STUDY GUIDE

STUDY GUIDE
Death, Disease and Demographics
Chronic Diseases
Infectious diseases are diseases that you can “catch”. How are chronic diseases different from infectious diseases?
What are some examples of chronic diseases?
What are some ways that you develop a chronic disease?
Why are we seeing more chronic diseases today?
Why is it important to study cancer?
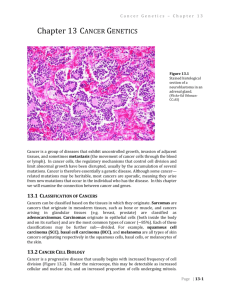
Are there many different forms of cancer?
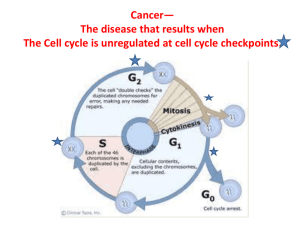
What is one trait that is common to all different types of cancer?
What do cancer cells do that normal cells don’t do?
What has happened to the incidence of cancer in the last 200 years? Why?
Why are there differences in the prevalence of cancer in different countries?
Some say that cancer is a disease of the cell cycle. What does this mean?
Cancers usually involve mutations of genes. Are all cases of cancer hereditary? Are any? Explain.
What is the difference between a malignant and a benign tumor?
What does metastasize mean?
1
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are both involved in cancer. Be able to identify each of their role in cancer and understand how mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are involved.
What can cause a mutation that can lead to cancer? Be able to give some examples.
Understand that the mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA 2 genes are linked to ovarian and breast cancer.
What are some environmental factors that can lead to cancer?
What are HeLa cells and why are they important.
What is heart disease?
Why is it important to study heart disease?
What are the two causes of heart disease?
What happens in Coronary Artery Disease?
What is a myocardial infarction? What are symptoms?
What is congestive heart disease? What causes it?
2
What is a stroke? What are the symptoms?
What are some unchangeable risk factors?
What are some changeable risk factors?
What is cholesterol? Why is it good, why is it bad?
What is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?
Why are fats good for you?
What are saturated fats and why are they bad for you?
What types of fats are good for you? Why?
Why are trans fats bad for you?
What is Omega 3, why is it good and how can you get it?
How is obesity related to heart disease?
3
How is diabetes related to heart disease?
How is physical activity related to heart disease?
How is smoking related to heart disease?
How is alcohol consumption related to heart disease?
What is Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery?
What is Angioplasty?
How can you prevent cardiovascular disease?
There are many different genetic disorders. Most are recessive. What does this mean?
What happens in Tay Sachs?
If two parents who are carriers (heterozygous) for Tay Sachs, what is the chance that their child will have Tay Sachs?
Name one other disease that is recessively inherited.
If diseases can kill you, why are some still inherited? In other words, why aren’t these alleles selected out of our population completely?
4