2. Aggressive Behavior
advertisement

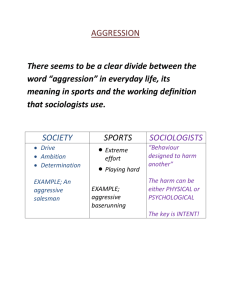
Psy 100 Spring 2003 Madigan Aggressive Behavior 1. Three Views 2. Aggression in non-human species Aggression as an adaptation predation, defense Iintraspecies aggression Response to pain, loss, frustration 3. Sex Differences 4. Brain mechanisms Hormonal influences Genetics and individual differences 5. Aggression as Learned Behavior Aggression as an instrumental response Frustration-aggression hypothesis Social leaning and imitation Three Views of Aggression “No human being has ever been born with aggressive or hostile impulses, and no one becomes aggressive without learning to do so.” (Ashley Montagu, anthropologist) “There carmot be any doubt, in the opinion of any biologically minded scientist, that intraspecific aggression is, in man, just as much a spontaneous instinctive drive as in most other higher vertebrates.” (Konrad Lorenz, ethologist) “Aggression is a biological mechanism shaped by natural selection into an adaptive force which helps to establish and maintain primate societies.” (Bernstein & Gordon, primate researchers). Skinner: Aggression as Instrumental Behavior Aggressive behavior can be acquired and maintained because of its consequences just like any other behavior. Which reactions have been punished in the past? Which reactions have been reinforced? ... Frustration Aggression Hypothesis Frustration = reaction to blockage of goal-directed behavior. Original version:Frustration is a sufficient condition for aggression. Frustration effects in operant conditioning: failure to obtain an expected or “deserved” reinforcer leads to intensification of behavior emotional arousal, aggressive acts. Psy 100 Spring 2003 Madigan Social Learning (Modified Frustration-Aggression Theory) Social learning theory: what is the learning experience of the individual? Which reactions have been punished? Which reactions have been reinforced? What stimuli / cues are present? What associations do they activate? How is the situation construed / interpreted? The “traits” complication: stable, possibly biologically-based individual differences in characteristic reactions. Examples: heritable traits, including social avoidance; hormone levels Partial reinforcement, disappointment & frustration are facts of ljfe How do you deal with them?