Muscle contraction WebQuest - TCHS
advertisement

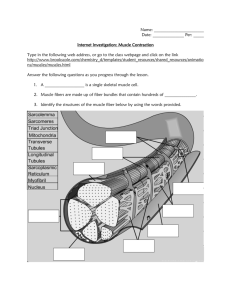
Name: _________________________ Date: ____________ Muscle Contraction WebQuest http://zunal.com/process.php?w=107815 Read Through the Introduction and Task Then answer the questions under each link below by hitting on that link on the Process page Task 1: Review of muscle contraction concepts. Watch the following animations in order and then answer the questions that follow. Neuromuscular junction 1. What causes voltage-gated calcium ion channels to open? 2. Calcium moving into the neuron causes vesicles to release a neurotransmitter. What’s the name of this neurotransmitter? 3. What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down Ach? 4. What causes a depolarization of the membrane? Action Potentials and Muscle Contractions 5. Explain what you think a neuromuscular junction is. 6. The depolarization of the T tubule membrane causes what to happen? 7. What is the name of the protein that covers up the myosin binding sites on actin? 8. How would you describe a cross-bridge? Breakdown of ATP and Cross-Bridge Movement during Muscle Contraction 9. What is needed to move tropomysoin out of the way? 10. Where do the myosin heads attach to? 11. How is the bond between actin and myosin broken? Muscular System, Sliding Filament Theory 1 12. What is the connective tissue that connects muscle to bone called? 13. What is the connective tissue that separates bundles of muscle fibers? 14. What is the connective tissue that separates individual muscle fibers? 15. What makes up the basic unit of muscle contraction? Muscular System, Sliding Filament Theory 2 16. What is initially released to start muscle contraction? 17. What else does muscle contraction require? 18. Why do you think the mechanism of muscle contraction is referred to as the “Sliding Filament Theory”? 19. Do muscles get longer or shorter when they contract? Task 2: Summary animation with self-quizzes. Watch the following animation and answer the three questions below by completing the quiz part of the tutorial. Muscle Contraction Summary & Quiz 20. The sliding filament theory states that, during muscle contraction and relaxation, a. Actin & myosin filaments shorten, then lengthen b. Actin & c. myosin filaments change positions relative to one another d. Troponin & Tropomyosin slide past one another 21. During muscle contraction, calcium ions bind to a. Troponin b. Tropomyosin c. Actin d. Myosin 22. After a myosin head has performed a power stroke, it must first bind to ________ in order to perform another power stroke. a. Actin b. Troponin c. Tropomyosin d. ATP Go to the following website: http://phsgirard.org/Anatomy.html Scroll down to Link 5 Skeletal Muscle Contraction Tutorial (Hit this link) 1. Read the instructions and then hit the play button at the bottom (arrow pointing to the right) 2. Read the introduction on the right then hit the play button again a. Skeletal muscles are made of fiber bundles which contain hundreds of _________________ b. A muscle fiber is a single ____________________________________ c. What does it mean by multinucleate (break the word apart to figure it out)? ______________ d. Hit play again 3. Notice the highlighted myofibrils in the picture. a. What is the main job of a myofibril? ___________________________ b. Hit play 4. Notice what is being highlighted now in the picture a. Myofibrils are composed of individual units called ___________________. b. How many of these are being shown to you in this picture? _______ c. Hit play 5. What is the sacrolemma? ________________________________________________________________________________________ a. Hit play 6. Extensions of the sacrolemma that separate the individual sacromeres are called ___________________________________________. Notice the highlighted portion in the picture. a. Hit play 7. Nerve impulses are transmitted through the sacrolemma to individual ___________________. a. Hit play 8. What is the sacroplasmic reticulum and what does it surround? _____________________________________________________________________ a. Hit play 9. What are the 2 things the longitudinal tubules connect? _______________________ and ___________________________ a. Hit play 10. This connection by longitudinal tubules is called _____________________. 11. The triad is composed of what? ________________________________________________________________________(notice what it is in the picture) a. Hit play 12. Where is the mitochondria found? __________________________________________________________ a. Hit play 13. Take this quiz. Once this is completed, hit play Fill in the picture below with the correct parts of the microscopic muscle. 