Western Legal Tradition Timeline
advertisement
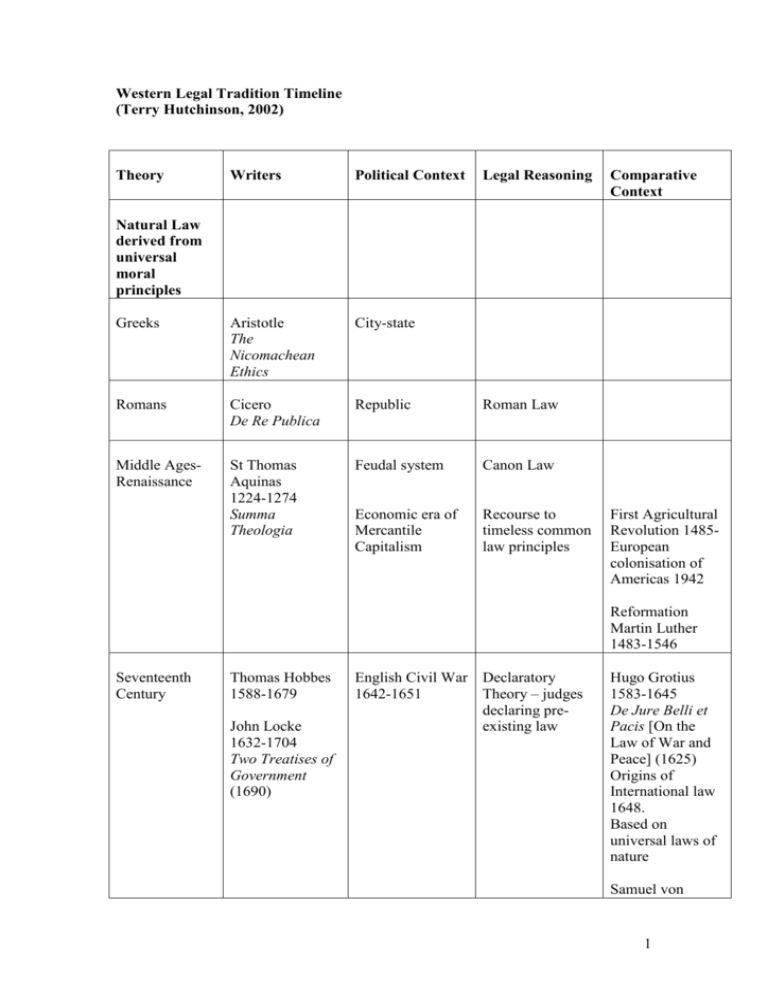
Western Legal Tradition Timeline (Terry Hutchinson, 2002) Theory Writers Political Context Legal Reasoning Greeks Aristotle The Nicomachean Ethics City-state Romans Cicero De Re Publica Republic Roman Law Middle AgesRenaissance St Thomas Aquinas 1224-1274 Summa Theologia Feudal system Canon Law Economic era of Mercantile Capitalism Recourse to timeless common law principles Comparative Context Natural Law derived from universal moral principles First Agricultural Revolution 1485European colonisation of Americas 1942 Reformation Martin Luther 1483-1546 Seventeenth Century Thomas Hobbes 1588-1679 John Locke 1632-1704 Two Treatises of Government (1690) English Civil War Declaratory 1642-1651 Theory – judges declaring preexisting law Hugo Grotius 1583-1645 De Jure Belli et Pacis [On the Law of War and Peace] (1625) Origins of International law 1648. Based on universal laws of nature Samuel von 1 Pufendorf 16321694 De Jure Naturae et gentium (1672) Eighteenth Century Age of Reason Sir William Blackstone 17231780 Commentaries on the Laws of England (1765-9) American Revolution 17751783 French Revolution 1789 Beginning of Rights based Liberalism US Bill of Rights & French Declaration of the Rights of Man Blackstone’s Rules for the application of law in conquered territories1770 Australia ‘settled’ not conquered Twentieth Century Revival of Natural Law John Finnis 1940- Natural Law and Natural Rights (1980) WW 1 1914-1918 WW 2 1939-1945 MIEA v Teoh (1995) 183 CLR 273 Rights of the Child Human Rights Agreements Beginning of economic era of Industrial Capitalism Law as science No necessary connection between law and morality Codification of laws in Europe Common law use of precedent syllogistic reasoning – law applied in a mechanical manner formalism Industrial Revolution Positivism Legal rules created by human institutions Eighteenth Century Age of Reason Nineteenth Century David Hume 1711-1776 An Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding (1748) Jeremy Bentham 1748-1832 An Introduction to the Principles of Morals and Legislation (1789) Bentham’s Utilitarianism – ‘greatest good for the greatest number’ John Austin 1790-1859 The Province of Jurisprudence Determined (1832) Austin’s The Law is objective Existence of law and value free is one thing; its merits or demerits another’ Development of contract based societies 2 Twentieth Century HLA Hart 19071992 The Concept of Law (1961) ‘Strict legalism’ 1952 Owen Dixon CJ High Court SGIC v Trigwell (1978) 142 CLR 617 US Legal Realism 1930s Oliver Wendel Holmes Distinction made between public and private realm of law Industrial Revolution 17601820 French Revolution Protection of individual vis-àvis State Liberalism Primacy of the individual in society Eighteenth Century Age of Reason Two World Wars Adam Smith 1723-1740 Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776) ‘classical’ political economist Importance of private property Nineteenth Century John Stuart Mill 1806-1873 On Liberty (1859) Welfare Liberalism 1870Mills Harm to others’ principle Twentieth Century Leonard Hobhouse 1864-1929 Liberalism (1911) A kind of social liberalism derived from Utilitarianism Milton Friedman 1912 – John Keynes 1883-1946 The End of Laissez Faire (1926) Ayn Rand 19051982 John Rawls International law permitting use of force in international relations Contracts enforced strictly Equitable doctrines applied pedantically Classical Liberal Theory and Night-watchman State UK parliament 