files/Chapter 3 Study Guide KEY
advertisement

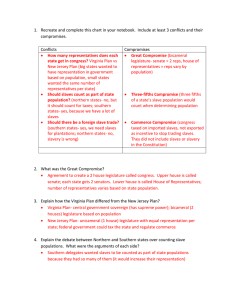
Chapter 3 Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. “No taxation without representation!” This slogan was a direct result of which event? The Stamp Act Which of the following best defines the principles of popular sovereignty? Ultimate source of governmental authority is the people The principles that people are the ultimate source of the authority and legitimacy of a government. Popular Sovereignty How many amendments were originally proposed to the states in the Bill of Rights? 12 The idea of representative government first developed where? Roman Republic Who is known as the Father of the Constitution and as the principal author of the Bill of Rights? James Madison Which of these historic documents first established the principal of the rule of law? Magna Carta This plan of government called for a bicameral legislature, with each house based on population. It also called for three branches of government, a legislative branch, executive branch, and judicial branch. ( Part of answer to No. 37) Virginia Plan The idea that the power of a government should be split between two or more strongly independent branches to prevent any one person or group from gaining too much power. Separation of powers Which of the following was NOT a weakness of the Articles of Confederation? Congress only had two houses (C) The Principle that government is based on clear and fairly enforced laws, no one is above the law. Rule of Law Which complaint was the greatest barrier to ratifying the Constitution? It did not include a Bill of Rights What are natural rights? Life, liberty and property/pursuit of happiness Which of these issues at the Constitutional Convention was resolved by what is known as the Great Compromise? ( Answer to No. 40) The representation of the states in congress The Articles of Confederation reflected American’s fear of what? A strong central government Which political philosopher favored separate legislative, executive, and judicial branches? Baron de Montesquieu Where did colonial thinkers get their ideas about representative democracy? Roman Republic How were the colonies governed at the local level? Colonists developed a legislative body to govern themselves locally (Direct Democracy). How did the 13 new state constitutions limit democracy? -- Only gave voting rights to white male property owners/taxpayers. -- None of the states made slavery illegal -- All southern states denied slaves equal rights as human beings What did the federalists favor? Strong national government. 21. Who is considered the Father of the Constitution? James Madison 22. What did the Magna Carta do? -- Defined the rights and duties of English nobles -- Set limits on monarch’s power -- Established the rule of law 23. Why did the colonists become hostile toward Great Britain? Great Britain began imposing its authority over the colonies 24. What was one achievement of the government under the Articles of Confederation? It enacted the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 25. Why did the Anti-federalists oppose the Constitution? 26. Why did Madison initially oppose a bill of rights? He believed that people’s rights were already protected by the Constitution 27. On which point did Hobbes and Locke agree about the social contract? -- If govt. failed to protect the people’s rights, they had the right to over throw it. -- The people needed the powerful absolute ruler to protect them from themselves -- It was in the people’s self-interest to exchange some of their freedom for government protection. 28. Which principles did Jefferson include in the Declaration of Independence? --Government must protect natural rights -- govt. derives their power from the people -- if govt. doesn’t protect the peoples rights, the people may overthrow the govt. 29. Why did smaller states object to the Virginia plan? The VA. Plan gave more reps to larger states 30. How did the Federalists try to build support for the Constitution? Publishing a series of essays known as the Federalist Papers. 31. Why did it take so long for the Congress to approve a bill of rights? -- Some wanted to address more urgent matters -- some disagreed with Madison’s proposals --Some wanted to wait until flaws in the government emerged more clearly 32. Montesquieu believed in a principle that contributed to our three-branch system of government. What was that principle? Separation of Powers 33. Why did some people want George Washington to be “king”? Some believed Congress was incapable of governing the new nation 34. How did the Three-Fifths Compromise contradict the founding ideal of equality? Each slave was counted as 3/5 of a free person for the purpose of representation and taxation 35. What assurance did Massachusetts need before it would ratify the Constitution? That a Bill of Rights would be added after ratification 36. When was the Bill of Rights finally ratified? 1939 Short Answer: 37. Please explain the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan in detail. Virginia Plan: Bicameral legislature, number of representatives from each state is based on population New Jersey Plan: Unicameral legislature, same number of representatives from each state. 38. What was the result when both plans were suggested to congress? Great compromise: Bicameral legislative (1) House of Representatives; number of representatives are based on population, (2) Senate; two representatives from each state 39. What did the issue of the Virginia Plan and New Jersey plan try to resolve? How the states were going to be represented in the Congress. 40. What compromise took place and how did it satisfy both groups? 41. What compromise resolved the issue of slaves being counted as population? 3/5 Compromise; where every three out of five slaves count towards population. 42. Why was slavery counted towards population an issue in terms of representation? Northern states did not have slaves, while Southern states had a large percent of slaves however did not see them as people but as livestock/ property