14. Press play again to get a closer look. 15. What are the bands that mark the end of a sacromere? ____________________ a. Hit play 16. What marks the middle of the sacromere? _______________ a. Hit play 17. How can someone view the parts of the muscle cells? __________________________ a. The light areas in the micrograph are called _________________________ b. What is the primary protein of thin filaments? __________________ c. What other proteins can be found in thin filaments? ________________________________________________________________ d. Press play 18. The filaments with greater density are called ________________________________ a. These filaments are composed of ________________ proteins. b. Hit play 19. Do the thick and thin filaments ever overlap in the sacromere? _____________ a. Press Play 20. Complete the quiz and then press play. 21. For the sacromere to contract, the distance between the ___________ lines must be ______________. a. hit play 22. What year was muscle contraction figured out? ______ a. Press Play 23. Notice where the red and brown lines in the picture are located when a muscle is relaxed. a. Press Play 24. What happens in the picture when the muscle contracts? ______________________________ a. Press play 25. What is the H zone? ________________________________________________________________ a. Press Play 26. What happened in the H zone when the muscle contracts? ________________________________________________________________________ a. Press play 27. What is the I band? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ a. Press Play 28. What happened to the I band when the muscle contracted? ___________________________________ a. Press play 29. What happened to the total distance of the thick filaments during muscle contraction? __________________________________________________________________________________ a. Press Play b. Read what is says on the right and then hit play. 30. In the presence of ______________, the thin filaments slide _______________ the _______ disc along the thick filaments. This is called the ____________________ model. The ___________ zone and the ___ band _________ during contraction. a. Make sure you understand what is occurring in the picture before you continue for a possible future quiz. b. Hit play 31. Press Play again a. What is the filament in the center? (thick or thin) b. Press play 32. Press play again a. What are the Z lines (it was described earlier)? _______________________________________________________ b. Press play 33. Notice what happens in the picture and then press play again. a. What happens first during muscle contraction? ___________________________________________________________________________ b. Press play 34. A conformational change in the myosin heads causes _________________________________________________________________________________ a. Press play 35. In the most contracted state, do the thin filaments completely overlap the thick filaments? _______ a. Why don’t the thick and thin filaments totally overlap? ____________________ b. What is the name of the disc where no myosin heads are located? ___________ c. Press play 36. What occurs to the thin and thick filaments when the sacromere relaxes? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ a. Press Play 37. What is the job of the Titin filament? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ a. Press Play 38. Press play again for a closer look a. Muscle contraction is driven by _______________________________. b. Muscle contraction is triggered by ___________ from the sacroplasmic reticulum. c. Notice the location of these in the picture. d. Press Play 39. The nervous system sends __________________________ signal to the sacrolemma (remember what this is). The signal is then transferred to the ________________________________ which releases ________ to the muscle fiber. a. Press Play 40. Calcium binds to _______________ in the __________ filaments which exposes what? _____________________________________________________ a. If no Calcium is available, the myosin head will not bind to _______________________. b. Press Play 41. The calcium allows the __________ heads to bind with actin of the _________ filaments. a. Press play 42. When binding occurs, it stimulates the release of ___________ (what does P stand for), and this causes a conformational change in the _________________ which pulls the thin filaments ___________. a. This movement is called a ___________________________ . b. Press play 43. The muscle will stay contacted in the absence of what? ____________ a. When ATP is present, it binds to _________________ and causes the ___________ of the myosin from actin. b. Press Play 44. When the thin filament moves back to relaxed position, what happens to the ATP? _____________________________ a. What binds to the myosin head causing a conformational change? ________________ b. Press play 45. Complete the final quiz.