18321870 Donognue v Stevenson [1932] AC 562 Neighbour Principle Industrial Regulation – Safety, Children Wages Friedrich August von Hayek 18991992 The Road to Serfdom (1944) UN Charter 1945 – Outlawing force in international relations Rand’s Individualism, Laissez faire Capitalism, 3 1921A Theory of Justice (1972) Neo-Classical Liberalism Robert Nozick 1938Anarchy, State and Eotopia (1974) Ronald Dworkin 1931Taking Rights Seriously (1977) Economic Analysis of Law – Law should be economically efficient ---maximazing the wealth of society (Richard Posner) In the footsteps of John Locke, Adam Smith, David Hume, Jeremy Bentham, JS Mill from the SeventeenthNineteenth Centuries Twentieth Century Ronald Coase Coase Theorem (1959) The Firm, the Market and the Law (1988) Guido Calabresi The Cost of Accidents (1970) Richard Posner Economic Analysis of Law (1922) Critical Legal StudiesCritiques Liberalism Law advantages the powerful in ‘Market-oriented’ GovernmentsPresident Ronald Reagan USA, Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher UK Privatisation Corporation Hilmer Reform US Legal Realism 1930s Julius StoneAustralian Realism Decolonisation Civil Rights Movement Post-Industrial Age 1940s Chicago School 1960- Public Choice Theory SelfDetermination in international Law 1975 Human Rights Conventions The law is not objective, but based in Liberalism Growth of multinational corporations Dworkin’s Rights-based Liberalism 1972 Withdrawal of Australian troops from Vietnam Roberto M. Unger The Critical Legal Studies Movement (1986) Mark Tushnet Milirrpum v Nabalco (1971) 17 FLR 141 Terra nullius 1989 The Berlin Wall separating Anti-formalism in the High Court: 1986 Explosion of nuclear power station at 4 society Red, White, and Blue: A Critical Analysis of Constitutional Law (1988) East Germany fromWest Germany is opened Mabo v Queensland (No.2) (1992) 175 CLR 1 Native Title Chernobyl FeminismLaw advantages men in society Carol Smart Feminism and the Power of Law (1989) Carol Gilligan In a Different Voice (1982) Catherine MacKinnon Toward a Feminist Theory of the State (1989) Regina Graycar The Hidden Gender of Law (1990) Margaret Davies Asking the Law Question (1994) 1970s Equal pay for equal work in Australia Liberal Feminism AntiDiscrimination and equity approaches Cultural Feminism Communication and technology explosion Critical Race Theory Law advantages particular racial groups Late twentieth Century Twenty-first Century PostModernism Rejection of common experience/ Subjectivity Late Twentieth Century Government funding for child care Radical Feminism Globalisation Kimberly Crenshaw Critical Race Theory (1995) Justice Mary Gaudron appointed to High Court 1987 R v Lavallee [1990] 1 SCR 852 Battered Woman Syndrome Wik People v Qld (1996) 187 CLR 1 Pastoral leases and native title Australian Law Reform Commission Report on the Recognition of Aboriginal Customary Laws 1986 Masciantonio v R (1995) 183 CLR 58 Ethnicity and the ordinary person Increasing use of the internet Growth of Global economies Larissa Behrendt Richard Delgado Critical Race Theory: An Introduction (2001) Racial Discrimination Act 1975 (Cth) Native Title Act 1993 (Cth) Mary Joe Frug Posmodern Legal Feminism (1924) Jean François Lyotard ‘Answering the Question: What is 1991 Soviet Union dissolved Emergence of Social Democrat GovernmentsClinton in US, Blair in UK, 5 Postmodernism?’ (1984) Costas Douzinas, Ronnie Warrington and Shaun McVeigh Postmodern Jurisprudence (1991) Schroeder in Germany Terrorism 2001 World Trade Centre attack 6







