Characteristics Of Waves
advertisement
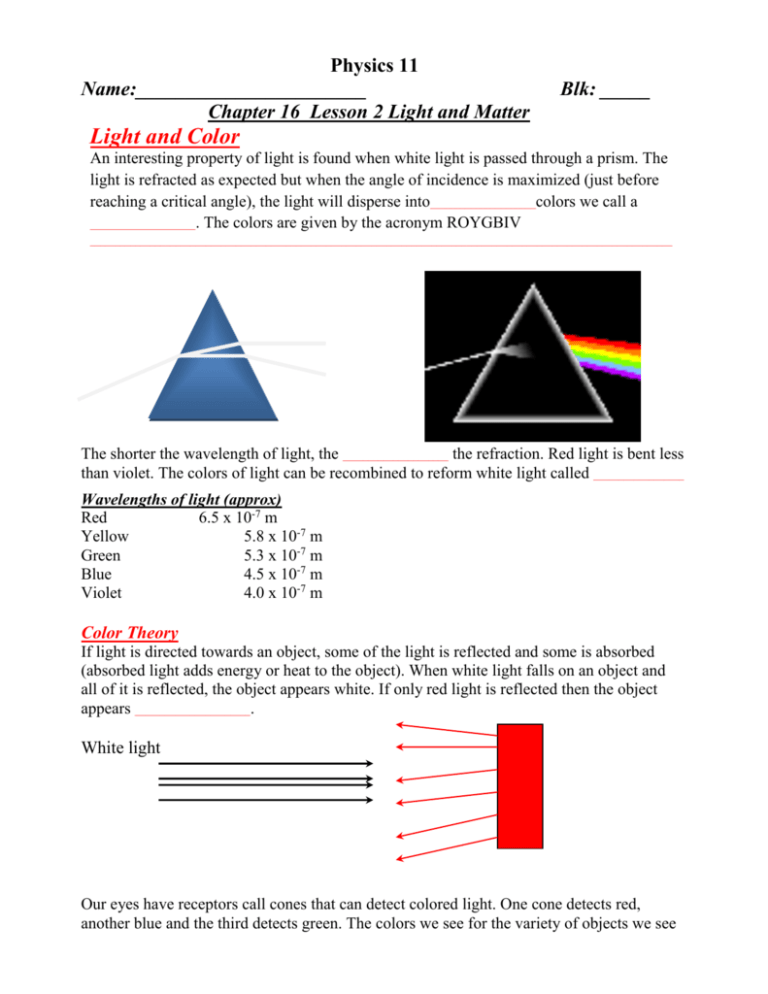
Physics 11 Name:_______________________ Chapter 16 Lesson 2 Light and Matter Blk: _____ Light and Color An interesting property of light is found when white light is passed through a prism. The light is refracted as expected but when the angle of incidence is maximized (just before reaching a critical angle), the light will disperse into_____________________colors we call a _____________________. The colors are given by the acronym ROYGBIV ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ The shorter the wavelength of light, the _____________________ the refraction. Red light is bent less than violet. The colors of light can be recombined to reform white light called __________________ Wavelengths of light (approx) Red 6.5 x 10-7 m Yellow 5.8 x 10-7 m Green 5.3 x 10-7 m Blue 4.5 x 10-7 m Violet 4.0 x 10-7 m Color Theory If light is directed towards an object, some of the light is reflected and some is absorbed (absorbed light adds energy or heat to the object). When white light falls on an object and all of it is reflected, the object appears white. If only red light is reflected then the object appears _______________________. White light Our eyes have receptors call cones that can detect colored light. One cone detects red, another blue and the third detects green. The colors we see for the variety of objects we see are the interpretations by our brains that filter through the information from only these three cones. Additive Theory of Light There are three primary colors of light: _______________________________________________. All other colors can be created from varying the amount of these three primaries. (Not to be confused with the subtractive color theory of light used by painters!!) Our brain works according to this principle to help us interpret all of the rich colors of our surroundings. For example, by stimulating a red and a green cone, we interpret the light as yellow. Televisions use this to principle to display images! A cathode ray tube or tube screen uses thousands of sets of colored pixels (3 pixels per set - one for each primary) on the screen that are hit by electrons causing them to glow. Rear projections TV use three coordinated lights to display an image. Snell’s Law of Refraction Refraction is the __________________________ that takes place at __________________________ between two materials having different indices of refraction. Refraction is due to _____________________________________________as it passes from one medium to another. The boundary ________________________________________________________________________________ At a boundary, an incident ray can undergo _______________________________ or, in certain situations, ____________________________________________ No bending of the incident ray occurs if it strikes the boundary along the normal. The ____________________________ is the ray approaching the boundary. It strikes the boundary at the point of incidence. The ____________________ is the ray leaving the boundary through the second medium. The reflected ray is the ray undergoing partial (or total) reflection at the boundary. The normal is a construction line drawn perpendicular to the boundary at the point of incidence. The angle of incidence (i) is _______________________________________________________________________________ The angle of reflection (r) is _______________________________________________________________________________ The angle of refraction (R) is _______________________________________________________________________________ Both Reflection and Refraction occur when the light is incident on a more refractive medium. Whenever light (or any wave) passes from one medium to another medium it may be ______________________________ from its original path. A Dutch mathematician Willebrord Snell (15911626) discovered that there is an exact relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for light traveling from one medium into another. This