Ch 5 - Photosynthesis
advertisement
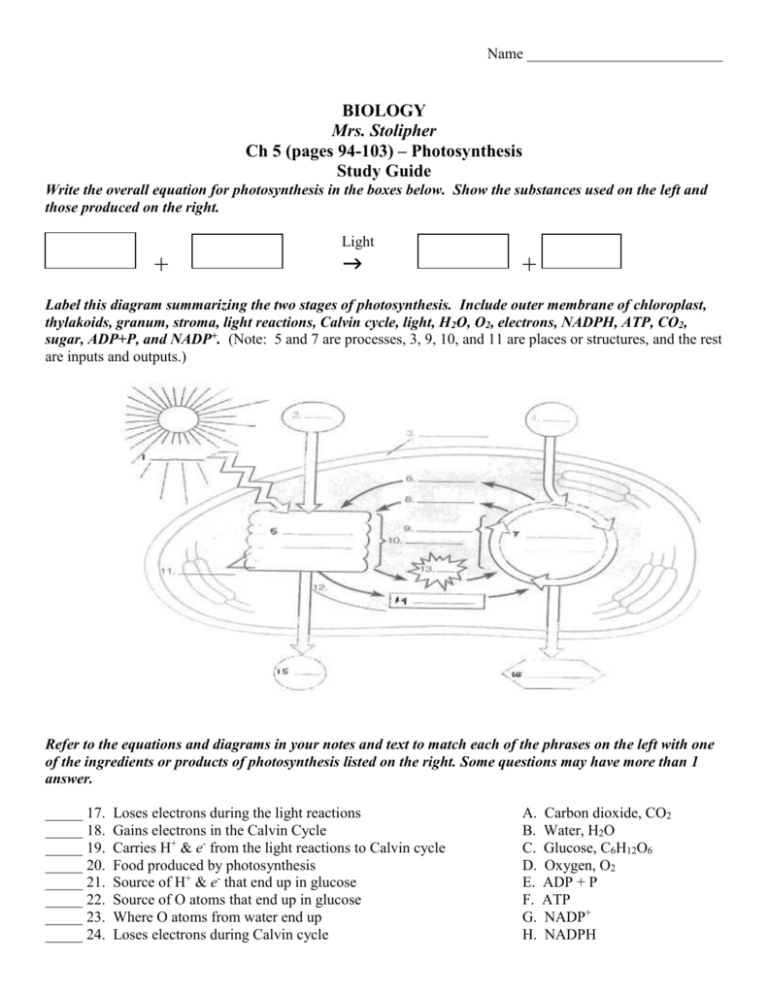
Name __________________________ BIOLOGY Mrs. Stolipher Ch 5 (pages 94-103) – Photosynthesis Study Guide Write the overall equation for photosynthesis in the boxes below. Show the substances used on the left and those produced on the right. Light + + Label this diagram summarizing the two stages of photosynthesis. Include outer membrane of chloroplast, thylakoids, granum, stroma, light reactions, Calvin cycle, light, H2O, O2, electrons, NADPH, ATP, CO2, sugar, ADP+P, and NADP+. (Note: 5 and 7 are processes, 3, 9, 10, and 11 are places or structures, and the rest are inputs and outputs.) Refer to the equations and diagrams in your notes and text to match each of the phrases on the left with one of the ingredients or products of photosynthesis listed on the right. Some questions may have more than 1 answer. _____ 17. _____ 18. _____ 19. _____ 20. _____ 21. _____ 22. _____ 23. _____ 24. Loses electrons during the light reactions Gains electrons in the Calvin Cycle Carries H+ & e- from the light reactions to Calvin cycle Food produced by photosynthesis Source of H+ & e- that end up in glucose Source of O atoms that end up in glucose Where O atoms from water end up Loses electrons during Calvin cycle A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Carbon dioxide, CO2 Water, H2O Glucose, C6H12O6 Oxygen, O2 ADP + P ATP NADP+ NADPH _____ 25. _____ 26. _____ 27. _____ 28. _____ 29. _____ 30. _____ 31. _____ 32. _____ 33. _____ 34. Reduced in the light reactions Supplies energy to the Calvin cycle Where C and O atoms in carbon dioxide end up Recycled from the Calvin cycle to make ATP Supplies energy to the light reactions Gas produced by reactions in the thylakoids Gas consumed by reactions in the stroma Source of carbon for carbon fixation Source of H+ for the Calvin cycle Picks up energized e- from reactions in the thylakoids I. Light State whether each of the following would be likely to WARM or COOL the Earth through alteration of the greenhouse effect. ______________ 35. ______________ 36. ______________ 37. ______________ 38. ______________ 39. ______________ 40. ______________ 41. ______________ 42. ______________ 43. ______________ 44. Increased burning of coal to produce electricity Increased rate of growth of algae in the oceans Increased cloud cover, which would reflect more sunlight Hybrid cars that go farther on a tank of gasoline. Increased cutting of tropical rain forests Using nuclear power instead of coal & oil to make electricity Reforesting deforested and overgrazed land Increased rate of decomposition of organic matter Slowing the population growth rate Using solar cells to generate electricity. Circle the letter of the choice that best answers each question or statement. 45. The ultimate source of energy in the sugar molecules produced by photosynthesis is A. sugar B. the sun C. oxygen D. ATP E. chlorophyll 46. Which of the following is produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis and consumed by the Calvin cycle? A. NADPH B. O2 C. H2O D. sugar E. ADP+P 47. Which of these wavelengths is least useful for photosynthesis? A. green B. yellow C. blue D. orange 48. When chloroplast pigments absorb light, A. they become reduced C. their electrons become excited E. their photons become excited E. red B. they lose potential energy D. the Calvin cycle is triggered 49. The light reactions of photosynthesis generate high-energy electrons, which end up in _____. They also produce _____ and ______. A. ATP … NADPH … O2 B. O2 … sugar … ATP C. chlorophyll … ATP … NADPH D. water … sugar … O2 E. NADPH … ATP … O2 50. The overall function of the Calvin cycle is A. capturing sunlight C. producing CO2 E. oxidizing glucose B. making sugar D. splitting water 51. Which of the following correctly matches each of the inputs of the Calvin cycle with its role in the cycle? A. CO2: high-energy electrons; ATP: energy; NADPH: oxidation B. CO2: carbon; ATP: energy; NADPH: high-energy electrons C. CO2: high-energy electrons; ATP: carbon; NADPH: energy D. CO2: energy; ATP: carbon; NADPH: high-energy electrons E. CO2: hydrogen; ATP: carbon; NADPH: energy 52. The main photoautotrophs in aquatic environments are A. plants & animals B. plants & fungi D. algae & bacteria E. plants & bacteria C. animals & algae 53. Which of the following is not a product of the light reactions of