4.3 Review Answers
advertisement
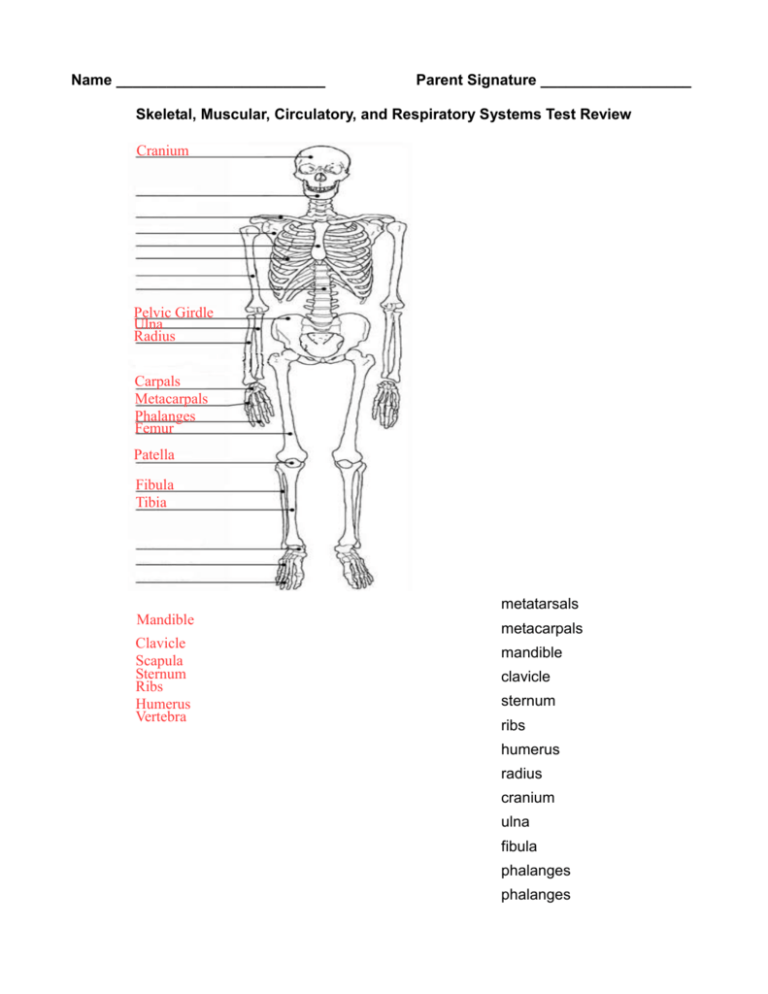
Name _________________________ Parent Signature __________________ Skeletal, Muscular, Circulatory, and Respiratory Systems Test Review Cranium Pelvic Girdle Ulna Radius Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Patella Fibula Tibia metatarsals Mandible Clavicle Scapula Sternum Ribs Humerus Vertebra metacarpals mandible clavicle sternum ribs humerus radius cranium ulna fibula phalanges phalanges Pelvic girdle carpals femur Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges vertebra patella tibia tarsals scapula Label Extensor and Flexor: Label the three types of muscles: Cardiac Muscle Extensor Flexor h Muscle Skeletal Muscle Flexion Tendon Extension Clot Ligament Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Red Yellow Voluntary Involuntary Away Heart Nutrients Oxygen Cartilage To Capillaries 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. RED marrow produces blood cells. YELLOW marrow replaces red marrow and is made of fat. The bending movement that decreases the angle of a bone joint is FLEXION. EXTENSION is the movement of a joint that increases the angle of the joint. LIGAMENTS connects bone to bone and TENDON connects bone to muscle. Muscle tissue only found in the heart is CARDIAC muscle. A muscle that is attached to the bones is called a SKELETAL muscle. It is in charge of movement. They move bones by working in pairs. 8. SMOOTH muscle is found inside many internal organs of the body, like the blood vessels. 9. INVOLUNTARY muscles never get tired and cannot be consciously controlled, while VOLUNTARY muscles can be consciously controlled. 10. A flexible tissue that acts as a shock absorber and reduces friction between bones is CARTILAGE. 11. Arteries carry blood AWAY from the heart, while veins carry blood TO the heart. 12. CAPILLARIES connect veins to arteries. 13. Red blood cells carry OXYGEN and NUTRIENTS to our cells. 14. Name the type of joint below: shoulder BALL & SOCKET knee HINGE neck PIVOT thumb SADDLE hands GLIDING 15. List the order that a blood would follow as it passes through the heart. Start with the R. Atrium. R. ATRIUM → R. VENTRICLE → PULMONARY ARTERY → LUNGS → PULMONARY VEINS → L. ATRIUM → L. VENTRICLE → AORTA → BODY 16. Complete the chart below: SYSTEM GENERAL FUNCTION STRUCTURE (at least 3) SKELTAL Protect organs, structure, and COMPACT BONE, SPONGY make bone marrow BONE, LIGAMENTS MUSCULAR Responsible for movement CIRCULATORY Pump oxygen and nutrients VEINS, ARTERIES, through the blood to the body CAPILLARIES RESPIRATORY Supply blood with oxygen and TRACHEA, BRONCHI, remove carbon dioxide ALVEOLI SMOOTH, CARDIAC, SKELETAL 17. Label the following heart: AORTA R. ATRIUM R. VENTRICLE PULMONARY ARTERY Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle Right Ventricle Aorta Pulmonary Artery L. ATRIUM L. VENTRICLE 18. Label the respiratory system: NASAL CAVITY PHARYNX LARYNX TRACHEA BRONCHI LUNG BRONCHIOLES ALVEOLI DIAPHRAGM 19. List the order that a air would follow as it passes through the respiratory system. NASAL CAVITY/MOUTH CAVITY → PHARYNX → LARYNX → TRACHEA → BRONCHI → BRONCHIOLES → ALVEOLI 20. Explain the process of gas exchange that occurs in your body: AS WE INHALE (DIAPHRAGM CONTRACTS) OXYGEN, IT TRAVELS THROUGH THE REPIRATORY SYSTEM UNTIL IT GETS TO THE ALVEOLI. IN THE ALVEOLI, THE OXYGEN DIFFUSES INTO THE BLOOD THE CARBON DIOXIDE WASTE THAT OUR CELLS PRODUCED DURING CELLULAR RESPIRATION, DIFFUSES INTO THE ALVEOLI (SO OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE SWITCH PLACES). THE OXYGEN IS THEN DELIVERED TO THE REST OF THE CELLS IN OUR BODY THE CARBON DIOXIDE IS EXHALED (DIAPHRAGM RELAXES) AS IT MOVES BACKWARDS THROUGH THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.