relationship is: sin i n sin r Where n is a constant for a particular medium and is called the ___________________________________. The index of refraction is measured relative to a vacuum, which is assigned 1. Examples of indices of refraction: Water (at 20˚C) Diamond Glass Air Ethanol Quartz Crystal 1.333 2.42 1.5-1.9 (depends upon composition) 1.00029 1.36 1.54 Note: the index of refraction depends upon the color of light used and on the purity, temperature and composition of the material into which the light is traveling. Snell’s Law can be expanded for any situation as follows: ni sin i nr sin r or sin i nr sin r ni Example 1: Light rays hit a quartz crystal at an angle of incidence of 25˚ from air. Determine the angle of refraction? Example 2: A ray of light traveling through air is incident upon a sheet of crown glass at an angle of 30.00. What is the angle of reflection? Example 3: A light wave traveling in air (refractive index of 1.0) passes into the water in a swimming pool at an angle of 35° to the normal. Calculate the direction of the light in the water, given that the refractive index of water is 1.4. ni sin i nr sin r (_____)sin(___ ) (1.4)sin r (______) sin r r sin 1 (______) _____ When light passes from a less dense medium (lower n value) to a more dense medium (higher n value), the light is bent towards the normal line. When light passes from a more dense medium (higher n value) to a less dense medium (lower n value), the light is bent away from the normal line. Applying Concepts Pg. 363 #5, 9 Problems Pg. 364 #2, 3, 4, 7, 10, 13 Applications Pg. 365 #20, 23 Physics 11 Name:_______________________ Blk: _____ Snell’s Law and Critical Angles Assignment 1. Light entering a block of glass at an angle of incidence of 18.5˚ leaves the boundary between the air and the glass at an angle of 12.0˚. What is the index of refraction of this type of glass? 2. Light is incident on diamond at an angle of 10.0˚. At what angle will it refract? 3. A beam of light is incident on a sheet of glass in a window at an angle of 30˚. Describe exactly what path the light beam will take (a) as it enters the glass and (b) as it leaves the other side of the glass. Assume n=1.500. 4. Light traveling in air has an angle of incidence of 40˚ as in passes into diamond. What is the refracted angle in the diamond? 5. A transparent material has a refractive index of 1.27. What is the angle of incidence in air when the angle of refraction in the substance is 43˚? 6. What is the index of refraction of a material if the angle of incidence in air is 50˚ and the angle of refraction in the material is 40˚? 7. A ray of light passes from water into carbon disulphide (n=1.63) with an angle of incidence of 30˚. What is the angle of refraction in the carbon disulphide? 8. Using Snell’s Law with n = 1.33 for water and n = 2.42 for diamond determine the angle of refraction in the diamond for the following situation. 53˚ Diamond water 9. Using Snell’s Law with n = 1.33 for water and n = 2.42 for diamond determine the angle of refraction in the water for the following situation. 63˚ diamond Water 10. a) Green light traveling in air has an angle of incidence of 50˚ as it passes into a certain glass. The refracted angle in the glass is 33˚. What is the refractive index for this type of glass? b) If the frequency of green light is 5.36 x 1014 Hz, what is the wavelength of green light in space? c) What is then the wavelength of this green light in the glass? 11. Calculate the critical angle for diamond. 12. What is the critical angle for a glass that has an index of refraction of 1.500? 13. A certain material has a critical angle of 52.0˚. What is its index of refraction? 14. Red light having a wavelength of 7.0 x 10-7 m travels at 3.00 x 108 m/s in space. What is the frequency of this color? 15. a) A certain blue light has a frequency of 6.8 x 1014 s-1. Its wavelength in water is 3.3 x 10-7 m. What is the speed of this blue light in water? b) What will be the wavelength of the same blue light in space?