photosynthesis? A. O2 B. sugar C. high-energy electrons D. ATP E. NADPH 54. In photosynthesis, plants use carbon from ____ to make sugar and other organic molecules. A. water B. the air C. chlorophyll D. the sun E. soil 55. In a rosebush, chlorophyll is located in A. chloroplasts, which are in mesophyll cells in the thylakoids of a leaf B. mesophyll cells, which are in the thylakoids in chloroplasts in a leaf C. thylakoids, which are in mesophyll cells in the chloroplasts in a leaf D. chloroplasts, which are in thylakoids in the mesophyll cells of a leaf E. thylakoids, which are in chloroplasts in the mesophyll cells of a leaf 56. The photo part of the word photosynthesis refers to _________, whereas synthesis refers to ________. A. the reactions that occur in the thylakoids … carbon fixation B. the reactions in the stroma … the reactions in the thylakoids C. the Calvin cycle … carbon fixation D. the Calvin cycle … the reactions in the stroma E. the light reactions … reactions in the thylakoids 57. The energy used to produce ATP in the light reactions of photosynthesis comes from A. the “burning” of sugar molecules B. splitting water C. movement of H+ through a membrane D. carbon fixation E. fluorescence 58. The following (P through U) are the main steps of chemiosmotic ATP synthesis in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Which answer places them in the correct order? P. H+ concentration gradient established Q. H+ diffuses through ATP synthase R. Carriers use energy from electrons to move H+ across membrane S. Electrons from photosystem II pass along electron transport chain T. Light excites electrons in photosystem II U. Energy of H+ flow used by ATP synthase to make ATP A. PQTSRU B. STPQRU C. TSRPQU D. TSRUQP E. PQUSTR 59. An oceanographer has suggested slowing the rate of green house warming by fertilizing the ocean to increase the growth of algae. How would this reduce the green house effect? A. It would produce oxygen, which reflects sunlight from the atmosphere. B. It would “repair” the Earth’s ozone layer. C. It would use up CO2, which traps heat in the atmosphere D. It would change the color of the ocean, reflecting the sun’s heat. E. It would trap sunlight that would otherwise warm the Earth Answer the following questions. 60. In an experiment, plants were grown under colored filters that allowed equal amounts of light of different colors to strike different plants. Under which filter do you think plants grew the slowest? Why? 61. State two activities of humans that tend to intensify the green house effect. Why are people concerned about this? State two actions we could take that would reduce our contribution to the greenhouse effect. 62. Identify four factors that affect photosynthesis and explain how they affect it. 63. What is an autotroph? Give examples: 64. What is a heterotrophy? Give examples: 65. Write the equation that shows how ADP is changed into ATP. 66. Write the equation that shows how ATP is changed into ADP. 67. What is a pigment? 68. What is the main pigment used by green plants to absorb energy? 69. What are the 2 kinds of chlorophyll? 70. Which wavelengths of light are best absorbed by chlorophyll a & b? 71. Which wavelengths are reflected? 72. How are carotenoid pigments different from chlorophyll? 73. Why do plants have these other pigments besides chlorophyll? 74. Place where light dependent reactions happen = _________________________ 75. Place where Calvin cycle happens = _________________________ 76. What is NADP+? What does it do? 77. Write an equation that shows how NADP+ is changed into NADPH. 78. Where does the H that ends up in NADPH ultimately come from? 79. Why does Photosystem II come before Photosystem I in the light reactions? 80. What is another name for the Calvin Cycle? 81. Which reactions in photosynthesis require light? 82. Which do not? 83. How and where are ATP and NADPH made? 84. What happens to water during the light reactions? 85. What are the reactants of the light reactions? 86. What are the products? 87. Which molecule is given off as a waste gas? 88. Which molecules produced by the light reactions are used during the Calvin Cycle? 89. What happens during the Calvin cycle? 90. What are the reactants of the Calvin cycle? 91. What are the products? 92. Where does the carbon and oxygen in glucose ultimately come from? 93. Where does the hydrogen in glucose ultimately come from?








