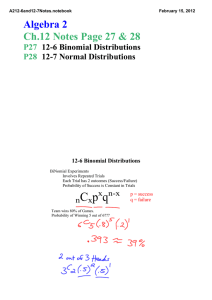
Unit 3
advertisement

AP STATISTICS UNIT 3: Probability Theory High School Mathematics The Practice of Statistics, 2nd Ed. Target Time Frame: 11 – 14 days STANDARD IIIA: Understand and apply the “Law of Large Numbers”, the addition and multiplication probability rules; find conditional probability; understand discrete random variables and their probability distributions, including binomial; conduct simulations of distributions, including binomial and geometric; compute the mean and standard deviation of a random variable; conduct transformation of a random variable. IIIB: Understand the difference between independent and dependent variables and independent and disjoint; find the mean and standard deviation for sums and differences of independent random variables. IIIC: Know properties of the normal distribution; use tables of the normal ESSENTIAL QUESTION What is the Law of Large Numbers? When would I ever use probability? How do I find the expected value of a discrete random variable? What does Craps have to do with statistics? What is the difference between a binomial distribution and a geometric one? What is the difference between independent and dependent variables? What does disjoint mean? If two random variables are normal/not normal, how does that affect their linear combination? What is a z-score? How do normal DEPTH for MASTERY All Sections COMMENTS Ch. 6.1, 6.3 Resources: The Game of Craps (Activity 7, TPOS) The Casino Lab (GRB) Ch. 7.1, 7.2 Activity 8A-Plinko (GRB) Chapter 8 Special Problem 7A Special Problem 6C (GRB) Ch. 5.3 2001-FR#2 All Ch. 6.2 Ch. 7.2 All Ch. 2.1, 2.2 Resources: 2002-FR#3 2003B-FR#2 Resources: APEX-Classtools Online distribution; use the normal distribution as a model for measurements. IIID: Identify and calculate statistics to describe sampling distributions of sample proportions and sample means, and distributions of the difference between 2 sample proportions and 2 sample means; apply the Central Limit Theorem; simulate a sampling distribution. distributions relate to probability distributions? What does it mean to have high variability of a statistic? Can I use normal approximations? What is the CLT? How do I use my calculator or computer to conduct a simulation? Ch. 7.1 All Ch. 5.3 Resources: Activity 9A (TPOS) Chapter 9 1998-FR#1 UNIT COMMENTS: This unit must be completed prior to the AP Exam. Notes in the Comments column that have a year and FR# refer to an AP Exam, noting the year and free response question number.