the status of slavery at the time of the constitutional convention (was it legal? Was it increasing or decreasing?) Section 1: “Race” - What is the common definition of race (used by most people in the US)? - Do Scientists use race to divide humans into groups? Why/why not? - Do most of our genes code for our external (visible) appearance? -Are members of different races BORN with different physical and mental abilities? Do such differences exist? Section 2: Slavery Leads to Civil War - By the time of the constitutional convention, slavery was in sharp decline. - What did the 3/5th compromise do? - What did the framers of the constitution expect to happen to slavery over time, even if they made it legal? - What impact did the invention of the Cotton Gin have on slavery in the United States? Section 3: Reconstruction - Was Andrew Johnson a popular president? - What was Lincoln’s main goal (had he lived) for Reconstruction? - What two branches of gov’t battled for control of Reconstruction? Who wins? - What things were granted to free slaves by the 13 th, 14th and 15th amendment? (you don’t need to know which amendment goes with which) - What level of equality with whites did freed slaves have during reconstruction? - WHY did reconstruction end? - What happened to black political power after reconstruction? - What is segregation and what did the Supreme Court rule about segregation in Plessy v. Ferguson? Unit 3: Industrial Revolution From Overview - We become wealthiest nation on earth...but WHO gets wealthy, and who doesn’t? Part 1: Shift from Agrarian to Industrial - Know the correct chronological order…Hunter-Gatherer, Agrarian, Industrial, Post Industrial - There will be a section where you will have to read statements describing an era of human history, and correctly identify that era. For instance, a statement might say “This is the era of human history the United States is currently in” - You do NOT need to know the percentages of the world living in each era - Look over the agrarian-industrial chart: focus on the ones that deal with work and family Part 2: Factors that led the US to have an Industrial Revolution - Know the main new source of energy and the main new building material - Know what a national market is, and what caused them to develop in the US Part 3: The Rise of Big Business During the IR - Vocabulary: corporation and monopoly - Know WHY corporations arose during the IR, and HOW they raised money - Know how corporations impacted the RISK of starting a new business - Vertical Integration - Monopolies…what are they, how do they impact price, quality and competition. - Consumers: do they benefit from monopolies? Why/why not? - What does “Laissez Faire” economics believe? …did we have a LF economic system during the IR? …do we have a LF economic system today? - Which groups are in favor of Laissez Faire Economics? Corporations? Consumers? Workers? - Business Leaders: know that they were both good and bad. On the positive side, they created a lot of employment and manufactured a lot of increasingly cheap consumer goods, but they treated their workers terribly, and most of the wealth they generated they kept for themselves, creating a class system of rich people and poor people that was new in the United States, and that has been with us ever since. At the end of their lives, many of them gave a lot of their money away to charitable causes. Part 4: The American Worker in the Industrial Revolution How did the typical job change in the IR? What impact did this have on… …The number of skilled laborers in the US? …The amount of “pride” taken in one’s work? …The amount of children in the work force? - Read/Know “the larger point” at end of section A - Labor Unions: what are they? What is a contract and what role do unions play in contracts? - What is a strike? - During the IR… …Did Unions attain their goals? …Who did Government side with? …Membership exclusions Unit 4: Immigration From Overview - What is meant by “Open” immigration? (when did we have “open” immigration? Do we have “open” immigration today? - Vocabulary: pushes and pulls…know the definitions and be able to identify (not memorize) examples. A Pushes/Pulls - From what part of the world did most immigrants come from during the late 1800’s? - Study the pushes and know what push caused immigrants from specific countries to come to the United States (and what pull would have most appealed to each group) B Coming to America - Steerage: be familiar with what conditions were like. C Processing at Ellis Island - Be familiar (from memory and the unit guide) with what kinds of things could get an immigrant deported and sent back. - Be familiar with what happened to immigrants who arrived sick - What were the chances of getting deported? - Where did most immigrants live when they first arrived? - What was life like in the tenements? D Affects of Immigrants on US Society - What kinds of jobs do immigrants typically do? - What was the political base of the machine…in other words, who voted for them? - Impact of political machines on immigrants (why did immigrants support the machines? - Be familiar with what Old immigrants thought of new immigrants F Anti-Immigrant backlash - What country was excluded by law from immigrating to the United States? G The Golden Door Closes - Countries from what geographic area were favored by the quota system? Unit 5: Progressive Era: Study the Unit Guide








